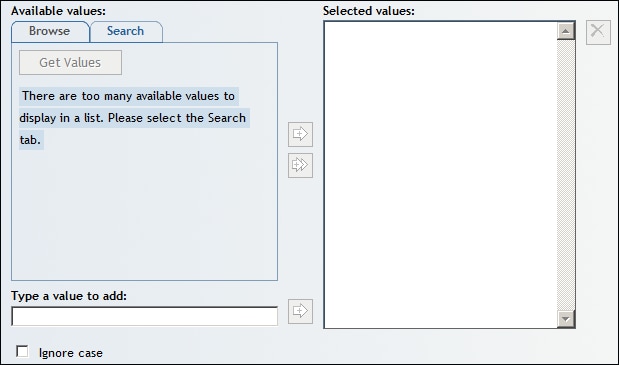
Browsing or Searching for Filter Values
About Browsing and Searching
There are two ways
to select values from a data item:
Browse for Relational Data Items
You can use the Browse tab
to browse all the values that are available in the data source and
then select one from a list. To browse the values in a relational
data source, complete these steps:
Search for Relational Data Items
Browse for Multidimensional Data Items
When the Browse tab
displays for multidimensional data, a tree representing the hierarchy
of the data items expands to the first available level. Note that
when portions of the tree are expanded, there might be a slight delay
in populating the list, because the data in the tree is loaded on
an as-needed basis.
To browse the values
in a multidimensional data source, complete these steps:
-
Select a value (or values) from the Browse tab. Click
 to move one or more values to the list of Selected
values. You can select a range of values using the SHIFT
or the CTRL key. Double-clicking expands or collapses the tree, depending
on the state of the tree node when you click it. Use
to move one or more values to the list of Selected
values. You can select a range of values using the SHIFT
or the CTRL key. Double-clicking expands or collapses the tree, depending
on the state of the tree node when you click it. Use  to move all values in the Browse list
to the list of Selected values. If an area
of the tree is not expanded, then the values in the subtree under
that tree value are not moved to the Selected values list.
to move all values in the Browse list
to the list of Selected values. If an area
of the tree is not expanded, then the values in the subtree under
that tree value are not moved to the Selected values list.
Search for Multidimensional Data Items
You can use the Search tab
to enter search arguments to narrow the list of values and then select
a value from that list. To browse the values in a multidimensional
data source, complete these steps:
-
Click Search. The search results display in the table below the button. If the table contains more than 50 entries, a page control appears above the table to let you move to the next or previous set of entries.In the table, Name is the data item value and Parent path is a list of the levels from the top of the hierarchy to the value. Because multidimensional data sources are hierarchical, data values need to be placed into the context of the hierarchies in which they reside. For example, your cube could contain both [New York].[Rochester] and [Minnesota].[Rochester]. If you see just the value Rochester, you need additional information to know in which state the city is located. In this example, the Parent path for one data value will be New York and Minnesota for the other data value.