Introduction to Access Management
About Access Management
Access management determines
which items a user can interact with. The permissions that you set
in SAS Management Console are part of a metadata-based access control
system that SAS provides. These permission settings supplement protections
in other layers (such as the operating system and the WebDAV). Across
layers, protections are cumulative. You cannot perform a task unless
you have sufficient access in all layers.
Granularity and Mechanics of Permissions
Repository-Level Controls
 Repository-level controls function as a gateway.
Participating users usually need ReadMetadata and WriteMetadata permissions
for the foundation repository. Repository-level controls also serve
as a parent-of-last-resort, defining access to resources that do not
have more specific settings. Repository-level controls are defined
on the Permission Pattern tab of the repository
ACT.
Repository-level controls function as a gateway.
Participating users usually need ReadMetadata and WriteMetadata permissions
for the foundation repository. Repository-level controls also serve
as a parent-of-last-resort, defining access to resources that do not
have more specific settings. Repository-level controls are defined
on the Permission Pattern tab of the repository
ACT.
Inheritance and Precedence of Permissions
Two Relationship Networks
Permission settings
are conveyed across two distinct relationship networks, a resource
network and an identity network. Permissions that are set directly
on an item have priority over permissions that are set on the item's
parent. For example, when access to a report is evaluated, a denial
that is set on the report (and assigned to the PUBLIC group) overrides
a grant that is set on the report's parent folder (even if the grant
is assigned to you).
The Resource Relationships Network
 Permissions that you set on one item can affect many
other items. For example, a report inherits permissions from the folder
in which the report is located. This relationship network consists
primarily of a folder tree. This list highlights exceptions:
Permissions that you set on one item can affect many
other items. For example, a report inherits permissions from the folder
in which the report is located. This relationship network consists
primarily of a folder tree. This list highlights exceptions:
-
In unusual circumstances, it is possible for an item to have more than one immediate parent. If there is a tie in this network (for example, if there are no settings on an item, the item has two immediate parents, and one parent provides a grant while the other parent provides a denial), the outcome is a grant. In other words, a grant from any inheritance path is sufficient to provide access.
The Identity Relationships Network
 Permissions that you assign to one group can affect
many other identities. For example, if you grant a group access to
an OLAP cube, that grant applies to all users who are members of the
group. This relationship network is governed by a precedence order
that starts with a primary identity, can incorporate multiple levels
of group memberships, and ends with implicit memberships in SASUSERS
and then PUBLIC. If there is a tie in this network (for example, if
you directly assign a user to two groups and give one group a grant
and another group a deny), the outcome is a deny.
Permissions that you assign to one group can affect
many other identities. For example, if you grant a group access to
an OLAP cube, that grant applies to all users who are members of the
group. This relationship network is governed by a precedence order
that starts with a primary identity, can incorporate multiple levels
of group memberships, and ends with implicit memberships in SASUSERS
and then PUBLIC. If there is a tie in this network (for example, if
you directly assign a user to two groups and give one group a grant
and another group a deny), the outcome is a deny.
Use and Enforcement of Each Permission
Use and Enforcement of Each Permission
|
Edit, delete, change
permissions for, or rename an item. For example, to edit a report
you need WM for the report. To delete a report you need WM for the
report (and WMM for the report's parent folder). WM affects the ability
to create associations. For example, you need WM on an application
server in order to associate a library to that server. WM affects
the ability to create items in certain containers. For example, to
add an item anywhere in a repository, you need WM at the repository
level. For folders, adding and deleting child items is controlled
by WMM, not WM.
|
|
|
Add an item to a folder
or delete an item from a folder. For example, to save a report to
a folder, you need WMM for the folder. To remove a report from a folder,
you need WMM for the folder (and WM for
the report). To enable someone to interact with a folder's
contents but with not the folder itself, grant WMM and deny WM.1
|
|
|
Check in and check out
items in a change-managed area. Applicable only in SAS Data Integration
Studio.2
|
|
1A folder's WMM settings
mirror its WM settings unless the folder has explicit 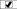 or ACT or ACT 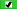 (green) settings of WMM. A grant (or deny) of WMM
on a folder becomes an inherited grant (or deny) of WM on the items
and subfolders within that folder. WMM is not inherited from one folder
to another. WMM is not applicable to specialized folders (such as
virtual folders, favorites folders, or search folders). (green) settings of WMM. A grant (or deny) of WMM
on a folder becomes an inherited grant (or deny) of WM on the items
and subfolders within that folder. WMM is not inherited from one folder
to another. WMM is not applicable to specialized folders (such as
virtual folders, favorites folders, or search folders).
|
|
| 2For any change-managed areas or resources, change-managed users should have CM (instead of WM or WMM). Change management is a SAS Data Integration Studio feature. | |



