How Engines Work with SAS Files
-
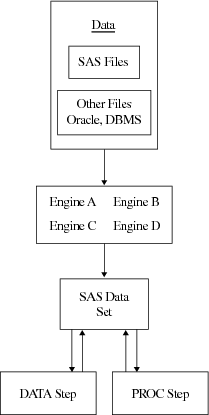
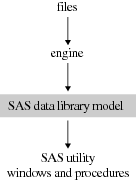
The engine opens the file and obtains the descriptive information that is required by SAS (for example, which variables are available and what attributes they have, whether the file has special processing characteristics such as indexes or compressed observations, and whether other engines are required for processing). The engine uses this information to organize the data in the standard logical form for SAS processing.
Data that
is accessed by an engine is organized into the SAS data set model,
and in the same way, groups of files that are accessed by an engine
are organized in the correct logical form for SAS processing. Once
files are accessed as a SAS library, you can use SAS utility windows
and procedures to list their contents and to manage them. See
SAS Libraries for more information about SAS libraries. The following
figure shows the relationship of engines to SAS libraries.