Example 9.8 Logistic and Probit Regression for Binary Response Models
A binary response Y is fit to a linear model according to
where 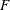 is some smooth probability distribution function. The normal and logistic distribution functions are supported. The method
is maximum likelihood via iteratively reweighted least squares (described by Charnes, Frome, and Yu (1976); Jennrich and Moore (1975); and Nelder and Wedderburn (1972)). The row scaling is done by the derivative of the distribution (density). The weighting is done by
is some smooth probability distribution function. The normal and logistic distribution functions are supported. The method
is maximum likelihood via iteratively reweighted least squares (described by Charnes, Frome, and Yu (1976); Jennrich and Moore (1975); and Nelder and Wedderburn (1972)). The row scaling is done by the derivative of the distribution (density). The weighting is done by 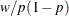 , where
, where 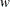 has the counts or other weights. The following program calculates logistic and probit regression for binary response models.
has the counts or other weights. The following program calculates logistic and probit regression for binary response models.
/* routine for estimating binary response models */
/* y is the binary response, x are regressors, */
/* wgt are count weights, */
/* model is choice of logit probit, */
/* parm has the names of the parameters */
proc iml ;
start binest;
b=repeat(0,ncol(x),1);
oldb=b+1; /* starting values */
do iter=1 to 20 while(max(abs(b-oldb))>1e-8);
oldb=b;
z=x*b;
run f;
loglik=sum(((y=1)#log(p) + (y=0)#log(1-p))#wgt);
btransp=b`;
print iter loglik btransp;
w=wgt/(p#(1-p));
xx=f#x;
xpxi=inv(xx`*(w#xx));
b=b + xpxi*(xx`*(w#(y-p)));
end;
p0=sum((y=1)#wgt)/sum(wgt); /* average response */
loglik0=sum(((y=1)#log(p0) + (y=0)#log(1-p0))#wgt);
chisq=(2#(loglik-loglik0));
df=ncol(x)-1;
prob=1-probchi(chisq,df);
print ,
'Likelihood Ratio, Intercept-only Model' chisq df prob,;
stderr=sqrt(vecdiag(xpxi));
tratio=b/stderr;
print parm b stderr tratio,,;
finish;
/*---routine to yield distribution function and density---*/
start f;
if model='LOGIT' then
do;
p=1/(1+exp(-z));
f=p#p#exp(-z);
end;
if model='PROBIT' then
do;
p=probnorm(z);
f=exp(-z#z/2)/sqrt(8*atan(1));
end;
finish;
/* Ingot data from COX (1970, pp. 67-68)*/
data={ 7 1.0 0 10, 14 1.0 0 31, 27 1.0 1 56, 51 1.0 3 13,
7 1.7 0 17, 14 1.7 0 43, 27 1.7 4 44, 51 1.7 0 1,
7 2.2 0 7, 14 2.2 2 33, 27 2.2 0 21, 51 2.2 0 1,
7 2.8 0 12, 14 2.8 0 31, 27 2.8 1 22,
7 4.0 0 9, 14 4.0 0 19, 27 4.0 1 16, 51 4.0 0 1};
nready=data[,3];
ntotal=data[,4];
n=nrow(data);
x=repeat(1,n,1)||(data[,{1 2}]); /* intercept, heat, soak */
x=x//x; /* regressors */
y=repeat(1,n,1)//repeat(0,n,1); /* binary response */
wgt=nready//(ntotal-nready); /* row weights */
parm={intercept, heat, soak}; /* names of regressors */
model={logit};
run binest; /* run logit model */
model={probit};
run binest; /* run probit model */
The results are shown in Output 9.8.1.
Output 9.8.1: Logistic and Probit Regression: Results
| 2 |
-76.29481 |
-2.159406 |
0.0138784 |
0.0037327 |
| 3 |
-53.38033 |
-3.53344 |
0.0363154 |
0.0119734 |
| 4 |
-48.34609 |
-4.748899 |
0.0640013 |
0.0299201 |
| 5 |
-47.69191 |
-5.413817 |
0.0790272 |
0.04982 |
| 6 |
-47.67283 |
-5.553931 |
0.0819276 |
0.0564395 |
| 7 |
-47.67281 |
-5.55916 |
0.0820307 |
0.0567708 |
| 8 |
-47.67281 |
-5.559166 |
0.0820308 |
0.0567713 |
| Likelihood Ratio, Intercept-only Model |
11.64282 |
2 |
0.0029634 |
| INTERCEPT |
-5.559166 |
1.1196947 |
-4.964895 |
| HEAT |
0.0820308 |
0.0237345 |
3.4561866 |
| SOAK |
0.0567713 |
0.3312131 |
0.1714042 |
| 2 |
-71.71043 |
-1.353207 |
0.008697 |
0.0023391 |
| 3 |
-51.64122 |
-2.053504 |
0.0202739 |
0.0073888 |
| 4 |
-47.88947 |
-2.581302 |
0.032626 |
0.018503 |
| 5 |
-47.48924 |
-2.838938 |
0.0387625 |
0.0309099 |
| 6 |
-47.47997 |
-2.890129 |
0.0398894 |
0.0356507 |
| 7 |
-47.47995 |
-2.89327 |
0.0399529 |
0.0362166 |
| 8 |
-47.47995 |
-2.893408 |
0.0399553 |
0.0362518 |
| 9 |
-47.47995 |
-2.893415 |
0.0399554 |
0.0362537 |
| 10 |
-47.47995 |
-2.893415 |
0.0399555 |
0.0362538 |
| 11 |
-47.47995 |
-2.893415 |
0.0399555 |
0.0362538 |
| Likelihood Ratio, Intercept-only Model |
12.028543 |
2 |
0.0024436 |
| INTERCEPT |
-2.893415 |
0.5006009 |
-5.779884 |
| HEAT |
0.0399555 |
0.0118466 |
3.3727357 |
| SOAK |
0.0362538 |
0.1467431 |
0.2470561 |
![]() is some smooth probability distribution function. The normal and logistic distribution functions are supported. The method
is maximum likelihood via iteratively reweighted least squares (described by Charnes, Frome, and Yu (1976); Jennrich and Moore (1975); and Nelder and Wedderburn (1972)). The row scaling is done by the derivative of the distribution (density). The weighting is done by
is some smooth probability distribution function. The normal and logistic distribution functions are supported. The method
is maximum likelihood via iteratively reweighted least squares (described by Charnes, Frome, and Yu (1976); Jennrich and Moore (1975); and Nelder and Wedderburn (1972)). The row scaling is done by the derivative of the distribution (density). The weighting is done by ![]() , where
, where ![]() has the counts or other weights. The following program calculates logistic and probit regression for binary response models.
has the counts or other weights. The following program calculates logistic and probit regression for binary response models.