The MODECLUS Procedure
This example uses pseudo-random samples from a uniform distribution, an exponential distribution, and a bimodal mixture of two normal distributions. Results are presented in Output 64.1.1 through Output 64.1.18 as plots displaying both the true density and the estimated density, as well as cluster membership.
The following statements produce Output 64.1.1 through Output 64.1.4:
title 'Modeclus Example with Univariate Distributions';
title2 'Uniform Distribution';
data uniform;
drop n;
true=1;
do n=1 to 100;
x=ranuni(123);
output;
end;
run;
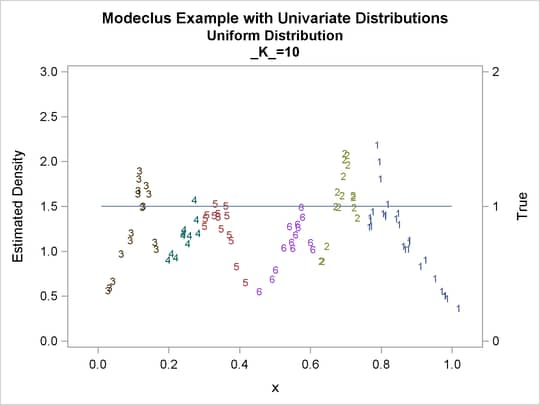
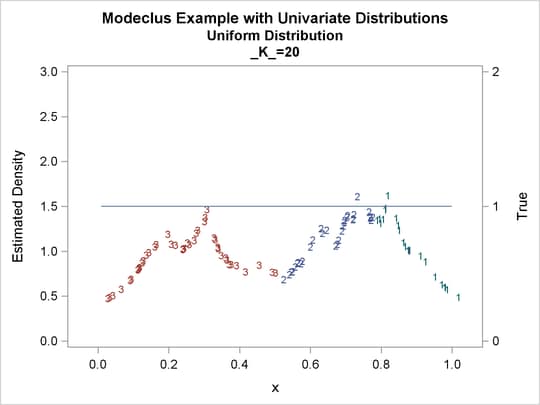
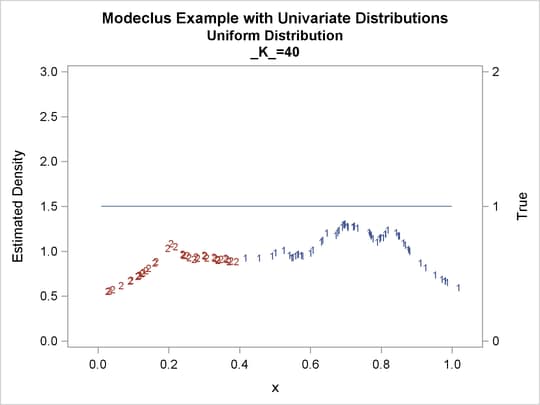
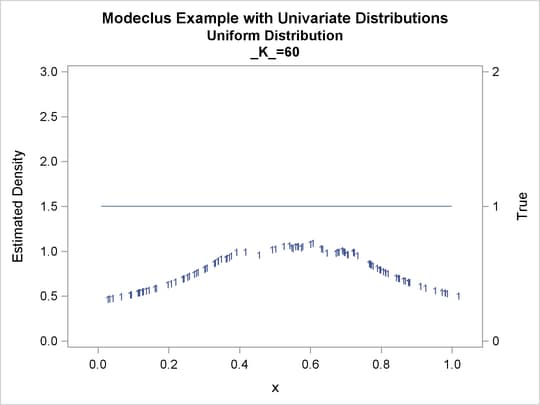
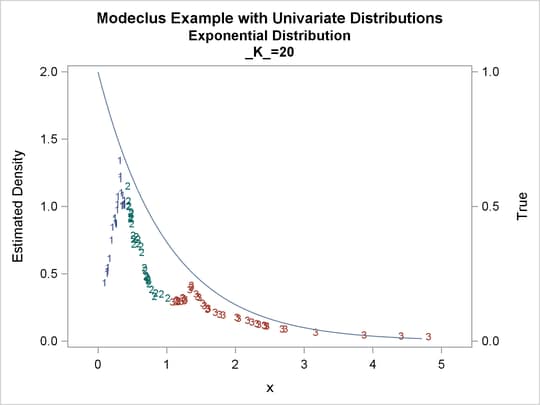
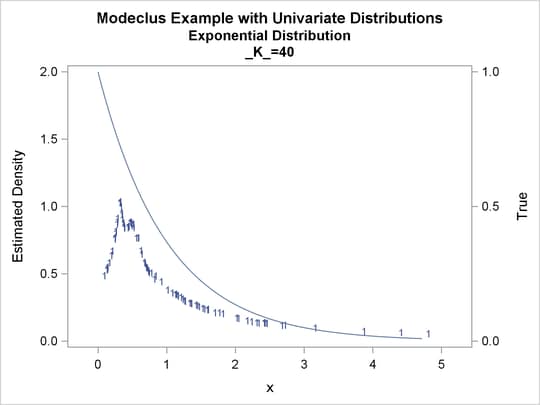
proc modeclus data=uniform m=1 k=10 20 40 60 out=out short; var x; run; proc sgplot data=out noautolegend; y2axis label='True' values=(0 to 2 by 1.); yaxis values=(0 to 3 by 0.5); scatter y=density x=x / markerchar=cluster group=cluster; pbspline y=true x=x / y2axis nomarkers lineattrs=(thickness= 1); by _K_; run;
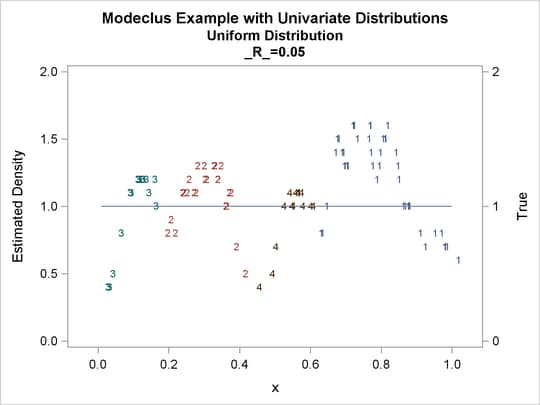
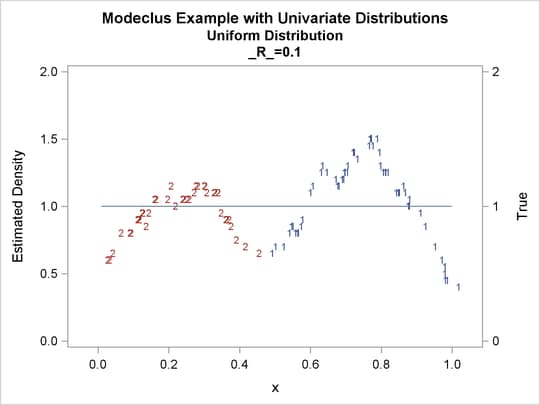
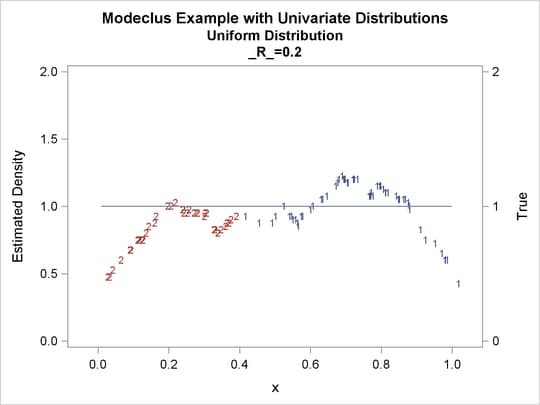
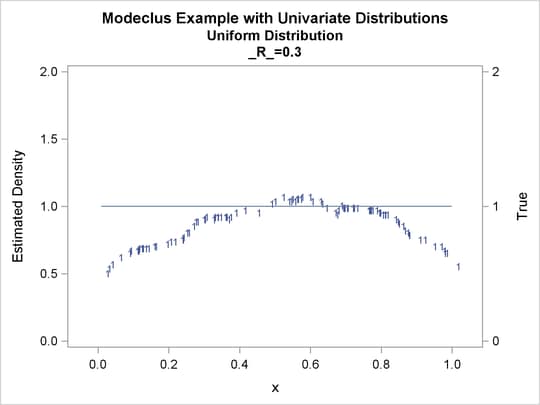
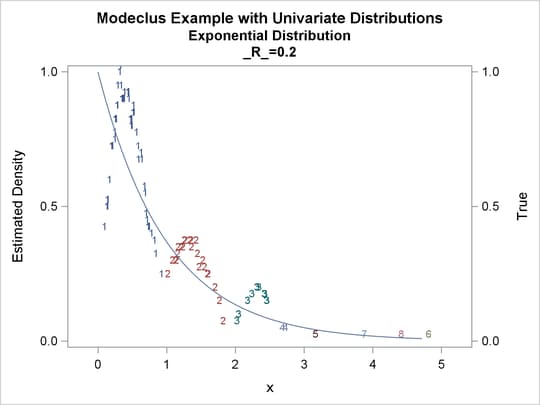
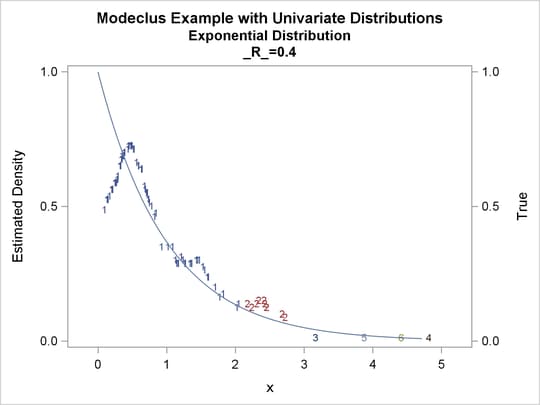
proc modeclus data=uniform m=1 r=.05 .10 .20 .30 out=out short; var x; run; proc sgplot data=out noautolegend; y2axis label='True' values=(0 to 2 by 1.); yaxis values=(0 to 2 by 0.5); scatter y=density x=x / markerchar=cluster group=cluster; pbspline y=true x=x / y2axis nomarkers lineattrs=(thickness= 1); by _R_; run;
Output 64.1.1: Cluster Analysis of Sample from a Uniform Distribution
| Modeclus Example with Univariate Distributions |
| Uniform Distribution |
| Cluster Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| K | Number of Clusters |
Frequency of Unclassified Objects |
| 10 | 6 | 0 |
| 20 | 3 | 0 |
| 40 | 2 | 0 |
| 60 | 1 | 0 |
Output 64.1.3: Cluster Analysis of Sample from a Uniform Distribution
| Modeclus Example with Univariate Distributions |
| Uniform Distribution |
| Cluster Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| R | Number of Clusters |
Frequency of Unclassified Objects |
| 0.05 | 4 | 0 |
| 0.1 | 2 | 0 |
| 0.2 | 2 | 0 |
| 0.3 | 1 | 0 |
The following statements produce Output 64.1.5 through Output 64.1.12:
data expon;
title2 'Exponential Distribution';
drop n;
do n=1 to 100;
x=ranexp(123);
true=exp(-x);
output;
end;
run;
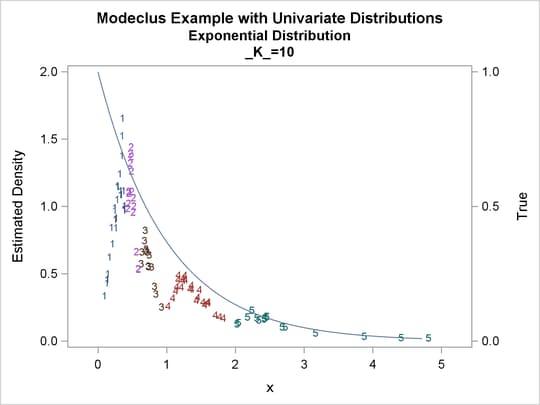
proc modeclus data=expon m=1 k=10 20 40 out=out short; var x; run; proc sgplot data=out noautolegend; y2axis label='True' values=(0 to 1 by .5); yaxis values=(0 to 2 by 0.5); scatter y=density x=x / markerchar=cluster group=cluster; pbspline y=true x=x / y2axis nomarkers lineattrs=(thickness= 1); by _K_; run;
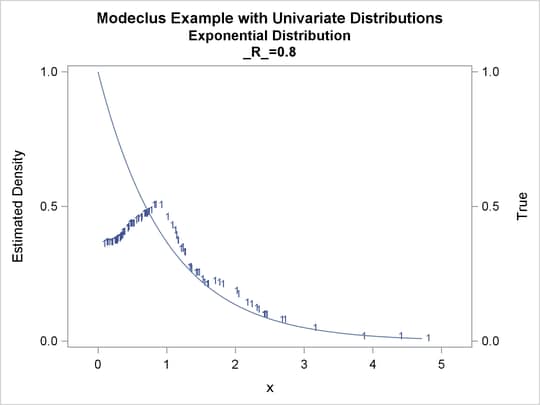
proc modeclus data=expon m=1 r=.20 .40 .80 out=out short; var x; run; proc sgplot data=out noautolegend; y2axis label='True' values=(0 to 1 by .5); yaxis values=(0 to 1 by 0.5); scatter y=density x=x / markerchar=cluster group=cluster; pbspline y=true x=x / y2axis nomarkers lineattrs=(thickness= 1); by _R_; run;
title3 'Different Density-Estimation and Clustering Windows';
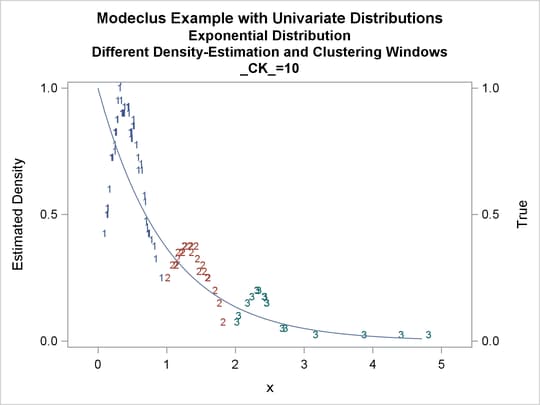
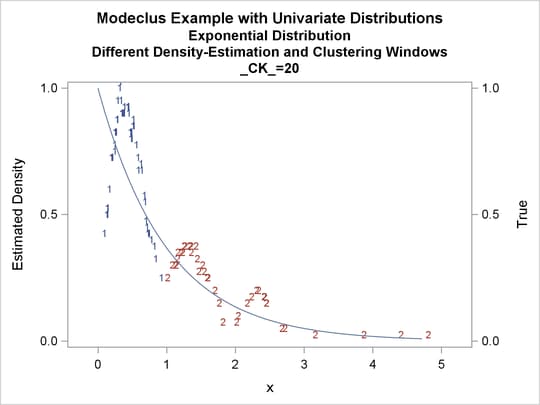
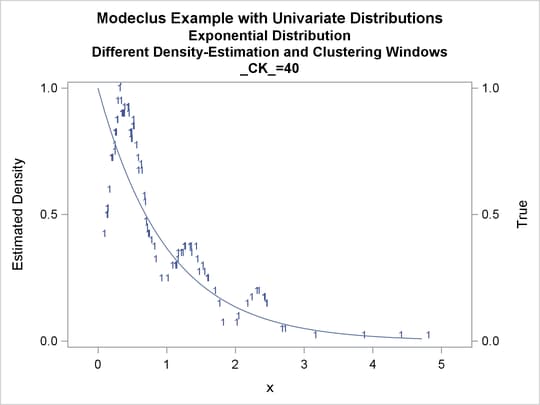
proc modeclus data=expon m=1 r=.20 ck=10 20 40
out=out short;
var x;
run;
proc sgplot data=out noautolegend;
y2axis label='True' values=(0 to 1 by .5);
yaxis values=(0 to 1 by 0.5);
scatter y=density x=x / markerchar=cluster group=cluster;
pbspline y=true x=x / y2axis nomarkers lineattrs=(thickness= 1);
by _CK_;
run;
title3 'Cascaded Density Estimates Using Arithmetic Means'; proc modeclus data=expon m=1 r=.20 cascade=1 2 4 am out=out short; var x; run; proc sgplot data=out noautolegend; y2axis label='True' values=(0 to 1 by .5); yaxis values=(0 to 1 by 0.5); scatter y=density x=x / markerchar=cluster group=cluster; pbspline y=true x=x / y2axis nomarkers lineattrs=(thickness= 1); by _R_ _CASCAD_; run;
Output 64.1.5: Cluster Analysis of Sample from an Exponential Distribution
| Modeclus Example with Univariate Distributions |
| Exponential Distribution |
| Cluster Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| K | Number of Clusters |
Frequency of Unclassified Objects |
| 10 | 5 | 0 |
| 20 | 3 | 0 |
| 40 | 1 | 0 |
Output 64.1.7: Cluster Analysis of Sample from an Exponential Distribution
| Modeclus Example with Univariate Distributions |
| Exponential Distribution |
| Cluster Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| R | Number of Clusters |
Frequency of Unclassified Objects |
| 0.2 | 8 | 0 |
| 0.4 | 6 | 0 |
| 0.8 | 1 | 0 |
Output 64.1.9: Cluster Analysis of Sample from an Exponential Distribution
| Modeclus Example with Univariate Distributions |
| Exponential Distribution |
| Different Density-Estimation and Clustering Windows |
| Cluster Summary | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| R | CK | Number of Clusters |
Frequency of Unclassified Objects |
| 0.2 | 10 | 3 | 0 |
| 0.2 | 20 | 2 | 0 |
| 0.2 | 40 | 1 | 0 |
Output 64.1.10: True Density, Estimated Density, and Cluster Membership by _R_=0.2 with Various _CK_ Values
Output 64.1.11: Cluster Analysis of Sample from an Exponential Distribution
| Modeclus Example with Univariate Distributions |
| Exponential Distribution |
| Cascaded Density Estimates Using Arithmetic Means |
| Cluster Summary | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| R | Cascade | Number of Clusters |
Frequency of Unclassified Objects |
| 0.2 | 1 | 8 | 0 |
| 0.2 | 2 | 8 | 0 |
| 0.2 | 4 | 7 | 0 |
Output 64.1.12: True Density, Estimated Density, and Cluster Membership by _R_=0.2 with Various _CASCAD_ Values
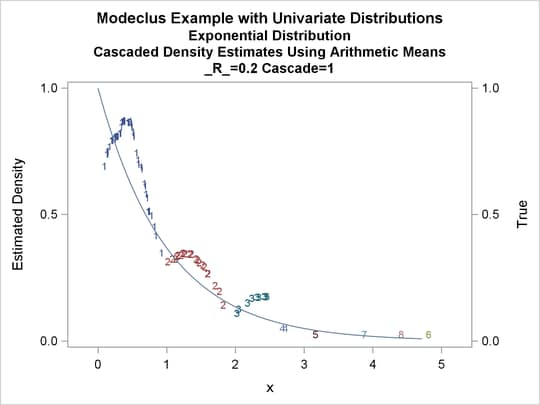
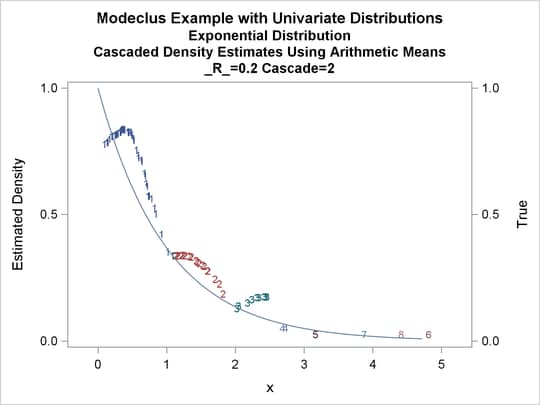
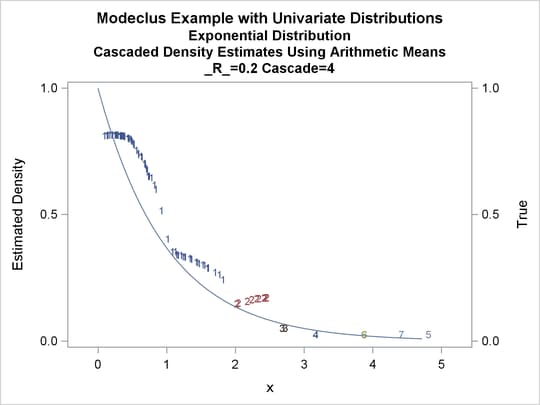
The following statements produce Output 64.1.13 through Output 64.1.18:
title2 'Normal Mixture Distribution';
data normix;
drop n sigma;
sigma=.125;
do n=1 to 100;
x=rannor(456)*sigma+mod(n,2)/2;
true=exp(-.5*(x/sigma)**2)+exp(-.5*((x-.5)/sigma)**2);
true=.5*true/(sigma*sqrt(2*3.1415926536));
output;
end;
run;
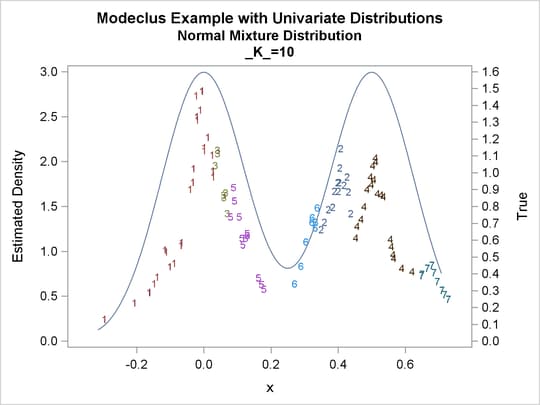
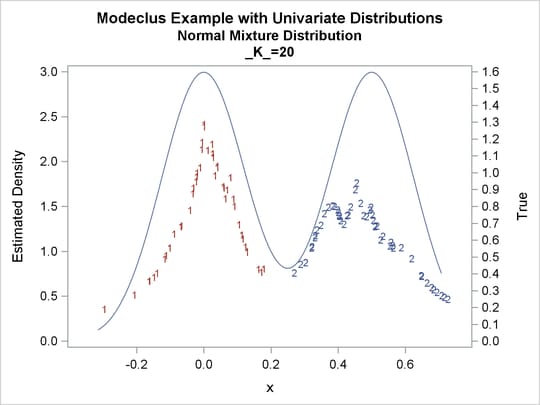
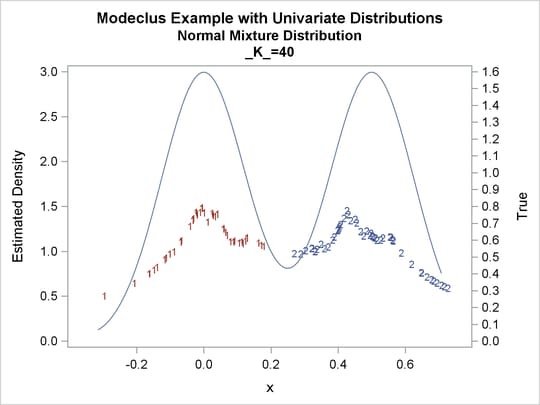
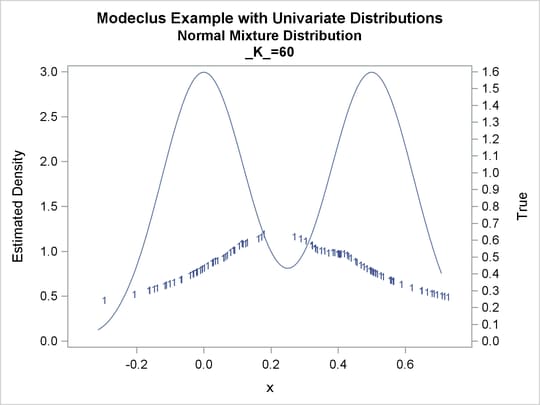
proc modeclus data=normix m=1 k=10 20 40 60 out=out short; var x; run; proc sgplot data=out noautolegend; y2axis label='True' values=(0 to 1.6 by .1); yaxis values=(0 to 3 by 0.5); scatter y=density x=x / markerchar=cluster group=cluster; pbspline y=true x=x / y2axis nomarkers lineattrs=(thickness= 1); by _K_; run;
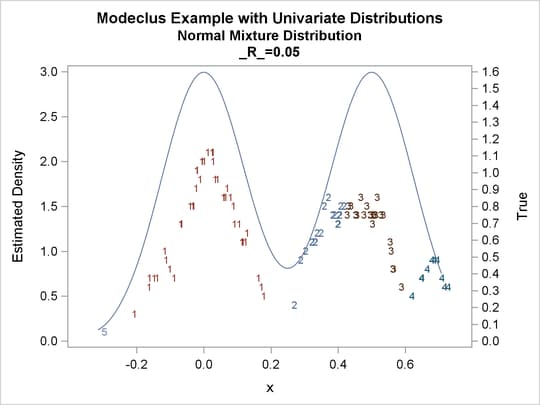
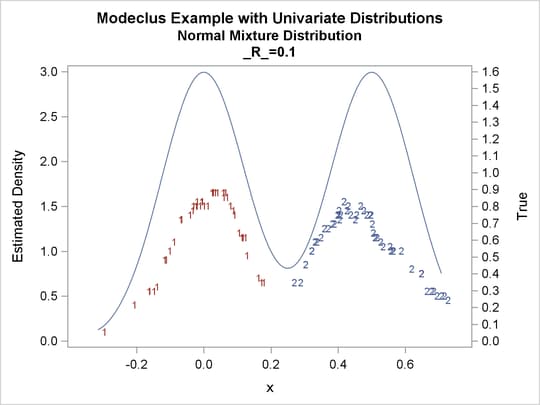
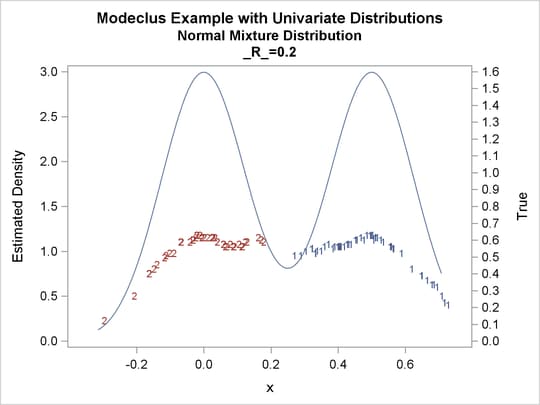
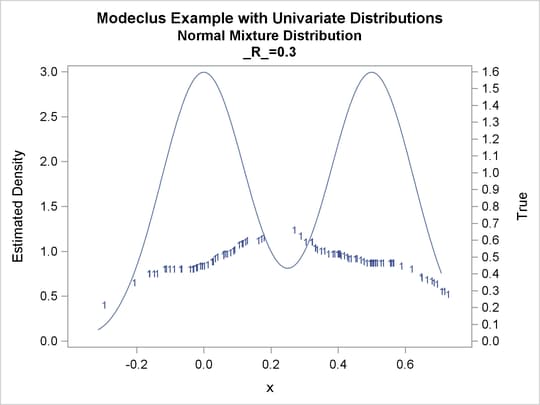
proc modeclus data=normix m=1 r=.05 .10 .20 .30 out=out short; var x; run; proc sgplot data=out noautolegend; y2axis label='True' values=(0 to 1.6 by .1); yaxis values=(0 to 3 by 0.5); scatter y=density x=x / markerchar=cluster group=cluster; pbspline y=true x=x / y2axis nomarkers lineattrs=(thickness= 1); by _R_; run;
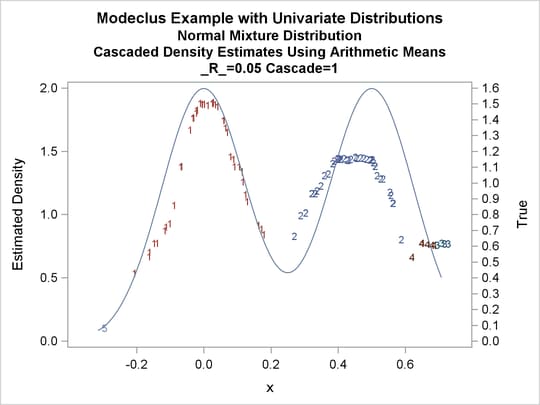
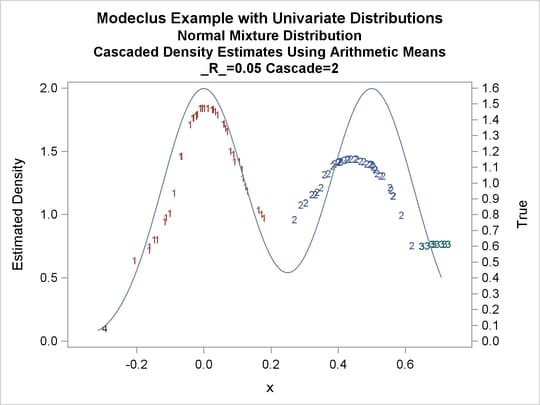
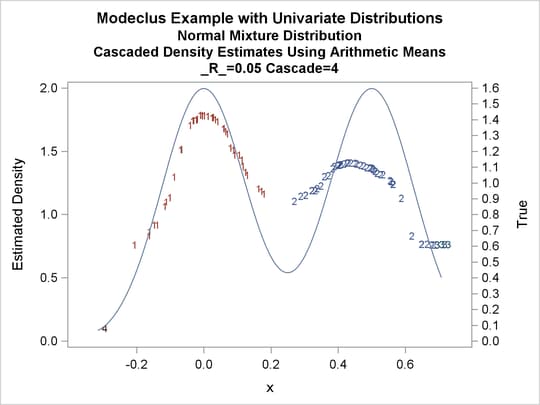
title3 'Cascaded Density Estimates Using Arithmetic Means'; proc modeclus data=normix m=1 r=.05 cascade=1 2 4 am out=out short; var x; run; proc sgplot data=out noautolegend; y2axis label='True' values=(0 to 1.6 by .1); yaxis values=(0 to 2 by 0.5); scatter y=density x=x / markerchar=cluster group=cluster; pbspline y=true x=x / y2axis nomarkers lineattrs=(thickness= 1); by _R_ _CASCAD_; run;
Output 64.1.13: Cluster Analysis of Sample from a Bimodal Mixture of Two Normal Distributions
| Modeclus Example with Univariate Distributions |
| Normal Mixture Distribution |
| Cluster Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| K | Number of Clusters |
Frequency of Unclassified Objects |
| 10 | 7 | 0 |
| 20 | 2 | 0 |
| 40 | 2 | 0 |
| 60 | 1 | 0 |
Output 64.1.15: Cluster Analysis of Sample from a Bimodal Mixture of Two Normal Distributions
| Modeclus Example with Univariate Distributions |
| Normal Mixture Distribution |
| Cluster Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| R | Number of Clusters |
Frequency of Unclassified Objects |
| 0.05 | 5 | 0 |
| 0.1 | 2 | 0 |
| 0.2 | 2 | 0 |
| 0.3 | 1 | 0 |
Output 64.1.17: Cluster Analysis of Sample from a Bimodal Mixture of Two Normal Distributions
| Modeclus Example with Univariate Distributions |
| Normal Mixture Distribution |
| Cascaded Density Estimates Using Arithmetic Means |
| Cluster Summary | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| R | Cascade | Number of Clusters |
Frequency of Unclassified Objects |
| 0.05 | 1 | 5 | 0 |
| 0.05 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| 0.05 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
Output 64.1.18: True Density, Estimated Density, and Cluster Membership by _R_=0.05 with Various _CASCAD_ Values