Building a Cube from a Detail Table
Overview
A detail, or base,
table is a table whose data pertains to a single area of interest.
It is any table defined in a SAS Metadata Repository that contains
the measures and levels for a cube. You can build an OLAP cube from
a detail table by using the Cube Designer wizard in SAS OLAP Cube Studio. In this example, you use data from
a product marketing campaign. You establish measures and summaries
of product statistics, geographic location of potential customers,
and revenue.
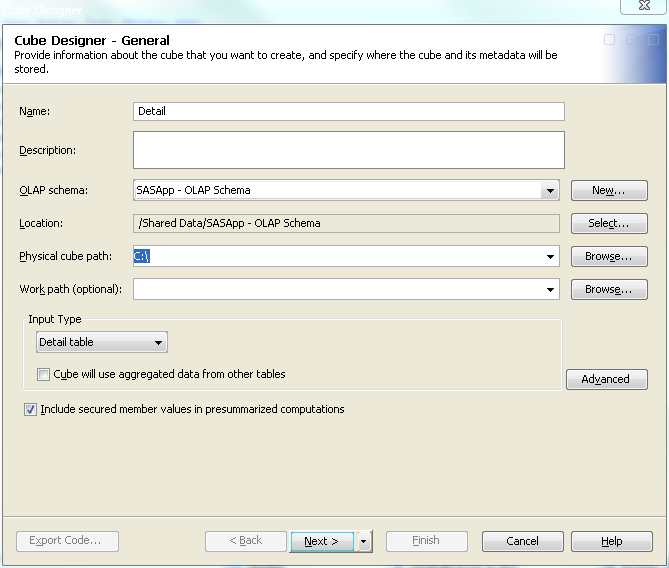
Enter General Cube Information
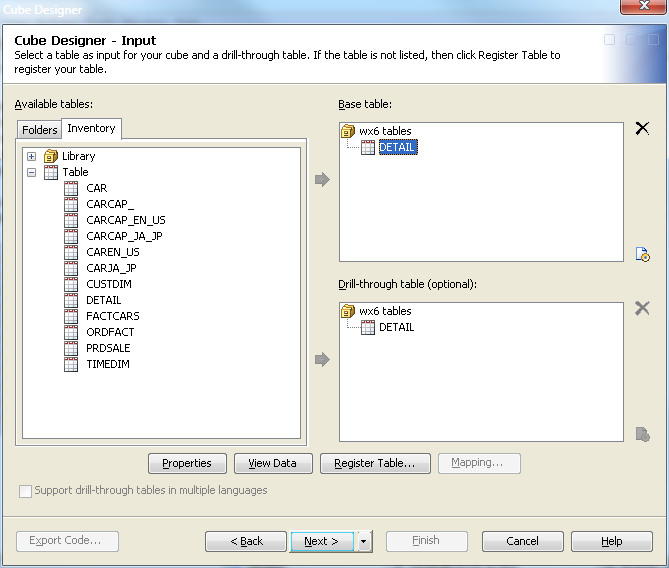
Select a Detail Table
Drill-Through Table
On the Cube
Designer – Input page, you can also select or
define an optional drill-through table. Drill-through tables can be
used by client applications to provide a view from processed data
into the underlying data source.
Table Options
On the Cube
Designer – Input page, you can specify the data
set options that are used to open either the detail table or drill-through
table for your cube. Click the  button next to either the Base table or Drill-through trees. The Table Options button opens the Table Options dialog box, which enables you to specify data set options that are
used to open the data set. For example, you could enter a WHERE clause
or other information to subset the selected table. The options are
stored as part of the cube and then reapplied when the data is accessed
at run time. You can also specify data set options in the Dimension Designer – General dialog box (for
use with star schemas) and the Stored Aggregates dialog box (for use with summarized tables). For more information,
see “Data Set Options” in the SAS Language
Reference: Concepts.
button next to either the Base table or Drill-through trees. The Table Options button opens the Table Options dialog box, which enables you to specify data set options that are
used to open the data set. For example, you could enter a WHERE clause
or other information to subset the selected table. The options are
stored as part of the cube and then reapplied when the data is accessed
at run time. You can also specify data set options in the Dimension Designer – General dialog box (for
use with star schemas) and the Stored Aggregates dialog box (for use with summarized tables). For more information,
see “Data Set Options” in the SAS Language
Reference: Concepts.
 button next to either the Base table or Drill-through trees. The Table Options button opens the Table Options dialog box, which enables you to specify data set options that are
used to open the data set. For example, you could enter a WHERE clause
or other information to subset the selected table. The options are
stored as part of the cube and then reapplied when the data is accessed
at run time. You can also specify data set options in the Dimension Designer – General dialog box (for
use with star schemas) and the Stored Aggregates dialog box (for use with summarized tables). For more information,
see “Data Set Options” in the SAS Language
Reference: Concepts.
button next to either the Base table or Drill-through trees. The Table Options button opens the Table Options dialog box, which enables you to specify data set options that are
used to open the data set. For example, you could enter a WHERE clause
or other information to subset the selected table. The options are
stored as part of the cube and then reapplied when the data is accessed
at run time. You can also specify data set options in the Dimension Designer – General dialog box (for
use with star schemas) and the Stored Aggregates dialog box (for use with summarized tables). For more information,
see “Data Set Options” in the SAS Language
Reference: Concepts.
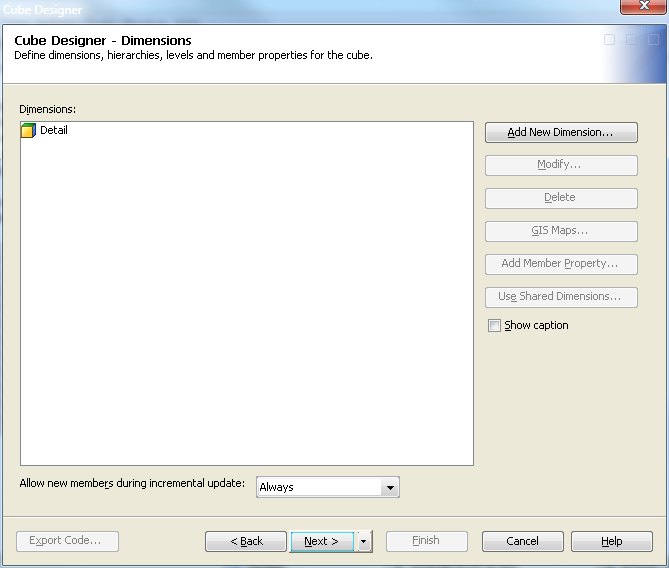
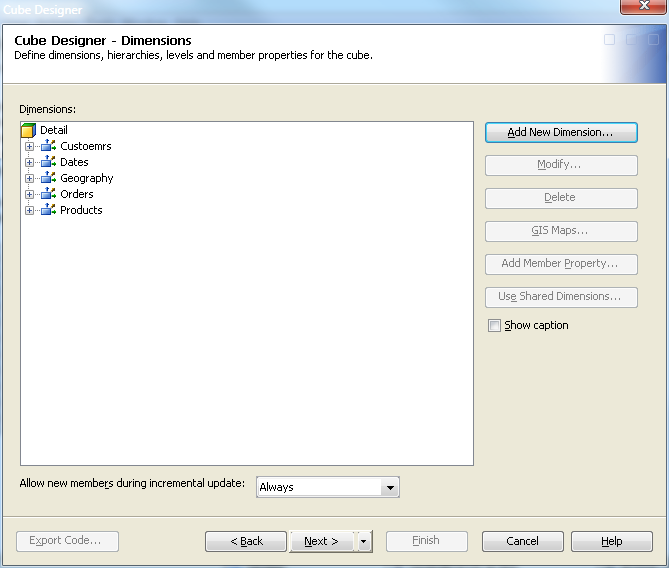
Define Dimensions, Levels, and Hierarchies
Overview
Now that your basic
metadata server and cube information has been entered, you can define
the different dimensions and their respective levels and hierarchies.
For this example, the following dimensions are created:
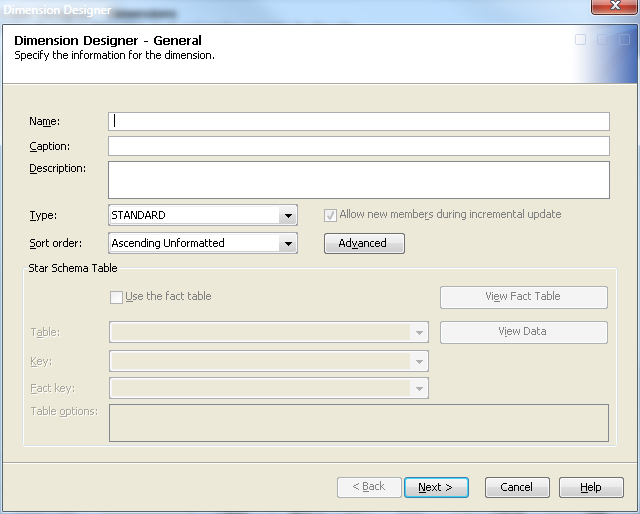
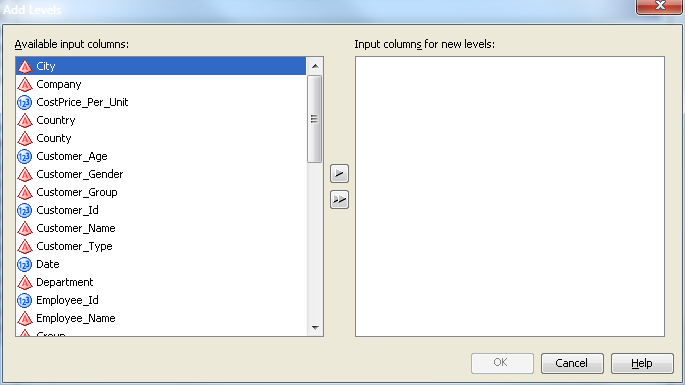
Click Next to open the Dimension Designer – Level page. Select Add to open the Add Levels page, as seen in the following display.
Select the levels that
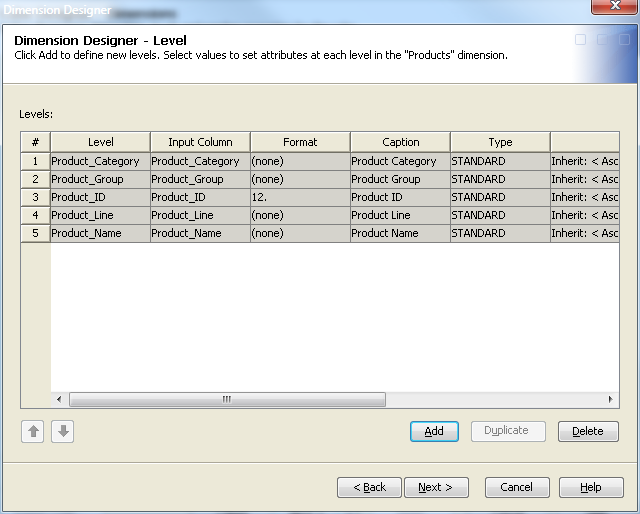
you want to add to the dimension. Select OK to return to the Dimension Designer – Level page, where the selected levels are listed. You can now define properties
such as format, time type, and sort order for the levels that you
have selected. See the following display.
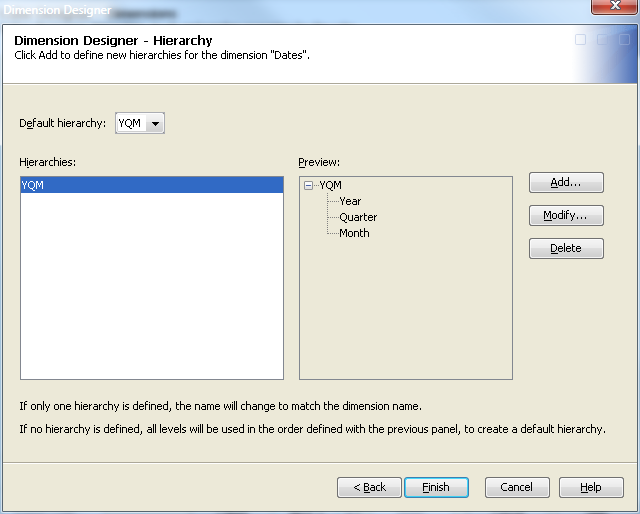
Next, define hierarchies
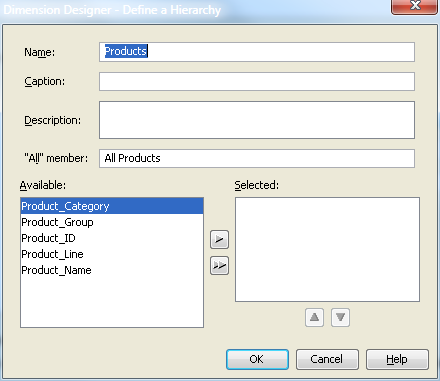
for the levels on the Dimension Designer – Hierarchy page. You can click Add to open the Define a Hierarchy page and individually select the
levels for the hierarchy.
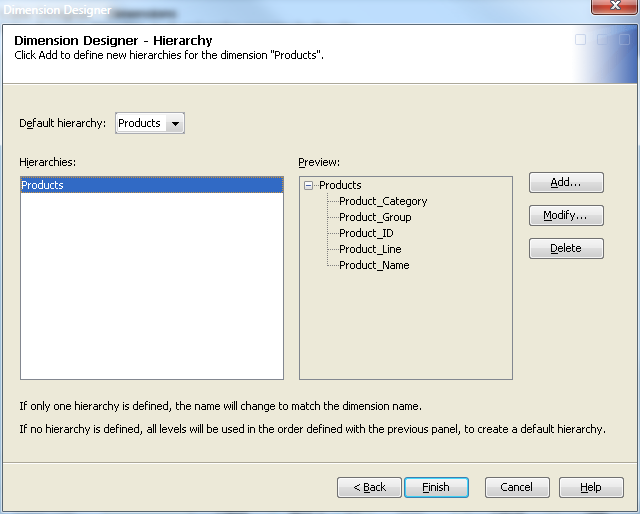
Or you can click Finish on the Dimension Designer - Hierarchy page to accept the order of the levels that are defined on the previous Dimension Designer – Level page. If you select
this option, the hierarchy is assigned the same name as the dimension.
See the following display.
Creating a Time Dimension
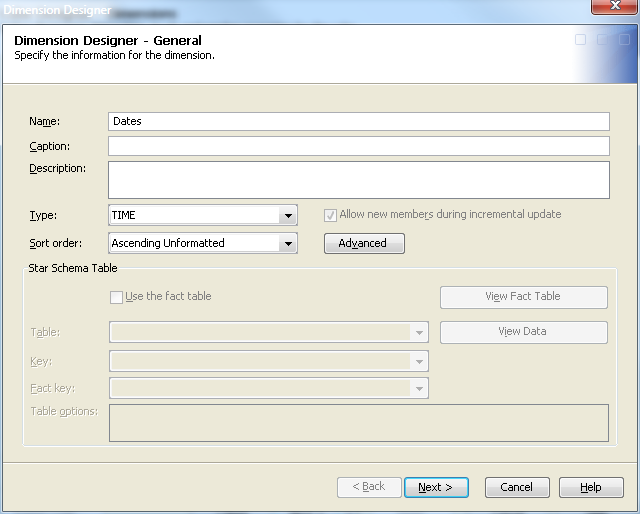
When you create the
Dates dimension, you must specify the TIME dimension type on the Dimension Designer – General page. See the following display.
Specifying the TIME
dimension type enables Add supplied time hierarchies on the Dimension Designer – Level page. The Add button is converted to a
drop-down list of options. The Add levels and Add supplied time hierarchies options
are now available for selection.
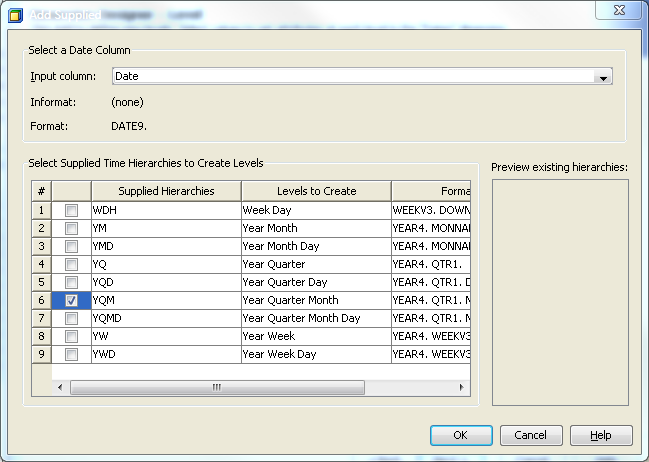
Select Add
supplied time hierarchies. This opens the Add Supplied dialog box. Select from the list of supplied
time hierarchies to create the time levels. This also creates the
hierarchies for the dimension. See the following display.
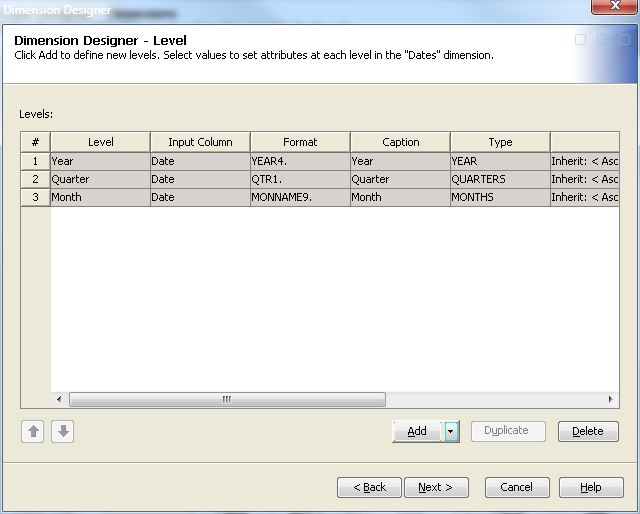
You can then define
properties such as time type and sort order for the levels that you
have selected. See the following display.
Define Member Properties
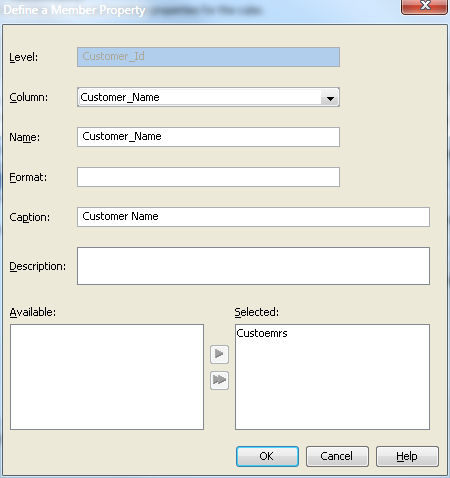
You can now define the
member properties for any needed cube members. A member property is
an attribute of a dimension member. A member property is also an optional
cube feature that is created in a dimension to provide users with
additional information about members. For this example, you can define
the customer gender as a member property. Define member properties
in the Cube Designer – Dimensions page.
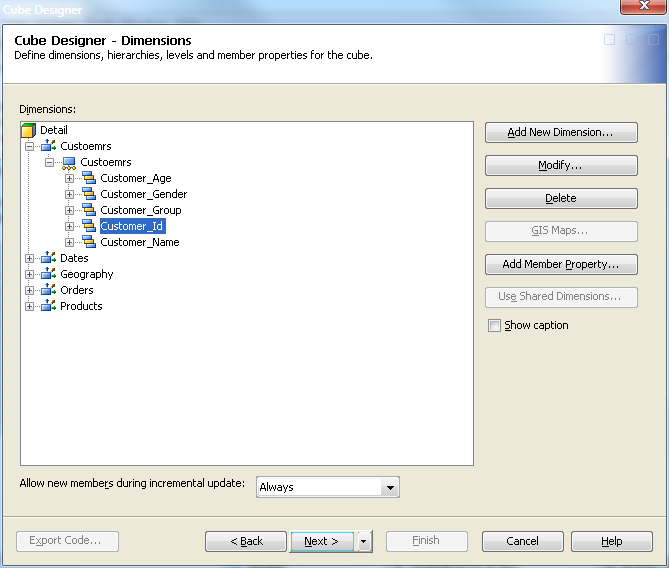
Select the Customer ID level, and then click
the Add Member Property button, as seen in
the following display.
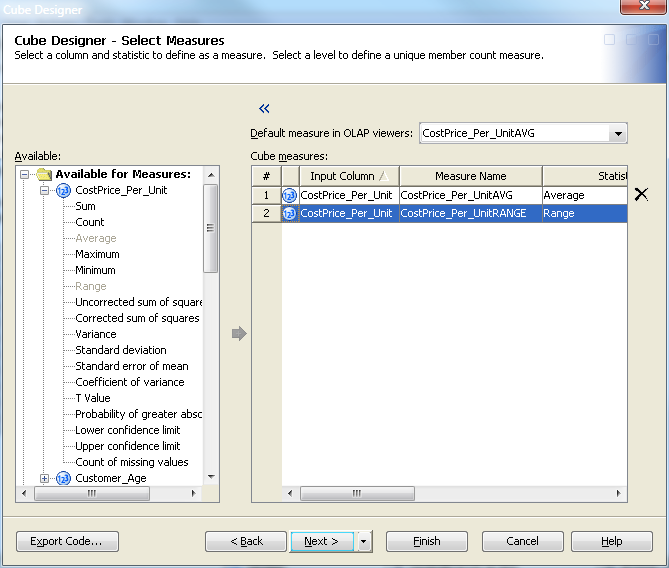
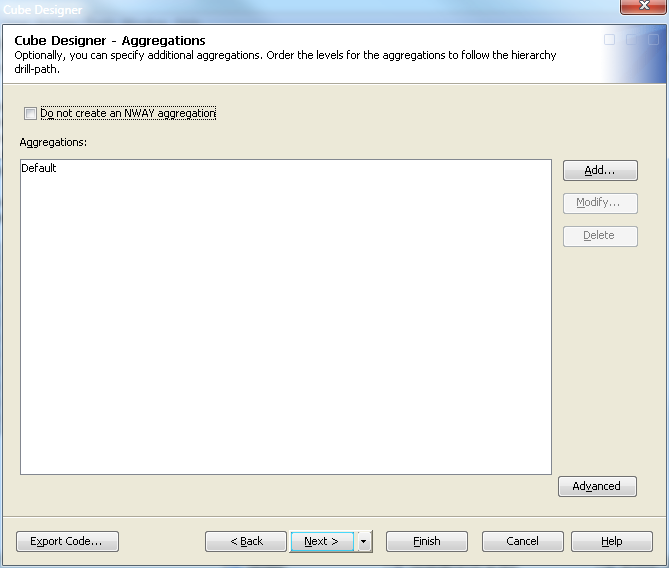
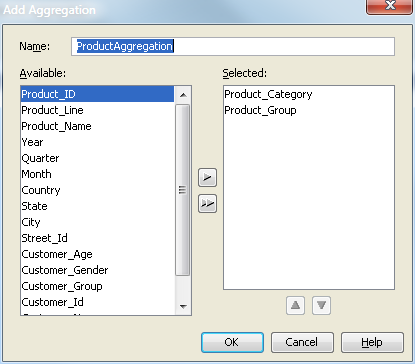
Define Aggregations
You can now define the
aggregations for the cube. Aggregations are summaries of detailed
data that are stored with a cube or referred to by a cube. They can
help contribute to faster query response. Define the aggregations
for the cube from the Cube Designer – Aggregations page, as shown in the following display.
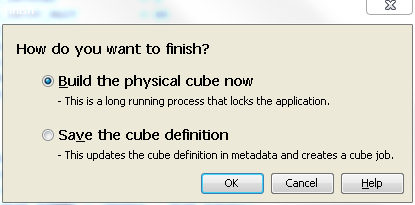
Build the Cube
You can now build the
cube. On the Cube Designer – Finish page, review the settings for the cube, and then click Finish. The Finish dialog box
is displayed as shown in the following display.
Choose to build the
physical cube or to generate cube metadata without building the physical
cube. Click OK to save your selection and
display the Summary of Selections page, as
shown in the following display.
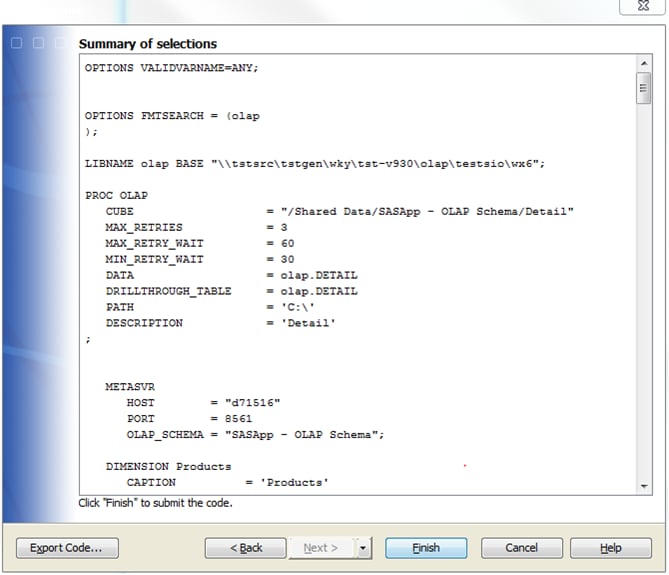
On the Summary
of Selections page, you can review the specifications
for your cube. At this point, you can click Back to make changes, Finish to build the cube,
or Export Code, as shown in the following
display.
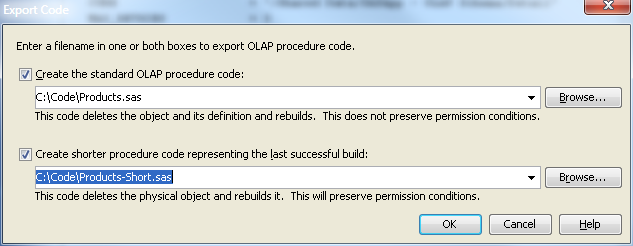
The Export
Code dialog box displays the current settings that determine
whether, how, and where you store generated SAS code. To export code
for a new cube or to export code for an existing cube without saving
permission conditions, click Create the standard OLAP
procedure code.
SAS OLAP Code Saved in Export
PROC OLAP Statements and Options for a Detail Table
The PROC OLAP code that
is generated when a detail cube is built is listed below. A detail
cube is unique in that it uses the DATA= option to specify the data
source for the cube. The statements each have options that are either
required or optional, depending on the cube structure.