Creating or Configuring a WHERE Clause
Tasks
Configure the WHERE Clause with the Where Tab
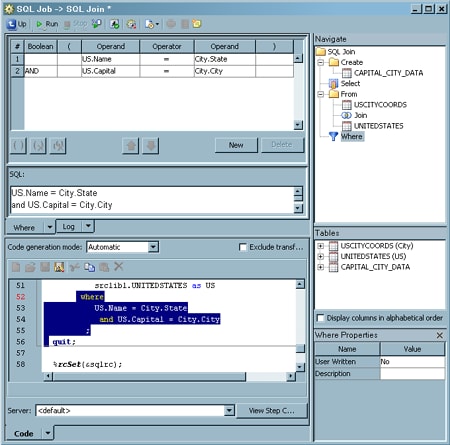
The WHERE
clause for the query is an SQL expression that creates subsets of
the source tables in the SQL query. It also defines the join criteria
for joining the source tables and the subquery to each other by specifying
which values to match. Perform the following steps to configure the Where tab:
-
If the Where clause object is missing from the process flow in the Diagram tab, double-click Where in the SQL Clauses pane. The Where clause object is added to the query flow in the Diagram tab. Note that Where clause objects are automatically populated into the Diagram tab. The WHERE clause is not automatically generated under the following circumstances:
Note that
the SQL code for the WHERE clause that is shown in the SQL field is identical to the highlighted WHERE clause
code that is displayed on the Code tab. To
highlight the code for a query object such as the Where object, right-click
the object in the Navigate pane and click Find In. Then, click Code in the submenu.