BOXCHART Statement: SHEWHART Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details

-
Examples
 Using Box Charts to Compare SubgroupsCreating Various Styles of Box-and-Whisker PlotsCreating Notched Box-and-Whisker PlotsCreating Box-and-Whisker Plots with Varying WidthsCreating Box-and-Whisker Plots with Different Line Styles and ColorsComputing the Control Limits for Subgroup MaximumsConstructing Multi-Vari Charts
Using Box Charts to Compare SubgroupsCreating Various Styles of Box-and-Whisker PlotsCreating Notched Box-and-Whisker PlotsCreating Box-and-Whisker Plots with Varying WidthsCreating Box-and-Whisker Plots with Different Line Styles and ColorsComputing the Control Limits for Subgroup MaximumsConstructing Multi-Vari Charts
The following notation is used in this section:
|
|
process mean (expected value of the population of measurements) |
|
|
process standard deviation (standard deviation of the population of measurements) |
|
|
mean of measurements in ith subgroup |
|
|
sample size of ith subgroup |
|
N |
the number of subgroups |
|
|
jth measurement in the ith subgroup, |
|
|
jth largest measurement in the ith subgroup: |
|
|
weighted average of subgroup means |
|
|
median of the measurements in the ith subgroup: |
|
|
average of the subgroup medians: |
|
|
median of the subgroup medians. Denote the jth largest median by |
|
|
standard error of the median of n independent, normally distributed variables with unit standard deviation (the value of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
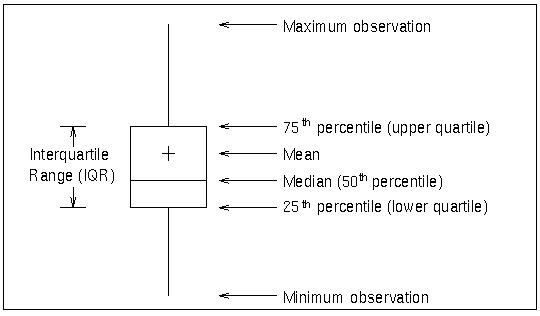
A box-and-whisker plot is displayed for the measurements in each subgroup on the box chart. Figure 17.14 illustrates the elements of each plot.
The skeletal style of the box-and-whisker plot shown in Figure 17.14 is the default. You can specify alternative styles with the BOXSTYLE= option; see Example 17.2 or the entry for BOXSTYLE= in Dictionary of Options: SHEWHART Procedure.
You can compute the limits in the following ways:
-
as a specified multiple (k) of the standard error of
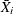 (or
(or 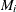 ) above and below the central line. The default limits are computed with k = 3 (these are referred to as
) above and below the central line. The default limits are computed with k = 3 (these are referred to as 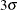 limits).
limits).
-
as probability limits defined in terms of
 , a specified probability that
, a specified probability that 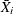 (or
(or 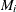 ) exceeds the limits
) exceeds the limits
The CONTROLSTAT= option specifies whether control limits are computed for subgroup means (the default) or subgroup medians. The following tables provide the formulas for the limits:
Table 17.5: Control Limits and Central Line for Box Charts
|
CONTROLSTAT=MEAN |
CONTROLSTAT=MEDIAN |
|---|---|
|
LCLX = lower limit = |
LCLM = lower limit = |
|
Central Line = |
Central Line = |
|
UCLX = upper limit = |
UCLM = upper limit = |
Table 17.6: Probability Limits and Central Line for Box Charts
|
CONTROLSTAT=MEAN |
CONTROLSTAT=MEDIAN |
|---|---|
|
LCLX = lower limit = |
LCLM = lower limit = |
|
Central Line = |
Central Line = |
|
UCLX = upper limit = |
UCLM = upper limit = |
In the preceding tables, replace ![]() with
with ![]() if you specify MEDCENTRAL=AVGMEAN in addition to CONTROLSTAT=MEDIAN. Likewise, replace
if you specify MEDCENTRAL=AVGMEAN in addition to CONTROLSTAT=MEDIAN. Likewise, replace ![]() with
with ![]() if you specify MEDCENTRAL=MEDMED in addition to CONTROLSTAT=MEDIAN. If standard values
if you specify MEDCENTRAL=MEDMED in addition to CONTROLSTAT=MEDIAN. If standard values ![]() and
and ![]() are available for
are available for ![]() and
and ![]() , replace
, replace ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() with
with ![]() in Table 17.5 and Table 17.6.
in Table 17.5 and Table 17.6.
Note that the limits vary with ![]() . The formulas for median limits assume that the data are normally distributed.
. The formulas for median limits assume that the data are normally distributed.
You can specify parameters for the limits as follows:
-
Specify k with the SIGMAS= option or with the variable
_SIGMAS_in a LIMITS= data set. -
Specify
 with the ALPHA= option or with the variable
with the ALPHA= option or with the variable _ALPHA_in a LIMITS= data set. -
Specify a constant nominal sample size
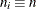 for the control limits with the LIMITN= option or with the variable
for the control limits with the LIMITN= option or with the variable _LIMITN_in a LIMITS= data set. -
Specify
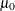 with the MU0= option or with the variable
with the MU0= option or with the variable _MEAN_in a LIMITS= data set. -
Specify
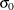 with the SIGMA0= option or with the variable
with the SIGMA0= option or with the variable _STDDEV_in a LIMITS= data set.
Note: You can suppress the display of the control limits with the NOLIMITS option. This is useful for creating standard side-by-side box-and-whisker plots.