Setting LIBNAME Options That Affect Performance of SPD Engine Tables
The following LIBNAME options can be used to tune performance
of the SPD Engine. You can set these options when you use the New
Library wizard to register an SPD Engine library in the
metadata repository. The LIBNAME options are available on the Options
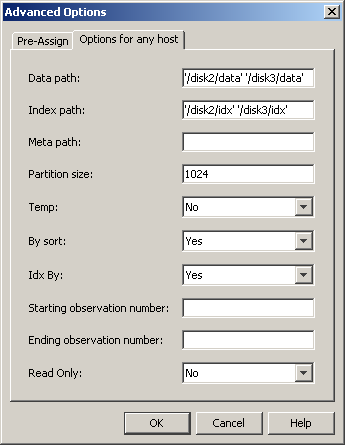
for any host tab in the Advanced Options dialog
box. To access the Advanced Options dialog
box, click the Advanced Options button on
the Library Options window of the New
Library wizard. The Advanced Options dialog
box is shown in the following figure:
Data path (DATAPATH=)
specifies a list of
paths in which to store partitions (DPF) files for an SPD Engine table.
The engine creates as many partitions as are needed to store all the
data. The size of the partitions is set using the PARTSIZE= option.
Partitions are created in the specified paths in a cyclic fashion.
The data path area is best configured as multiple paths. Allot one
I/O controller per data path to provide high I/O throughput, which
is the rate at which requests for work are serviced by a computer
system. The data path area is best configured for redundancy (RAID
1).
Index path (INDEXPATH=)
specifies a path or
a list of paths in which to store the two index component files (HBX
and IDX) that are associated with an SPD Engine table. Additional
specified paths accept the overflow from the immediately preceding
path. The index path area is best configured as multiple paths. Use
a volume manager file system that is striped across multiple disks
(RAID 0) to enable adequate index performance, both when evaluating
WHERE clauses and creating indexes in parallel. Redundancy (RAID 5
or RAID 10) is also recommended.
Meta path (METAPATH=)
specifies a list of
overflow paths in which to store metadata component (MDF) files for
an SPD Engine table. The metadata component file for each table must
begin in the primary path. When that primary path is full, the overflow
is sent to the specified METAPATH= location. The metadata path area
is best configured for redundancy (RAID 1) so that metadata about
the data and its indexes is not lost.
Partition size (PARTSIZE=)
specifies the size
(in megabytes) of the data component partitions when an SPD Engine
table is created. By splitting the data portion of an SPD Engine table
at fixed-size intervals, you can gain a high degree of scalability
for some operations. For example, the SPD Engine can spawn threads
in parallel, up to one thread per partition for WHERE evaluations.
Temp (TEMP=)
specifies whether to
create a temporary subdirectory of the directory specified in the
Path field on the Library Properties window.
The directory is used to temporarily store the metadata component
files associated with table creation. It is deleted at the end of
the SAS session.
By sort (BYSORT=)
specifies that the
SPD Engine should perform an automatic implicit sort when it finds
a BY statement for processing data in the library (unless the data
is indexed on the BY column). Valid values are YES (perform the sort)
and NO (do not perform the sort). The default is YES.
In addition to the LIBNAME
options, there are also table and system options that can be used
to tune SPD Engine performance. For example, the SPDEUTILLOC= system
option allots space for temporary files that are generated during
SPD Engine operations. This area is best configured as multiple paths.
Use a volume manager file system that is striped across multiple disks
(RAID 0) to reduce out-of-space conditions and improve performance.
Redundancy (RAID 5 or RAID 10) is also recommended because losing
the work area could stop the SPD Engine from functioning.