-
COEFFPRIOR=JEFFREYS<(option)> | NORMAL<(options)> | UNIFORM
COEFF=JEFFREYS<(options)> | NORMAL<(options)> | UNIFORM
CPRIOR=JEFFREYS<(options)> | NORMAL<(options)> | UNIFORM
-
specifies the prior distribution for the regression coefficients. The default is COEFFPRIOR=UNIFORM, which specifies the noninformative
and improper prior of a constant.
Jeffreys’ prior is specified by COEFFPRIOR=JEFFREYS, which can be followed by the following option in parentheses. Jeffreys’
prior is proportional to 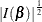 , where
, where 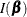 is the Fisher information matrix. See the section Jeffreys’ Prior and Ibrahim and Laud (1991) for more details.
is the Fisher information matrix. See the section Jeffreys’ Prior and Ibrahim and Laud (1991) for more details.
-
CONDITIONAL
-
specifies that the Jeffreys’ prior, conditional on the current Markov chain value of the generalized linear model precision
parameter  , is proportional to
, is proportional to 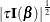 .
.
The normal prior is specified by COEFFPRIOR=NORMAL, which can be followed by one of the following options enclosed in parentheses. However, if you do not specify an option, the normal prior 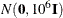 , where
, where 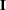 is the identity matrix, is used. See the section Normal Prior for more details.
is the identity matrix, is used. See the section Normal Prior for more details.
-
CONDITIONAL
-
specifies that the normal prior, conditional on the current Markov chain value of the generalized linear model precision parameter
 , is
, is 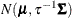 , where
, where 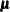 and
and 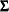 are the mean and covariance of the normal prior specified by other normal options.
are the mean and covariance of the normal prior specified by other normal options.
-
INPUT=SAS-data-set
-
specifies a SAS data set containing the mean and covariance information of the normal prior. The data set must have a _TYPE_ variable to represent the type of each observation and a variable for each regression coefficient. If the data set also contains
a _NAME_ variable, the values of this variable are used to identify the covariances for the _TYPE_=’COV’ observations; otherwise, the _TYPE_=’COV’ observations are assumed to be in the same order as the explanatory variables in the MODEL statement. PROC GENMOD reads
the mean vector from the observation with _TYPE_=’MEAN’ and reads the covariance matrix from observations with _TYPE_=’COV’. For an independent normal prior, the variances can be specified with _TYPE_=’VAR’; alternatively, the precisions (inverse of the variances) can be specified with _TYPE_=’PRECISION’.
-
RELVAR<=c>
-
specifies the normal prior 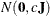 , where
, where 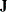 is a diagonal matrix with diagonal elements equal to the variances of the corresponding ML estimator. By default,
is a diagonal matrix with diagonal elements equal to the variances of the corresponding ML estimator. By default, 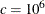 .
.
-
VAR<=c>
-
specifies the normal prior 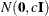 , where
, where 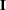 is the identity matrix.
is the identity matrix.
-
DIAGNOSTICS=ALL | NONE | (keyword-list)
DIAG=ALL | NONE | (keyword-list)
-
controls the number of diagnostics produced. You can request all the following diagnostics by specifying DIAGNOSTICS=ALL.
If you do not want any of these diagnostics, specify DIAGNOSTICS=NONE. If you want some but not all of the diagnostics, or
if you want to change certain settings of these diagnostics, specify a subset of the following keywords. The default is DIAGNOSTICS=(AUTOCORR ESS GEWEKE).
-
AUTOCORR <(LAGS= numeric-list)>
-
computes the autocorrelations of lags given by LAGS= list for each parameter. Elements in the list are truncated to integers
and repeated values are removed. If the LAGS= option is not specified, autocorrelations of lags 1, 5, 10, and 50 are computed
for each variable. See the section Autocorrelations in Chapter 7: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures, for details.
-
ESS
-
computes Carlin’s estimate of the effective sample size, the correlation time, and the efficiency of the chain for each parameter.
See the section Effective Sample Size in Chapter 7: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures, for details.
-
GELMAN <(gelman-options)>
-
computes the Gelman and Rubin convergence diagnostics. You can specify one or more of the following gelman-options:
-
NCHAIN | N=number
-
specifies the number of parallel chains used to compute the diagnostic, and must be 2 or larger. The default is NCHAIN=3.
If an INITIAL= data set is used, NCHAIN defaults to the number of rows in the INITIAL= data set. If any number other than
this is specified with the NCHAIN= option, the NCHAIN= value is ignored.
-
ALPHA=value
-
specifies the significance level for the upper bound. The default is ALPHA=0.05, resulting in a 97.5% bound.
See the section Gelman and Rubin Diagnostics in Chapter 7: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures, for details.
-
GEWEKE <(geweke-options)>
-
computes the Geweke spectral density diagnostics, which are essentially a two-sample t test between the first 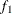 portion and the last
portion and the last 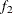 portion of the chain. The default is
portion of the chain. The default is 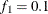 and
and 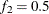 , but you can choose other fractions by using the following geweke-options:
, but you can choose other fractions by using the following geweke-options:
-
FRAC1=value
-
specifies the fraction 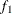 for the first window.
for the first window.
-
FRAC2=value
-
specifies the fraction 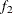 for the second window.
for the second window.
See the section Geweke Diagnostics in Chapter 7: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures, for details.
-
HEIDELBERGER <(heidel-options)>
-
computes the Heidelberger and Welch diagnostic for each variable, which consists of a stationarity test of the null hypothesis
that the sample values form a stationary process. If the stationarity test is not rejected, a halfwidth test is then carried
out. Optionally, you can specify one or more of the following heidel-options:
See the section Heidelberger and Welch Diagnostics in Chapter 7: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures, for details.
-
MCSE
MCERROR
-
computes the Monte Carlo standard error for each parameter. The Monte Caro standard error, which measures the simulation accuracy,
is the standard error of the posterior mean estimate and is calculated as the posterior standard deviation divided by the
square root of the effective sample size. See the section Standard Error of the Mean Estimate in Chapter 7: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures, for details.
-
RAFTERY<(raftery-options)>
-
computes the Raftery and Lewis diagnostics that evaluate the accuracy of the estimated quantile (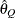 for a given
for a given 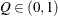 ) of a chain.
) of a chain. 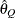 can achieve any degree of accuracy when the chain is allowed to run for a long time. A stopping criterion is when the estimated
probability
can achieve any degree of accuracy when the chain is allowed to run for a long time. A stopping criterion is when the estimated
probability 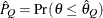 reaches within
reaches within 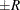 of the value Q with probability S; that is,
of the value Q with probability S; that is, 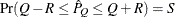 . The following raftery-options enable you to specify
. The following raftery-options enable you to specify 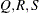 , and a precision level
, and a precision level  for the test:
for the test:
-
QUANTILE | Q=value
-
specifies the order (a value between 0 and 1) of the quantile of interest. The default is 0.025.
-
ACCURACY | R=value
-
specifies a small positive number as the margin of error for measuring the accuracy of estimation of the quantile. The default
is 0.005.
-
PROBABILITY | S=value
-
specifies the probability of attaining the accuracy of the estimation of the quantile. The default is 0.95.
-
EPSILON | EPS=value
-
specifies the tolerance level (a small positive number) for the stationary test. The default is 0.001.
See the section Raftery and Lewis Diagnostics in Chapter 7: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures, for details.
-
DISPERSIONPRIOR=GAMMA<(options)> | IGAMMA<(options)> | IMPROPER
DPRIOR=GAMMA<(options)> | IGAMMA<(options)> | IMPROPER
-
specifies that Gibbs sampling be performed on the generalized linear model dispersion parameter and the prior distribution
for the dispersion parameter, if there is a dispersion parameter in the model. For models that do not have a dispersion parameter
(the Poisson and binomial), this option is ignored. Note that you can specify Gibbs sampling on either the dispersion parameter
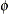 , the scale parameter
, the scale parameter 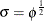 , or the precision parameter
, or the precision parameter 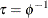 , with the DPRIOR=, SPRIOR=, and PPRIOR= options, respectively. These three parameters are transformations of one another,
and you should specify Gibbs sampling for only one of them.
, with the DPRIOR=, SPRIOR=, and PPRIOR= options, respectively. These three parameters are transformations of one another,
and you should specify Gibbs sampling for only one of them.
A gamma prior 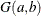 with density
with density 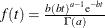 is specified by DISPERSIONPRIOR=GAMMA, which can be followed by one of the following gamma-options enclosed in parentheses. The hyperparameters a and b are the shape and inverse-scale parameters of the gamma distribution, respectively. See the section Gamma Prior for details. The default is
is specified by DISPERSIONPRIOR=GAMMA, which can be followed by one of the following gamma-options enclosed in parentheses. The hyperparameters a and b are the shape and inverse-scale parameters of the gamma distribution, respectively. See the section Gamma Prior for details. The default is 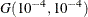 .
.
An inverse gamma prior 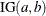 with density
with density 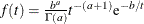 is specified by DISPERSIONPRIOR=IGAMMA, which can be followed by one of the following inverse gamma-options enclosed in parentheses. The hyperparameters a and b are the shape and scale parameters of the inverse gamma distribution, respectively. See the section Inverse Gamma Prior for details. The default is
is specified by DISPERSIONPRIOR=IGAMMA, which can be followed by one of the following inverse gamma-options enclosed in parentheses. The hyperparameters a and b are the shape and scale parameters of the inverse gamma distribution, respectively. See the section Inverse Gamma Prior for details. The default is 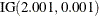 .
.
An improper prior with density 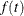 proportional to
proportional to 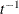 is specified with DISPERSIONPRIOR=IMPROPER.
is specified with DISPERSIONPRIOR=IMPROPER.
-
INITIAL=SAS-data-set
-
specifies the SAS data set that contains the initial values of the Markov chains. The INITIAL= data set must contain all the
variables of the model. You can specify multiple rows as the initial values of the parallel chains for the Gelman-Rubin statistics,
but posterior summaries, diagnostics, and plots are computed only for the first chain. If the data set also contains the variable
_SEED_, the value of the _SEED_ variable is used as the seed of the random number generator for the corresponding chain.
-
INITIALMLE
-
specifies that maximum likelihood estimates of the model parameters be used as initial values of the Markov chain. If this
option is not specified, estimates of the mode of the posterior distribution obtained by optimization are used as initial
values.
-
METROPOLIS=YES | NO
-
specifies the use of a Metropolis step to generate Gibbs samples for posterior distributions that are not log concave. The
default value is METROPOLIS=YES.
-
NBI=number
-
specifies the number of burn-in iterations before the chains are saved. The default is 2000.
-
NMC=number
-
specifies the number of iterations after the burn-in. The default is 10000.
-
OUTPOST=SAS-data-set
OUT=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set that contains the posterior samples. See the sections OUTPOST= Output Data Set and Posterior Samples Output Data Set for more information. Alternatively, you can create the output data set by specifying an ODS OUTPUT statement as follows:
ODS OUTPUT POSTERIORSAMPLE=SAS-data-set
-
PRECISIONPRIOR=GAMMA<(options)> | IMPROPER
PPRIOR=GAMMA<(options)> | IMPROPER
-
specifies that Gibbs sampling be performed on the generalized linear model precision parameter and the prior distribution
for the precision parameter, if there is a precision parameter in the model. For models that do not have a precision parameter
(the Poisson and binomial), this option is ignored. Note that you can specify Gibbs sampling on either the dispersion parameter
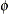 , the scale parameter
, the scale parameter 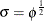 , or the precision parameter
, or the precision parameter 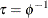 , with the DPRIOR=, SPRIOR=, and PPRIOR= options, respectively. These three parameters are transformations of one another,
and you should specify Gibbs sampling for only one of them.
, with the DPRIOR=, SPRIOR=, and PPRIOR= options, respectively. These three parameters are transformations of one another,
and you should specify Gibbs sampling for only one of them.
A gamma prior 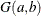 with density
with density 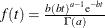 is specified by PRECISIONPRIOR=GAMMA, which can be followed by one of the following gamma-options enclosed in parentheses. The hyperparameters a and b are the shape and inverse-scale parameters of the gamma distribution, respectively. See the section Gamma Prior for details. The default is
is specified by PRECISIONPRIOR=GAMMA, which can be followed by one of the following gamma-options enclosed in parentheses. The hyperparameters a and b are the shape and inverse-scale parameters of the gamma distribution, respectively. See the section Gamma Prior for details. The default is 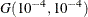 .
.
An improper prior with density 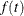 proportional to
proportional to 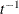 is specified with PRECISIONPRIOR=IMPROPER.
is specified with PRECISIONPRIOR=IMPROPER.
-
PLOTS<(global-plot-options)>=plot-request
PLOTS<(global-plot-options)>=(plot-request < …plot-request>)
-
controls the display of diagnostic plots. Three types of plots can be requested: trace plots, autocorrelation function plots,
and kernel density plots. By default, the plots are displayed in panels unless the global-plot-option UNPACK is specified. Also, when you are specifying more than one type of plots, the plots are displayed by parameters unless
the global-plot-option GROUPBY is specified. When you specify only one plot-request, you can omit the parentheses around the plot-request. For example:
plots=none
plots(unpack)=trace
plots=(trace autocorr)
ODS Graphics must be enabled before requesting plots. For example, the following SAS statements enable ODS Graphics:
ods graphics on;
proc genmod;
model y=x;
bayes plots=trace;
run;
ods graphics off;
The global-plot-options are as follows:
-
FRINGE
-
creates a fringe plot on the X axis of the density plot.
-
GROUPBY=PARAMETER
GROUPBY=TYPE
-
specifies how the plots are grouped when there is more than one type of plot.
-
GROUPBY=TYPE
-
specifies that the plots be grouped by type.
-
GROUPBY=PARAMETER
-
specifies that the plots be grouped by parameter.
GROUPBY=PARAMETER is the default.
-
LAGS=n
-
specifies that autocorrelations be plotted up to lag n. If this option is not specified, autocorrelations are plotted up to lag 50.
-
SMOOTH
-
displays a fitted penalized B-spline curve for each trace plot.
-
UNPACKPANEL
UNPACK
-
specifies that all paneled plots be unpacked, meaning that each plot in a panel is displayed separately.
The plot-requests include the following:
-
ALL
-
specifies all types of plots. PLOTS=ALL is equivalent to specifying PLOTS=(TRACE AUTOCORR DENSITY).
-
AUTOCORR
-
displays the autocorrelation function plots for the parameters.
-
DENSITY
-
displays the kernel density plots for the parameters.
-
NONE
-
suppresses all diagnostic plots.
-
TRACE
-
displays the trace plots for the parameters. See the section Visual Analysis via Trace Plots in Chapter 7: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures, for details.
-
SAMPLING=option
-
specifies an algorithm used to sample the posterior distribution. The following options are available:
-
ARMS
GIBBS
-
use the ARMS algorithm.
-
GAMERMAN
GAM
-
use the Gamerman algorithm. This is the default method except for the normal distribution with a conjugate prior. In this
case a closed form for the posterior distribution is available, and samples are obtained directly from the posterior distribution.
-
IM
-
Use the independent Metropolis algorithm.
-
SCALEPRIOR=GAMMA<(options)> | IMPROPER
SPRIOR=GAMMA<(options)> | IMPROPER
-
specifies that Gibbs sampling be performed on the generalized linear model scale parameter and the prior distribution for
the scale parameter, if there is a scale parameter in the model. For models that do not have a scale parameter (the Poisson
and binomial), this option is ignored. Note that you can specify Gibbs sampling on either the dispersion parameter 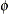 , the scale parameter
, the scale parameter 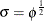 , or the precision parameter
, or the precision parameter 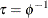 , with the DPRIOR=, SPRIOR=, and PPRIOR= options, respectively. These three parameters are transformations of one another,
and you should specify Gibbs sampling for only one of them.
, with the DPRIOR=, SPRIOR=, and PPRIOR= options, respectively. These three parameters are transformations of one another,
and you should specify Gibbs sampling for only one of them.
A gamma prior 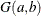 with density
with density 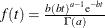 is specified by SCALEPRIOR=GAMMA, which can be followed by one of the following gamma-options enclosed in parentheses. The hyperparameters a and b are the shape and inverse-scale parameters of the gamma distribution, respectively. See the section Gamma Prior for details. The default is
is specified by SCALEPRIOR=GAMMA, which can be followed by one of the following gamma-options enclosed in parentheses. The hyperparameters a and b are the shape and inverse-scale parameters of the gamma distribution, respectively. See the section Gamma Prior for details. The default is 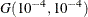 .
.
An improper prior with density 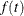 proportional to
proportional to 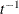 is specified with SCALEPRIOR=IMPROPER.
is specified with SCALEPRIOR=IMPROPER.
-
SEED=number
-
specifies an integer seed in the range 1 to 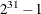 for the random number generator in the simulation. Specifying a seed enables you to reproduce identical Markov chains for
the same specification. If the SEED= option is not specified, or if you specify a nonpositive seed, a random seed is derived
from the time of day.
for the random number generator in the simulation. Specifying a seed enables you to reproduce identical Markov chains for
the same specification. If the SEED= option is not specified, or if you specify a nonpositive seed, a random seed is derived
from the time of day.
-
STATISTICS <(global-options)> = ALL | NONE | keyword | (keyword-list)
STATS <(global-options)> = ALL | NONE | keyword | (keyword-list)
-
controls the number of posterior statistics produced. Specifying STATISTICS=ALL is equivalent to specifying STATISTICS= (SUMMARY
INTERVAL COV CORR). If you do not want any posterior statistics, you specify STATISTICS=NONE. The default is STATISTICS=(SUMMARY
INTERVAL). See the section Summary Statistics in Chapter 7: Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures, for details. The global-options include the following:
-
ALPHA=numeric-list
-
controls the probabilities of the credible intervals. The ALPHA= values must be between 0 and 1. Each ALPHA= value produces
a pair of 100(1–ALPHA)% equal-tail and HPD intervals for each parameters. The default is the value of the ALPHA= option in
the MODEL statement, or 0.05 if that option is not specified (yielding the 95% credible intervals for each parameter).
-
PERCENT=numeric-list
-
requests the percentile points of the posterior samples. The PERCENT= values must be between 0 and 100. The default is PERCENT=25,
50, 75, which yield the 25th, 50th, and 75th percentile points, respectively, for each parameter.
The list of keywords includes the following:
-
CORR
-
produces the posterior correlation matrix.
-
COV
-
produces the posterior covariance matrix.
-
SUMMARY
-
produces the means, standard deviations, and percentile points for the posterior samples. The default is to produce the 25th,
50th, and 75th percentile points, but you can use the global PERCENT= option to request specific percentile points.
-
INTERVAL
-
produces equal-tail credible intervals and HPD intervals. The default is to produce the 95% equal-tail credible intervals
and 95% HPD intervals, but you can use the global ALPHA= option to request intervals of any probabilities.
-
THINNING=number
THIN=number
-
controls the thinning of the Markov chain. Only one in every k
samples is used when THINNING=k, and if NBI=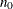 and NMC=n, the number of samples kept is
and NMC=n, the number of samples kept is
where [a] represents the integer part of the number a. The default is THINNING=1.


 PROC GENMOD StatementASSESS StatementBAYES StatementBY StatementCLASS StatementCODE StatementCONTRAST StatementDEVIANCE StatementEFFECTPLOT StatementESTIMATE StatementEXACT StatementEXACTOPTIONS StatementFREQ StatementFWDLINK StatementINVLINK StatementLSMEANS StatementLSMESTIMATE StatementMODEL StatementOUTPUT StatementProgramming StatementsREPEATED StatementSLICE StatementSTORE StatementSTRATA StatementVARIANCE StatementWEIGHT StatementZEROMODEL Statement
PROC GENMOD StatementASSESS StatementBAYES StatementBY StatementCLASS StatementCODE StatementCONTRAST StatementDEVIANCE StatementEFFECTPLOT StatementESTIMATE StatementEXACT StatementEXACTOPTIONS StatementFREQ StatementFWDLINK StatementINVLINK StatementLSMEANS StatementLSMESTIMATE StatementMODEL StatementOUTPUT StatementProgramming StatementsREPEATED StatementSLICE StatementSTORE StatementSTRATA StatementVARIANCE StatementWEIGHT StatementZEROMODEL Statement Generalized Linear Models TheorySpecification of EffectsParameterization Used in PROC GENMODType 1 AnalysisType 3 AnalysisConfidence Intervals for ParametersF StatisticsLagrange Multiplier StatisticsPredicted Values of the MeanResidualsMultinomial ModelsZero-Inflated ModelsTweedie Distribution For Generalized Linear ModelsGeneralized Estimating EquationsAssessment of Models Based on Aggregates of ResidualsCase Deletion Diagnostic StatisticsBayesian AnalysisExact Logistic and Exact Poisson RegressionMissing ValuesDisplayed Output for Classical AnalysisDisplayed Output for Bayesian AnalysisDisplayed Output for Exact AnalysisODS Table NamesODS Graphics
Generalized Linear Models TheorySpecification of EffectsParameterization Used in PROC GENMODType 1 AnalysisType 3 AnalysisConfidence Intervals for ParametersF StatisticsLagrange Multiplier StatisticsPredicted Values of the MeanResidualsMultinomial ModelsZero-Inflated ModelsTweedie Distribution For Generalized Linear ModelsGeneralized Estimating EquationsAssessment of Models Based on Aggregates of ResidualsCase Deletion Diagnostic StatisticsBayesian AnalysisExact Logistic and Exact Poisson RegressionMissing ValuesDisplayed Output for Classical AnalysisDisplayed Output for Bayesian AnalysisDisplayed Output for Exact AnalysisODS Table NamesODS Graphics Logistic RegressionNormal Regression, Log Link Gamma Distribution Applied to Life DataOrdinal Model for Multinomial DataGEE for Binary Data with Logit Link FunctionLog Odds Ratios and the ALR AlgorithmLog-Linear Model for Count DataModel Assessment of Multiple Regression Using Aggregates of ResidualsAssessment of a Marginal Model for Dependent DataBayesian Analysis of a Poisson Regression ModelExact Poisson RegressionTweedie Regression
Logistic RegressionNormal Regression, Log Link Gamma Distribution Applied to Life DataOrdinal Model for Multinomial DataGEE for Binary Data with Logit Link FunctionLog Odds Ratios and the ALR AlgorithmLog-Linear Model for Count DataModel Assessment of Multiple Regression Using Aggregates of ResidualsAssessment of a Marginal Model for Dependent DataBayesian Analysis of a Poisson Regression ModelExact Poisson RegressionTweedie Regression