The X12 Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax
 Functional SummaryPROC X12 StatementADJUST StatementARIMA StatementAUTOMDL StatementBY StatementCHECK StatementESTIMATE StatementEVENT StatementFORECAST StatementID StatementIDENTIFY StatementINPUT StatementOUTLIER StatementOUTPUT StatementPICKMDL StatementREGRESSION StatementSEATSDECOMP StatementTABLES StatementTRANSFORM StatementUSERDEFINED StatementVAR StatementX11 Statement
Functional SummaryPROC X12 StatementADJUST StatementARIMA StatementAUTOMDL StatementBY StatementCHECK StatementESTIMATE StatementEVENT StatementFORECAST StatementID StatementIDENTIFY StatementINPUT StatementOUTLIER StatementOUTPUT StatementPICKMDL StatementREGRESSION StatementSEATSDECOMP StatementTABLES StatementTRANSFORM StatementUSERDEFINED StatementVAR StatementX11 Statement -
Details
 Data RequirementsMissing ValuesSAS Predefined EventsUser-Defined Regression VariablesCombined Test for the Presence of Identifiable SeasonalityComputationsPICKMDL Model SelectionSEATS DecompositionDisplayed Output, ODS Table Names, and OUTPUT Tablename KeywordsUsing Auxiliary Variables to Subset Output Data SetsODS GraphicsOUT= Data SetSEATSDECOMP OUT= Data SetSpecial Data Sets
Data RequirementsMissing ValuesSAS Predefined EventsUser-Defined Regression VariablesCombined Test for the Presence of Identifiable SeasonalityComputationsPICKMDL Model SelectionSEATS DecompositionDisplayed Output, ODS Table Names, and OUTPUT Tablename KeywordsUsing Auxiliary Variables to Subset Output Data SetsODS GraphicsOUT= Data SetSEATSDECOMP OUT= Data SetSpecial Data Sets -
Examples
 ARIMA Model IdentificationModel EstimationSeasonal AdjustmentRegARIMA Automatic Model SelectionAutomatic Outlier DetectionUser-Defined RegressorsMDLINFOIN= and MDLINFOOUT= Data SetsSetting Regression ParametersCreating an MDLINFO= Data Set for Use with the PICKMDL StatementIllustration of ODS GraphicsAUXDATA= Data Set
ARIMA Model IdentificationModel EstimationSeasonal AdjustmentRegARIMA Automatic Model SelectionAutomatic Outlier DetectionUser-Defined RegressorsMDLINFOIN= and MDLINFOOUT= Data SetsSetting Regression ParametersCreating an MDLINFO= Data Set for Use with the PICKMDL StatementIllustration of ODS GraphicsAUXDATA= Data Set - References
This example demonstrates the use of the OUTLIER statement to automatically detect and remove outliers from a time series to be seasonally adjusted. The data set is the same as in the section Basic Seasonal Adjustment and the previous examples. Adding the OUTLIER statement to Example 37.3 requests that outliers be detected by using the default critical value as described in the section OUTLIER Statement. The tables associated with outlier detection for this example are shown in Output 37.5.1. The first table shows the critical values; the second table shows that a single potential outlier was identified; the third table shows the estimates for the ARMA parameters. Since no outliers are included in the regression model, the "Regression Model Parameter Estimates" table is not displayed. Because only a potential outlier was identified, and not an actual outlier, in this case the A1 series and the B1 series are identical.
title 'Automatic Outlier Identification'; proc x12 data=sales date=date; var sales; transform function=log; arima model=( (0,1,1)(0,1,1) ); outlier; estimate; x11; output out=nooutlier a1 b1 d10; run ;
Output 37.5.1: PROC X12 Output When Potential Outliers Are Identified
| Note: | The following time series values might later be identified as outliers when data are added or revised. They were not identified as outliers in this run either because their test t-statistics were slightly below the critical value or because they were eliminated during the backward deletion step of the identification procedure, when a non-robust t-statistic is used. |
| Potential Outliers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| For Variable sales | |||
| Type of Outlier | Date | t Value for AO | t Value for LS |
| AO | NOV1989 | -3.48 | -1.51 |
In the next example, reducing the critical value to 3.3 causes the outlier identification routine to more aggressively identify outliers as shown in Output 37.5.2. The first table shows the critical values. The second table shows that three additive outliers and a level-shift have been included in the regression model. The third table shows how the inclusion of outliers in the model affects the ARMA parameters.
proc x12 data=sales date=date; var sales; transform function=log; arima model=((0,1,1) (0,1,1)); outlier cv=3.3; estimate; x11; output out=outlier(obs=50) a1 a8 a8ao a8ls b1 d10; run;
proc print data=outlier(obs=50); run;
Output 37.5.2: PROC X12 Output When Outliers Are Identified
| Regression Model Parameter Estimates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| For Variable sales | ||||||
| Type | Parameter | NoEst | Estimate | Standard Error |
t Value | Pr > |t| |
| Automatically Identified | AO JAN1981 | Est | 0.09590 | 0.02168 | 4.42 | <.0001 |
| LS FEB1983 | Est | -0.09673 | 0.02488 | -3.89 | 0.0002 | |
| AO OCT1983 | Est | -0.08032 | 0.02146 | -3.74 | 0.0003 | |
| AO NOV1989 | Est | -0.10323 | 0.02480 | -4.16 | <.0001 | |
The first 50 observations of the A1, A8, A8AO, A8LS, B1, and D10 series are displayed in Output 37.5.3. You can confirm the following relationships from the data:
The seasonal factors are stored in the variable sales_D10.
Output 37.5.3: PROC X12 Output Series Related to Outlier Detection
| Automatic Outlier Identification |
| Obs | DATE | sales_A1 | sales_A8 | sales_A8AO | sales_A8LS | sales_B1 | sales_D10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SEP78 | 112 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 101.674 | 0.90496 |
| 2 | OCT78 | 118 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 107.121 | 0.94487 |
| 3 | NOV78 | 132 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 119.830 | 1.04711 |
| 4 | DEC78 | 129 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 117.107 | 1.00119 |
| 5 | JAN79 | 121 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 109.844 | 0.94833 |
| 6 | FEB79 | 135 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 122.553 | 1.06817 |
| 7 | MAR79 | 148 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 134.355 | 1.18679 |
| 8 | APR79 | 148 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 134.355 | 1.17607 |
| 9 | MAY79 | 136 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 123.461 | 1.07565 |
| 10 | JUN79 | 119 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 108.029 | 0.91844 |
| 11 | JUL79 | 104 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 94.412 | 0.81206 |
| 12 | AUG79 | 118 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 107.121 | 0.91602 |
| 13 | SEP79 | 115 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 104.397 | 0.90865 |
| 14 | OCT79 | 126 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 114.383 | 0.94131 |
| 15 | NOV79 | 141 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 128.000 | 1.04496 |
| 16 | DEC79 | 135 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 122.553 | 0.99766 |
| 17 | JAN80 | 125 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 113.475 | 0.94942 |
| 18 | FEB80 | 149 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 135.263 | 1.07172 |
| 19 | MAR80 | 170 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 154.327 | 1.18663 |
| 20 | APR80 | 170 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 154.327 | 1.18105 |
| 21 | MAY80 | 158 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 143.433 | 1.07383 |
| 22 | JUN80 | 133 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 120.738 | 0.91930 |
| 23 | JUL80 | 114 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 103.490 | 0.81385 |
| 24 | AUG80 | 140 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 127.093 | 0.91466 |
| 25 | SEP80 | 145 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 131.632 | 0.91302 |
| 26 | OCT80 | 150 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 136.171 | 0.93086 |
| 27 | NOV80 | 178 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 161.589 | 1.03965 |
| 28 | DEC80 | 163 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 147.972 | 0.99440 |
| 29 | JAN81 | 172 | 1.21243 | 1.10065 | 1.10156 | 141.864 | 0.95136 |
| 30 | FEB81 | 178 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 161.589 | 1.07981 |
| 31 | MAR81 | 199 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 180.653 | 1.18661 |
| 32 | APR81 | 199 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 180.653 | 1.19097 |
| 33 | MAY81 | 184 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 167.036 | 1.06905 |
| 34 | JUN81 | 162 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 147.064 | 0.92446 |
| 35 | JUL81 | 146 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 132.539 | 0.81517 |
| 36 | AUG81 | 166 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 150.695 | 0.91148 |
| 37 | SEP81 | 171 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 155.234 | 0.91352 |
| 38 | OCT81 | 180 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 163.405 | 0.91632 |
| 39 | NOV81 | 193 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 175.206 | 1.03194 |
| 40 | DEC81 | 181 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 164.312 | 0.98879 |
| 41 | JAN82 | 183 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 166.128 | 0.95699 |
| 42 | FEB82 | 218 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 197.901 | 1.09125 |
| 43 | MAR82 | 230 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 208.795 | 1.19059 |
| 44 | APR82 | 242 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 219.688 | 1.20448 |
| 45 | MAY82 | 209 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 189.731 | 1.06355 |
| 46 | JUN82 | 191 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 173.391 | 0.92897 |
| 47 | JUL82 | 172 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 156.142 | 0.81476 |
| 48 | AUG82 | 194 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 176.114 | 0.90667 |
| 49 | SEP82 | 196 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 177.930 | 0.91200 |
| 50 | OCT82 | 196 | 1.10156 | 1.00000 | 1.10156 | 177.930 | 0.89970 |
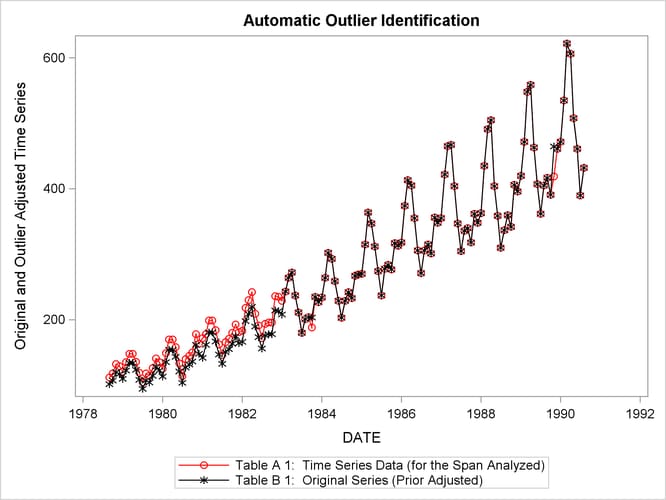
From the two previous examples, you can examine how outlier detection affects the seasonally adjusted series. Output 37.5.4 shows a plot of A1 versus B1 in the series where outliers are detected. B1 has been adjusted for the additive outliers and the level-shift.
proc sgplot data=outlier;
series x=date y=sales_A1 / name='A1' markers
markerattrs=(color=red symbol='circle')
lineattrs=(color=red);
series x=date y=sales_B1 / name='B1' markers
markerattrs=(color=black symbol='asterisk')
lineattrs=(color=black);
yaxis label='Original and Outlier Adjusted Time Series';
run;
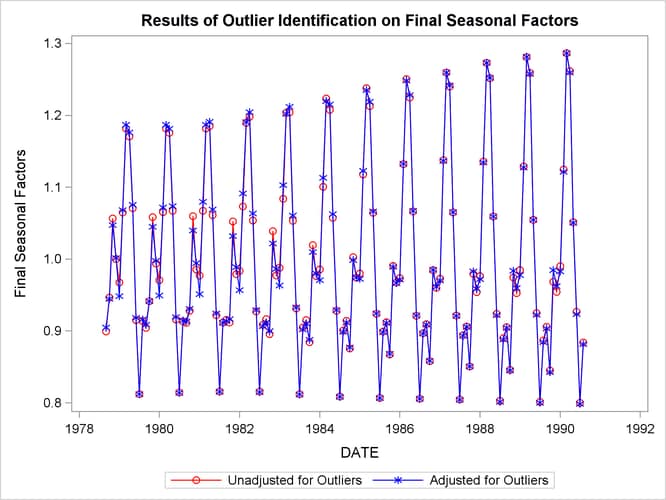
Output 37.5.5 compares the seasonal factors (table D10) of the series unadjusted for outliers to the series adjusted for outliers. The seasonal factors are based on the B1 series.
data both;
merge nooutlier(rename=(sales_D10=unadj_D10)) outlier;
run;
title 'Results of Outlier Identification on Final Seasonal Factors';
proc sgplot data=both;
series x=date y=unadj_D10 / name='unadjusted' markers
markerattrs=(color=red symbol='circle')
lineattrs=(color=red)
legendlabel='Unadjusted for Outliers';
series x=date y=sales_D10 / name='adjusted' markers
markerattrs=(color=blue symbol='asterisk')
lineattrs=(color=blue)
legendlabel='Adjusted for Outliers';
yaxis label='Final Seasonal Factors';
run;