Introduction
The MDC procedure provides maximum likelihood (ML) or simulated maximum likelihood estimates of multinomial discrete choice models in which the choice set consists of unordered multiple alternatives.
The MDC procedure supports the following models and features:
-
conditional logit
-
nested logit
-
heteroscedastic extreme value
-
multinomial probit
-
mixed logit
-
pseudo-random or quasi-random numbers for simulated maximum likelihood estimation
-
bounds imposed on the parameter estimates
-
linear restrictions imposed on the parameter estimates
-
SAS data set containing predicted probabilities and linear predictor (
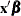 ) values
) values
-
decision tree and nested logit
-
model fit and goodness-of-fit measures including
-
likelihood ratio
-
Aldrich-Nelson
-
Cragg-Uhler 1
-
Cragg-Uhler 2
-
Estrella
-
Adjusted Estrella
-
McFadden’s LRI
-
Veall-Zimmermann
-
Akaike Information Criterion (AIC)
-
Schwarz Criterion or Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC)
-
The QLIM procedure analyzes univariate and multivariate limited dependent variable models where dependent variables take discrete values or dependent variables are observed only in a limited range of values. This procedure includes logit, probit, Tobit, and general simultaneous equations models. The QLIM procedure supports the following models:
-
linear regression model with heteroscedasticity
-
probit with heteroscedasticity
-
logit with heteroscedasticity
-
Tobit (censored and truncated) with heteroscedasticity
-
Box-Cox regression with heteroscedasticity
-
bivariate probit
-
bivariate Tobit
-
sample selection models
-
multivariate limited dependent models
The COUNTREG procedure provides regression models in which the dependent variable takes nonnegative integer count values. The COUNTREG procedure supports the following models:
-
Poisson regression
-
negative binomial regression with quadratic and linear variance functions
-
zero inflated Poisson (ZIP) model
-
zero inflated negative binomial (ZINB) model
-
fixed and random effect Poisson panel data models
-
fixed and random effect NB (negative binomial) panel data models
The PANEL procedure deals with panel data sets that consist of time series observations on each of several cross-sectional units.
The models and methods the PANEL procedure uses to analyze are as follows:
-
one-way and two-way models
-
fixed and random effects
-
autoregressive models
-
the Parks method
-
dynamic panel estimator
-
the Da Silva method for moving-average disturbances
-