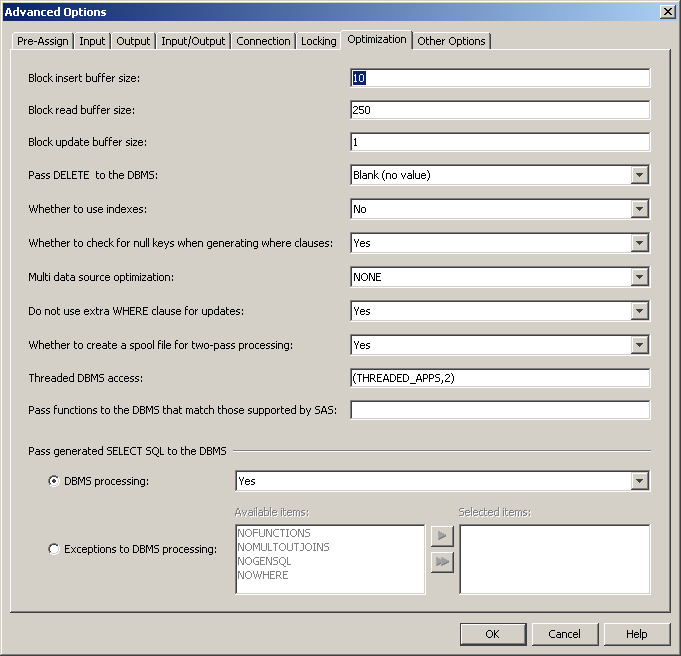
Setting LIBNAME Options That Affect Performance of SAS/ACCESS Databases
The following LIBNAME options can be used to tune performance of the SAS/ACCESS engines. You can set
these options when you use the New Library wizard
to register the database libraries in the metadata repository. To
access the Advanced Options dialog box, click
the Advanced Options button on the Library
Options window of the New Library wizard.
The tabs that are available
in the Advanced Options dialog box, as well
as the options on each of the tabs, vary between database management
systems. The following list provides a description of the options
on Optimization tab for DB2 libraries for
UNIX and PC:
Block insert buffer size (INSERTBUFF=)
specifies the number
of rows in a single Insert operation. See Buffering Data for DB2 (UNIX and PC), ODBC, OLE DB, Oracle, SQL Server, and Sybase Tables.
Block read buffer size (READBUFF=)
specifies the number
of rows of DBMS data to read into the buffer. See Buffering Data for DB2 (UNIX and PC), ODBC, OLE DB, Oracle, SQL Server, and Sybase Tables.
Pass functions to the DBMS that match those supported by
SAS (SQL_ FUNCTIONS=)
when set to ALL, specifies
that functions that match functions supported by SAS should be passed
to the DBMS. The functions that are passed are: DATE, DATEPART, DATETIME,
TIME, TIMEPART, TODAY, QRT, COMPRESS, SUBSTR, DAY, SECOND, INDEX,
TRANWRD, HOUR, WEEKDAY, LENGTH, TRIMN, MINUTE, YEAR, REPEAT, MOD,
MONTH, BYTE, and SOUNDEX. Use of this option can cause unexpected
results, especially if used for NULL processing and date, time, and
timestamp handling. Exercise care when using this option.
Pass DELETE to the DBMS (DIRECT_EXE=)
specifies that an
SQL delete statement is passed directly to the DBMS for processing.
Selecting this option improves performance because SAS does not have
to read the entire result set and delete one row at a time.
Whether to use indexes (DBINDEX=)
specifies whether SAS
uses indexes that are defined on DBMS columns to process a join. Valid
values are YES or NO. For more information about indexes, see Indexing Data.
Whether to check for null keys when generating WHERE clauses
(DBNULLKEYS=)
specifies whether the
WHERE clause should detect NULL values in columns. Valid values are
YES or NO. YES is the default for most interfaces and enables SAS
to prepare the statement once and use it for any value (NULL or NOT
NULL) in the column.
Multiple data source optimization (MULTI_ DATASRC_OPT=)
when processing a join
between two tables, specifies whether an IN clause should be created
to optimize the join. Valid values are NONE and IN_CLAUSE. IN_CLAUSE
specifies that an IN clause containing the values read from a smaller
table are used to retrieve the matching values in a larger table
based on a key column designated in an equijoin.
Whether to create a spool file for two-pass processing (SPOOL=)
specifies whether
to create a utility spool file during transactions that read data
more than once. In some cases, SAS processes data in more than one
pass through the same set of rows. Spooling is the process of writing
rows that have been retrieved during the first pass of a data Read
to a spool file. In the second pass, rows can be re-read without performing
I/O to the DBMS a second time. In cases where the data needs to be
read more than once, spooling improves performance. Spooling also
guarantees that the data remains the same between passes. Valid values
are YES or NO.
Threaded DBMS access (DBSLICEPARM=)
specifies the scope
of DBMS threaded Reads and the number of threads. If this option is
set to the default, then PROC SQL does not use threading to read data
for a Web report. To force a specified number of threads for a threaded
Read from the DBMS server, change the default to (ALL,number-of-threads).
Note: If PROC SQL attempts implicit
pass-through, then threading is disabled, regardless of the Threaded
DBMS access setting. To disable implicit pass-through,
set the Pass generated SELECT SQL to the DBMS - DBMS processing
option to
NO.
For more information
about threaded Reads, see Using Threaded Reads.
Pass generated SELECT SQL to the DBMS - DBMS processing
(DIRECT_SQL=)
specifies whether
generated SQL is passed to the DBMS for processing. Valid values are
YES or NO.
Pass generated SELECT SQL to the DBMS - exceptions to DBMS processing
(DIRECT_SQL=)
if the value for the
previous option is YES, then this option specifies how generated SQL
is passed to the DBMS for processing. For example, NOWHERE prevents
WHERE clauses from being passed to the DBMS for processing.
The Other
Options tab, which is available for all database management
systems, can be used to specify LIBNAME options such as the COMPRESS= option.
For more information, see Compressing Data.