-
COVARIANCE
COV
-
computes the principal components from the covariance matrix. If you omit the COV option, the correlation matrix is analyzed. Use of the COV option causes variables with large variances
to be more strongly associated with components with large eigenvalues and causes variables with small variances to be more
strongly associated with components with small eigenvalues. You should not specify the COV option unless the units in which
the variables are measured are comparable or the variables are standardized in some way.
-
DATA=SAS-data-set
-
specifies the SAS data set to be analyzed. The data set can be an ordinary SAS data set or a TYPE=ACE, TYPE=CORR, TYPE=COV,
TYPE=FACTOR, TYPE=SSCP, TYPE=UCORR, or TYPE=UCOV data set (see Appendix A: Special SAS Data Sets,). Also, the PRINCOMP procedure can read the _TYPE_=‘COVB’ matrix from a TYPE=EST data set. If you omit the DATA= option, the procedure uses the most recently created SAS data
set.
-
N=number
-
specifies the number of principal components to be computed. The default is the number of variables. The value of the N= option
must be an integer greater than or equal to zero.
-
NOINT
-
omits the intercept from the model. In other words, the NOINT option requests that the covariance or correlation matrix not
be corrected for the mean. When you use the PRINCOMP procedure with the NOINT option, the covariance matrix and, hence, the
standard deviations are not corrected for the mean. If you are interested in the standard deviations corrected for the mean,
you can get them by using a procedure such as the MEANS procedure.
If you use a TYPE=SSCP data set as input to the PRINCOMP procedure and list the variable Intercept in the VAR statement, the procedure acts as if you had also specified the NOINT option. If you use NOINT and also create
an OUTSTAT= data set, the data set is TYPE=UCORR or TYPE=UCOV rather than TYPE=CORR or TYPE=COV.
-
NOPRINT
-
suppresses the display of all output. Note that this option temporarily disables the Output Delivery System (ODS). For more
information, see Chapter 20: Using the Output Delivery System.
-
OUT=SAS-data-set
-
creates an output SAS data set that contains all the original data as well as the principal component scores.
If you want to create a SAS data set in a permanent library, you must specify a two-level name. For more information about
permanent libraries and SAS data sets, see
SAS Language Reference: Concepts. For details about OUT= data sets, see the section Output Data Sets.
-
OUTSTAT=SAS-data-set
-
creates an output SAS data set that contains means, standard deviations, number of observations, correlations or covariances,
eigenvalues, and eigenvectors. If you specify the COV option, the data set is TYPE=COV or TYPE=UCOV, depending on the NOINT
option, and it contains covariances; otherwise, the data set is TYPE=CORR or TYPE=UCORR, depending on the NOINT option, and
it contains correlations. If you specify the PARTIAL statement, the OUTSTAT= data set contains R squares as well.
If you want to create a SAS data set in a permanent library, you must specify a two-level name. For more information about
permanent libraries and SAS data sets, see
SAS Language Reference: Concepts. For details about OUTSTAT= data sets, see the section Output Data Sets.
-
PLOTS <(global-plot-options)> <= plot-request <(options)>>
PLOTS <(global-plot-options)> <= (plot-request <(options)> <... plot-request <(options)>>)>
-
controls the plots produced through ODS Graphics. When you specify only one plot request, you can omit the parentheses around the plot request. Here are some examples:
plots=none
plots=(scatter pattern)
plots(unpack)=scree
plots(ncomp=3 flip)=(pattern(circles=0.5 1.0) score)
ODS Graphics must be enabled before plots can be requested. For example:
ods graphics on;
proc princomp plots=all;
var x1--x10;
run;
ods graphics off;
For more information about enabling and disabling ODS Graphics, see the section Enabling and Disabling ODS Graphics in Chapter 21: Statistical Graphics Using ODS.
If ODS Graphics is enabled, but do not specify the PLOTS= option, PROC PRINCOMP produces the scree plot by default.
The global plot options include the following:
-
FLIP
-
flips or interchanges the X-axis and Y-axis dimension for the component score plots and the component pattern plots. For example,
if there are three components, the default plots (y * x) are Component 2 * Component 1, Component 3 * Component 1, and Component 3 * Component 2. When you specify PLOTS(FLIP), the plots are Component 1 * Component 2, Component 1 * Component 3, and Component 2 * Component 3.
-
NCOMP=n
-
specifies the number of components 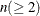 to be plotted for the component pattern plots and the component score plots. If the NCOMP= option is again specified in an
individual plot, such as PLOTS=SCORE(NCOMP= m), the value m will determine the number of components to be plotted in the component score plots. Be aware that the number of plots (
to be plotted for the component pattern plots and the component score plots. If the NCOMP= option is again specified in an
individual plot, such as PLOTS=SCORE(NCOMP= m), the value m will determine the number of components to be plotted in the component score plots. Be aware that the number of plots (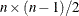 ) produced grows quadratically when n increases. The default is 5 or the total number of components
) produced grows quadratically when n increases. The default is 5 or the total number of components 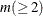 , whichever is smaller. If
, whichever is smaller. If 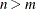 , NCOMP= m will be used.
, NCOMP= m will be used.
-
ONLY
-
suppresses the default plots. Only plots specifically requested are displayed.
-
UNPACKPANEL
UNPACK
-
suppresses paneling in the scree plot. By default, multiple plots can appear in an output panel. Specify UNPACKPANEL to get
each plot in a separate panel. You can specify PLOTS(UNPACKPANEL) to unpack the default plots. You can also specify UNPACKPANEL
as a suboption with SCREE (such as PLOTS=SCREE(UNPACKPANEL)).
The plot requests include the following:
-
ALL
-
produces all appropriate plots. You can specify other options with ALL; for example, to request all plots and unpack only
the scree plot, specify PLOTS=(ALL SCREE(UNPACKPANEL)).
-
EIGEN | EIGENVALUE | SCREE < ( UNPACKPANEL ) >
-
produces the scree plot of eigenvalues and proportion variance explained. By default, both plots are output in a panel. Specify
PLOTS= SCREE(UNPACKPANEL) to get each plot in a separate panel.
-
MATRIX
-
produces the matrix plot of principal component scores.
-
NONE
-
suppresses the display of all graphics output.
-
PATTERN < ( pattern-options ) >
-
produces the pairwise component pattern plots. Each variable is plotted as an observation whose coordinates are correlations
between the variable and the two corresponding components on the plot. Use the NCOMP= option (for instance, PLOTS=PATTERN(NCOMP=3))
described in the following to control the number of plots to be displayed.
The available pattern-options are as follows:
-
CIRCLES < = number list >
-
plots the variance percentage circles. Each number in the list must be greater than 0. If the number is greater than or equal
to 1, it is interpreted as a percentage and divided by 100; CIRCLES=0.05 and CIRCLES=5 are equivalent. For each number (c) specified, a (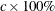 ) variance circle is created.
) variance circle is created.
By default, there is no circle for the scatter pattern plot (PLOTS=PATTERN) and a unit circle with a 100% variance circle
is plotted for the vector pattern plot (PLOTS=PATTERN (VECTOR)). You can display multiple circles by specifying PLOTS=PATTERN(CIRCLES=
). For example, specifying PLOTS=PATTERN(CIRCLES= .3 .6 1.0) will display the 30%, 60%, and 100% variance circles in the pattern
plots.
-
FLIP
-
flips or interchanges the X-axis and Y-axis dimensions for the component pattern plots. Specify PLOTS=PATTERN(FLIP) to flip
the X-axis and Y-axis dimensions.
-
NCOMP=n
-
specifies the number of components 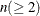 to be plotted. The default is 5 or the total number of components
to be plotted. The default is 5 or the total number of components 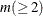 , whichever is smaller. If
, whichever is smaller. If 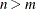 , NCOMP= m will be used. Be aware that the number of plots (
, NCOMP= m will be used. Be aware that the number of plots (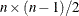 ) produced grows quadratically when n increases.
) produced grows quadratically when n increases.
-
VECTOR
-
plots pattern in a vector form.
-
PATTERNPROFILE | PROFILE
-
produces the pattern profile plot. There is a profile for each component. The Y-axis value represents the correlation between
the variable (corresponding to the X-axis value) and the profiled principal component.
-
SCORE < ( score-options ) >
-
produces the pairwise component score plots. Use the NCOMP= option (for instance, PLOTS=SCORE(NCOMP=3)) described in the following
to control the number of plots to be displayed.
The available score-options are as follows:
-
ALPHA=number list
-
specifies a list of numbers for the prediction ellipses to be displayed in the score plots. Each value ( ) in the list must be greater than 0. If
) in the list must be greater than 0. If  is greater than or equal to 1, it is interpreted as a percentage and divided by 100; ALPHA=0.05 and ALPHA=5 are equivalent.
is greater than or equal to 1, it is interpreted as a percentage and divided by 100; ALPHA=0.05 and ALPHA=5 are equivalent.
-
ELLIPSE
-
requests prediction ellipses for the principal component scores of a new observation to be created in the principal component
score plots. See the section “Confidence and Prediction Ellipses” in “The CORR Procedure” (
Base SAS Procedures Guide: Statistical Procedures), for details about the computation of a prediction ellipse.
-
FLIP
-
flips or interchanges the X-axis and Y-axis dimensions for the component score plots. Specify PLOTS=SCORE(FLIP) to flip the
X-axis and Y-axis dimensions.
-
NCOMP=n
-
specifies the number of components 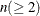 to be plotted. The default is 5 or the total number of components
to be plotted. The default is 5 or the total number of components 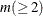 , whichever is smaller. If
, whichever is smaller. If 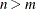 , NCOMP= m will be used. Be aware that the number of plots (
, NCOMP= m will be used. Be aware that the number of plots (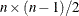 ) produced grows quadratically when n increases.
) produced grows quadratically when n increases.
-
PAINT <=position>
-
creates plots of component i versus component j, painted by component k. When there are at least three components, the PLOTS=SCORE option is specified, and the PAINT option is not specified, a
painted score plot for component 3 versus component 2, painted by component 1 is produced. Use the PAINT option when you want
to create painted score plots involving other triples of components.
PLOTS=SCORE(PAINT), PLOTS=SCORE(PAINT=F), and PLOTS=SCORE(PAINT= FIRST) are all equivalent and create painted plots of 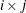 , painted by k for triples
, painted by k for triples 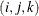 where
where 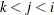 .
.
PLOTS=SCORE(PAINT=L) and PLOTS=SCORE(PAINT=LAST) are equivalent and create painted plots of 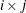 , painted by k for triples
, painted by k for triples 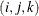 where
where 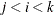 .
.
PLOTS=SCORE(PAINT=M) and PLOTS=SCORE(PAINT=MIDDLE) are equivalent and create painted plots of 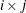 , painted by k for triples
, painted by k for triples 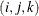 where
where 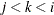 .
.
-
PREFIX=name
-
specifies a prefix for naming the principal components. By default, the names are Prin1, Prin2, …, Prinn. If you specify PREFIX=ABC, the components are named ABC1, ABC2, ABC3, and so on. The number of characters in the prefix plus the number of digits required to designate the variables should not
exceed the current name length defined by the VALIDVARNAME= system option.
-
PARPREFIX=name
PPREFIX=name
RPREFIX=name
-
specifies a prefix for naming the residual variables in the OUT= data set and the OUTSTAT= data set. By default, the prefix is R_. The number of characters in the prefix plus the maximum length of the variable names should not exceed the current name
length defined by the VALIDVARNAME= system option.
-
SINGULAR=p
SING=p
-
specifies the singularity criterion, where 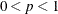 . If a variable in a PARTIAL statement has an R square as large as
. If a variable in a PARTIAL statement has an R square as large as 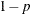 when predicted from the variables listed before it in the statement, the variable is assigned a standardized coefficient
of 0. By default, SINGULAR=1E–8.
when predicted from the variables listed before it in the statement, the variable is assigned a standardized coefficient
of 0. By default, SINGULAR=1E–8.
-
STANDARD
STD
-
standardizes the principal component scores in the OUT= data set to unit variance. If you omit the STANDARD option, the scores have variance equal to the corresponding eigenvalue. Note that STANDARD has no
effect on the eigenvalues themselves.
-
VARDEF=DF | N | WDF | WEIGHT | WGT
-
specifies the divisor used in calculating variances and standard deviations. By default, VARDEF=DF. The following table displays
the values and associated divisors.
|
Value
|
Divisor
|
Formula
|
|
DF
|
error degrees of freedom
|
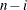
|
(before partialing)
|
| |
|
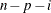
|
(after partialing)
|
|
N
|
number of observations
|
n
|
|
|
WEIGHT | WGT
|
sum of weights
|
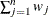
|
|
|
WDF
|
sum of weights minus one
|
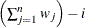
|
(before partialing)
|
| |
|
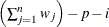
|
(after partialing)
|
In the formulas for VARDEF=DF and VARDEF=WDF, p is the number of degrees of freedom of the variables in the PARTIAL statement, and i is 0 if the NOINT option is specified and 1 otherwise.
