The REG Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 Missing ValuesInput Data SetsOutput Data SetsInteractive AnalysisModel-Selection MethodsCriteria Used in Model-Selection MethodsLimitations in Model-Selection MethodsParameter Estimates and Associated StatisticsPredicted and Residual ValuesModels of Less Than Full RankCollinearity DiagnosticsModel Fit and Diagnostic StatisticsInfluence StatisticsReweighting Observations in an AnalysisTesting for HeteroscedasticityTesting for Lack of FitMultivariate TestsAutocorrelation in Time Series DataComputations for Ridge Regression and IPC AnalysisConstruction of Q-Q and P-P PlotsComputational MethodsComputer Resources in Regression AnalysisDisplayed OutputPlot Options Superseded by ODS GraphicsODS Table NamesODS Graphics
Missing ValuesInput Data SetsOutput Data SetsInteractive AnalysisModel-Selection MethodsCriteria Used in Model-Selection MethodsLimitations in Model-Selection MethodsParameter Estimates and Associated StatisticsPredicted and Residual ValuesModels of Less Than Full RankCollinearity DiagnosticsModel Fit and Diagnostic StatisticsInfluence StatisticsReweighting Observations in an AnalysisTesting for HeteroscedasticityTesting for Lack of FitMultivariate TestsAutocorrelation in Time Series DataComputations for Ridge Regression and IPC AnalysisConstruction of Q-Q and P-P PlotsComputational MethodsComputer Resources in Regression AnalysisDisplayed OutputPlot Options Superseded by ODS GraphicsODS Table NamesODS Graphics -
Examples

- References
PROC REG <options> ;
The PROC REG statement invokes the REG procedure. The PROC REG statement is required. If you want to fit a model to the data, you must also use a MODEL statement. If you want to use only the PROC REG options, you do not need a MODEL statement, but you must use a VAR statement. If you do not use a MODEL statement, then the COVOUT and OUTEST= options are not available.
Table 83.1 summarizes the options available in the PROC REG statement. Note that any option specified in the PROC REG statement applies to all MODEL statements.
Table 83.1: PROC REG Statement Options
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Data Set Options |
|
|
Names a data set to use for the regression |
|
|
Outputs a data set that contains parameter estimates and other |
|
|
Outputs a data set that contains sums of squares and crossproducts |
|
|
Outputs the covariance matrix for parameter estimates to the |
|
|
Outputs the number of regressors, the error degrees of freedom, |
|
|
Outputs standard errors of the parameter estimates to the |
|
|
Outputs standardized parameter estimates to the OUTEST= data |
|
|
Outputs the variance inflation factors to the OUTEST= data set. |
|
|
Performs incomplete principal component analysis and outputs |
|
|
Outputs the PRESS statistic to the OUTEST= data set |
|
|
Performs ridge regression analysis and outputs estimates to the |
|
|
Same effect as the EDF option |
|
|
Outputs standard errors, confidence limits, and associated test |
|
|
ODS Graphics Options |
|
|
Produces ODS graphical displays |
|
|
Display Options |
|
|
Displays correlation matrix for variables listed in MODEL and |
|
|
Displays simple statistics for each variable listed in MODEL and |
|
|
Displays uncorrected sums of squares and crossproducts matrix |
|
|
Displays all statistics (CORR, SIMPLE, and USSCP) |
|
|
Suppresses output |
|
|
Other Options |
|
|
Sets significance value for confidence and prediction intervals and tests |
|
|
Sets criterion for checking for singularity |
|
Following are explanations of the options that you can specify in the PROC REG statement (in alphabetical order).
Note that any option specified in the PROC REG statement applies to all MODEL statements.
- ALL
-
requests the display of many tables. Using the ALL option in the PROC REG statement is equivalent to specifying ALL in every MODEL statement. The ALL option also implies the CORR, SIMPLE, and USSCP options.
- ALPHA=number
-
sets the significance level used for the construction of confidence intervals. The value must be between 0 and 1; the default value of 0.05 results in 95% intervals. This option affects the PROC REG option TABLEOUT; the MODEL options CLB, CLI, and CLM; the OUTPUT statement keywords LCL, LCLM, UCL, and UCLM; the PLOT statement keywords LCL., LCLM., UCL., and UCLM.; and the PLOT statement options CONF and PRED.
- CORR
-
displays the correlation matrix for all variables listed in the MODEL or VAR statement.
- COVOUT
-
outputs the covariance matrices for the parameter estimates to the OUTEST= data set. This option is valid only if the OUTEST= option is also specified. See the section OUTEST= Data Set.
- DATA=SAS-data-set
-
names the SAS data set to be used by PROC REG. The data set can be an ordinary SAS data set or a TYPE=CORR, TYPE=COV, or TYPE=SSCP data set. If one of these special TYPE= data sets is used, the OUTPUT, PAINT, PLOT, and REWEIGHT statements, ODS Graphics, and some options in the MODEL and PRINT statements are not available. See Appendix A: Special SAS Data Sets, for more information about TYPE= data sets. If the DATA= option is not specified, PROC REG uses the most recently created SAS data set.
- EDF
-
outputs the number of regressors in the model excluding and including the intercept, the error degrees of freedom, and the model R square to the OUTEST= data set.
- NOPRINT
-
suppresses the normal display of results. Note that this option temporarily disables the Output Delivery System (ODS); see Chapter 20: Using the Output Delivery System, for more information.
- OUTEST=SAS-data-set
-
requests that parameter estimates and optional model fit summary statistics be output to this data set. See the section OUTEST= Data Set for details. If you want to create a SAS data set in a permanent library, you must specify a two-level name. For more information about permanent libraries and SAS data sets, see SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
- OUTSEB
-
outputs the standard errors of the parameter estimates to the OUTEST= data set. The value SEB for the variable
_TYPE_identifies the standard errors. If the RIDGE= or PCOMIT= option is specified, additional observations are included and identified by the values RIDGESEB and IPCSEB, respectively, for the variable_TYPE_. The standard errors for ridge regression estimates and IPC estimates are limited in their usefulness because these estimates are biased. This option is available for all model selection methods except RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, and CP. - OUTSSCP=SAS-data-set
-
requests that the sums of squares and crossproducts matrix be output to this TYPE=SSCP data set. See the section OUTSSCP= Data Sets for details. If you want to create a SAS data set in a permanent library, you must specify a two-level name. For more information about permanent libraries and SAS data sets, see SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
- OUTSTB
-
outputs the standardized parameter estimates as well as the usual estimates to the OUTEST= data set when the RIDGE= or PCOMIT= option is specified. The values RIDGESTB and IPCSTB for the variable
_TYPE_identify ridge regression estimates and IPC estimates, respectively. - OUTVIF
-
outputs the variance inflation factors (VIF) to the OUTEST= data set when the RIDGE= or PCOMIT= option is specified. The factors are the diagonal elements of the inverse of the correlation matrix of regressors as adjusted by ridge regression or IPC analysis. These observations are identified in the output data set by the values RIDGEVIF and IPCVIF for the variable
_TYPE_. - PCOMIT=list
-
requests an incomplete principal component (IPC) analysis for each value m in the list. The procedure computes parameter estimates by using all but the last m principal components. Each value of m produces a set of IPC estimates, which are output to the OUTEST= data set. The values of m are saved by the variable
_PCOMIT_, and the value of the variable_TYPE_is set to IPC to identify the estimates. Only nonnegative integers can be specified with the PCOMIT= option.If you specify the PCOMIT= option, RESTRICT statements are ignored.
-
PLOTS <(global-plot-options)> <= plot-request<(options)>>
PLOTS <(global-plot-options)> <= (plot-request<(options)> <... plot-request<(options)>>)> -
controls the plots produced through ODS Graphics. When you specify only one plot request, you can omit the parentheses around the plot request. Here are some examples:
plots = none plots = diagnostics(unpack) plots = (all fit(stats)=none) plots(label) = (rstudentbyleverage cooksd) plots(only) = (diagnostics(stats=all) fit(nocli stats=(aic sbc)
ODS Graphics must be enabled before plots can be requested. For example:
ods graphics on; proc reg; model y = x1-x10; run; proc reg plots=diagnostics(stats=(default aic sbc)); model y = x1-x10; run; ods graphics off;
For more information about enabling and disabling ODS Graphics, see the section Enabling and Disabling ODS Graphics in Chapter 21: Statistical Graphics Using ODS.
If ODS Graphics is enabled but you do not specify the PLOTS= option, then PROC REG produces a default set of plots. Table 83.2 lists the default set of plots produced.
For models with multiple dependent variables, separate plots are produced for each dependent variable. For jobs with more than one MODEL statement, plots are produced for each model statement.
The global-options apply to all plots generated by the REG procedure, unless it is altered by a specific-plot-option. The following global-plot-options are available:
- LABEL
-
specifies that the LABEL option be applied to each plot that supports a LABEL option. See the descriptions of the specific plots for details.
- MAXPOINTS=NONE | max <heat-max>
-
suppresses most plots that require processing more than max points. When the number of points exceeds max but does not exceed heat-max divided by the number of independent variables, heat maps are displayed instead of scatter plots for the fit and residual plots. All other plots are suppressed when the number of points exceeds max. The default is MAXPOINTS=5000 150000. These cutoffs are ignored if you specify MAXPOINTS=NONE.
- MODELLABEL
-
requests that the model label be displayed in the upper-left corner of all plots. This option is useful when you use more than one MODEL statement.
- ONLY
-
suppress the default plots. Only plots specifically requested are displayed.
- STATS=ALL | DEFAULT | NONE | (plot-statistics)
-
requests statistics that are included on the fit plot and diagnostics panel. Table 83.3 lists the statistics that you can request. STATS=ALL requests all these statistics; STATS=NONE suppresses them.
Table 83.3: Statistics Available on Plots
Keyword
Default
Description
ADJRSQ
x
adjusted R-square
AIC
Akaike’s information criterion
BIC
Sawa’s Bayesian information criterion
CP
Mallows’
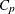 statistic
statistic
COEFFVAR
coefficient of variation
DEPMEAN
mean of dependent
DEFAULT
all default statistics
EDF
x
error degrees of freedom
GMSEP
estimated MSE of prediction, assuming multivariate normality
JP
final prediction error
MSE
x
mean squared error
NOBS
x
number of observations used
NPARM
x
number of parameters in the model (including the intercept)
PC
Amemiya’s prediction criterion
RSQUARE
x
R-square
SBC
SBC statistic
SP
SP statistic
SSE
error sum of squares
You request statistics in addition to the default set by including the keyword DEFAULT in the plot-statistics list.
- UNPACK
-
suppresses paneling.
- USEALL
-
specifies that predicted values at data points with missing dependent variable(s) be included on appropriate plots. By default, only points used in constructing the SSCP matrix appear on plots.
The following specific plots are available:
- ADJRSQ <(adjrsq-options)>
-
displays the adjusted R-square values for the models examined when you request variable selection with the SELECTION= option in the MODEL statement.
The following adjrsq-options are available for models where you request the RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, or CP selection method:
- LABEL
-
requests that the model number corresponding to the one displayed in the “Subset Selection Summary” table be used to label the model with the largest adjusted R-square statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- LABELVARS
-
requests that the list (excluding the intercept) of the regressors in the relevant model be used to label the model with the largest adjusted R-square statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- AIC <(aic-options)>
-
displays Akaike’s information criterion (AIC) for the models examined when you request variable selection with the SELECTION= option in the MODEL statement.
The following aic-options are available for models where you request the RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, or CP selection method:
- LABEL
-
requests that the model number corresponding to the one displayed in the “Subset Selection Summary” table be used to label the model with the smallest AIC statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- LABELVARS
-
requests that the list (excluding the intercept) of the regressors in the relevant model be used to label the model with the smallest AIC statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- ALL
-
produces all appropriate plots.
- BIC <(bic-options)>
-
displays Sawa’s Bayesian information criterion (BIC) for the models examined when you request variable selection with the SELECTION= option in the MODEL statement.
The following bic-options are available for models where you request the RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, or CP selection method:
- LABEL
-
requests that the model number corresponding to the one displayed in the “Subset Selection Summary” table be used to label the model with the smallest BIC statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- LABELVARS
-
requests that the list (excluding the intercept) of the regressors in the relevant model be used to label the model with the smallest BIC statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- COOKSD <(LABEL)>
-
plots Cook’s D statistic by observation number. Observations whose Cook’s D statistic lies above the horizontal reference line at value
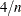 , where n is the number of observations used, are deemed to be influential (Rawlings, Pantula, and Dickey, 1998). If you specify the LABEL option, then points deemed as influential are labeled. If you do not specify an ID variable, the
observation number within the current BY group is used as the label. If you specify one or more ID variables in one or more
ID statements, then the first ID variable you specify is used for the labeling.
, where n is the number of observations used, are deemed to be influential (Rawlings, Pantula, and Dickey, 1998). If you specify the LABEL option, then points deemed as influential are labeled. If you do not specify an ID variable, the
observation number within the current BY group is used as the label. If you specify one or more ID variables in one or more
ID statements, then the first ID variable you specify is used for the labeling.
- CP <(cp-options)>
-
displays Mallows’
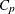 statistic for the models examined when you request variable selection with the SELECTION= option in the MODEL statement. For models where you request the RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, or CP selection, reference lines corresponding to the equations
statistic for the models examined when you request variable selection with the SELECTION= option in the MODEL statement. For models where you request the RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, or CP selection, reference lines corresponding to the equations
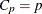 and
and 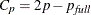 , where
, where 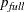 is the number of parameters in the full model (excluding the intercept) and p is the number of parameters in the subset model (including the intercept), are displayed on the plot of
is the number of parameters in the full model (excluding the intercept) and p is the number of parameters in the subset model (including the intercept), are displayed on the plot of 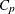 versus p. For the purpose of parameter estimation, Hocking (1976) suggests selecting a model where
versus p. For the purpose of parameter estimation, Hocking (1976) suggests selecting a model where 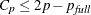 . For the purpose of prediction, Hocking suggests the criterion
. For the purpose of prediction, Hocking suggests the criterion 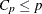 . Mallows (1973) suggests that all subset models with
. Mallows (1973) suggests that all subset models with 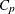 small and near p be considered for further study.
small and near p be considered for further study.
The following cp-options are available for models where you request the RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, or CP selection method:
- LABEL
-
requests that the model number corresponding to the one displayed in the “Subset Selection Summary” table be used to label the model with the smallest
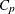 statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- LABELVARS
-
requests that the list (excluding the intercept) of the regressors in the relevant model be used to label the model with the smallest
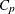 statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- CRITERIA | CRITERIONPANEL <(criteria-options)>
-
produces a panel of fit criteria for the models examined when you request variable selection with the SELECTION= option in the MODEL statement. The fit criteria displayed are R-square, adjusted R-square, Mallows’
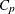 , Akaike’s information criterion (AIC), Sawa’s Bayesian information criterion (BIC), and Schwarz’s Bayesian information criterion
(SBC). For SELECTION=RSQUARE, SELECTION=ADJRSQ, or SELECTION=CP, scatter plots of these statistics versus the number of parameters
(including the intercept) are displayed. For other selection methods, line plots of these statistics as function of the selection
step number are displayed.
, Akaike’s information criterion (AIC), Sawa’s Bayesian information criterion (BIC), and Schwarz’s Bayesian information criterion
(SBC). For SELECTION=RSQUARE, SELECTION=ADJRSQ, or SELECTION=CP, scatter plots of these statistics versus the number of parameters
(including the intercept) are displayed. For other selection methods, line plots of these statistics as function of the selection
step number are displayed.
The following criteria-options are available:
- LABEL
-
requests that the model number corresponding to the one displayed in the “Subset Selection Summary” table be used to label the best model at each value of the number of parameters. This option applies only to the RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, and CP selection methods.
- LABELVARS
-
requests that the list (excluding the intercept) of the regressors in the relevant model be used to label the best model at each value of the number of parameters. Since these labels are typically long, LABELVARS is supported only when the panel is unpacked. This option applies only to the RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, and CP selection methods.
- UNPACK
-
suppresses paneling. Separate plots are produced for each of the six fit statistics. For models where you request the RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, or CP selection, two reference lines corresponding to the equations
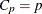 and
and 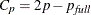 , where
, where 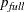 is the number of parameters in the full model (excluding the intercept) and p is the number of parameters in the subset model (including the intercept), are displayed on the plot of
is the number of parameters in the full model (excluding the intercept) and p is the number of parameters in the subset model (including the intercept), are displayed on the plot of 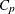 versus p. For the purpose of parameter estimation, Hocking (1976) suggests selecting a model where
versus p. For the purpose of parameter estimation, Hocking (1976) suggests selecting a model where 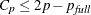 . For the purpose of prediction, Hocking suggests the criterion
. For the purpose of prediction, Hocking suggests the criterion 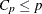 . Mallows (1973) suggests that all subset models with
. Mallows (1973) suggests that all subset models with 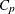 small and near p be considered for further study.
small and near p be considered for further study.
- DFBETAS <(DFBETAS-options)>
-
produces panels of DFBETAS by observation number for the regressors in the model. Note that each panel contains at most six plots, and multiple panels are used in the case where there are more than six regressors (including the intercept) in the model. Observations whose DFBETAS’ statistics for a regressor are greater in magnitude than
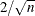 , where n is the number of observations used, are deemed to be influential for that regressor (Rawlings, Pantula, and Dickey, 1998).
, where n is the number of observations used, are deemed to be influential for that regressor (Rawlings, Pantula, and Dickey, 1998).
The following DFBETAS-options are available:
- COMMONAXES
-
specifies that the same DFBETAS axis be used in all panels when multiple panels are needed. By default, the DFBETAS axis is chosen independently for each panel. If you also specify the UNPACK option, then the same DFBETAS axis is used for each regressor.
- LABEL
-
specifies that observations whose magnitude are greater than
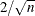 be labeled. If you do not specify an ID variable, the observation number within the current BY group is used as the label.
If you specify one or more ID variables on one or more ID statements, then the first ID variable you specify is used for the
labeling.
be labeled. If you do not specify an ID variable, the observation number within the current BY group is used as the label.
If you specify one or more ID variables on one or more ID statements, then the first ID variable you specify is used for the
labeling.
- UNPACK
-
suppresses paneling. The DFBETAS statistics for each regressor are displayed on separate plots.
- DFFITS <(LABEL)>
-
plots the DFFITS statistic by observation number. Observations whose DFFITS’ statistic is greater in magnitude than
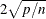 , where n is the number of observations used and p is the number of regressors, are deemed to be influential (Rawlings, Pantula, and Dickey, 1998). If you specify the LABEL option, then these influential observations are labeled. If you do not specify an ID variable,
the observation number within the current BY group is used as the label. If you specify one or more ID variables in one or
more ID statements, then the first ID variable you specify is used for the labeling.
, where n is the number of observations used and p is the number of regressors, are deemed to be influential (Rawlings, Pantula, and Dickey, 1998). If you specify the LABEL option, then these influential observations are labeled. If you do not specify an ID variable,
the observation number within the current BY group is used as the label. If you specify one or more ID variables in one or
more ID statements, then the first ID variable you specify is used for the labeling.
- DIAGNOSTICS <(diagnostics-options)>
-
produces a summary panel of fit diagnostics:
-
residuals versus the predicted values
-
studentized residuals versus the predicted values
-
studentized residuals versus the leverage
-
normal quantile plot of the residuals
-
dependent variable values versus the predicted values
-
Cook’s D versus observation number
-
histogram of the residuals
-
“Residual-Fit” (or RF) plot consisting of side-by-side quantile plots of the centered fit and the residuals
-
box plot of the residuals if you specify the STATS=NONE suboption
You can specify the following diagnostics-options:
- STATS=stats-options
-
determines which model fit statistics are included in the panel. See the global STATS= suboption for details. The PLOTS= suboption of the DIAGNOSTICSPANEL option overrides the global PLOTS= suboption.
- UNPACK
-
produces the eight plots in the panel as individual plots. Note that you can also request individual plots in the panel by name without having to unpack the panel.
-
- FITPLOT | FIT <(fit-options)>
-
produces a scatter plot of the data overlaid with the regression line, confidence band, and prediction band for models that depend on at most one regressor excluding the intercept. When the number of points exceeds the MAXPOINTS=max value, a heat map is displayed instead of a scatter plot. By default, heat maps are not displayed if the number of observations times the number of independent variables is greater than 150,000. See the MAXPOINTS= option.
You can specify the following fit-options:
- NOCLI
-
suppresses the prediction limits.
- NOCLM
-
suppresses the confidence limits.
- NOLIMITS
-
suppresses the confidence and prediction limits.
- STATS=stats-options
-
determines which model fit statistics are included in the panel. See the global STATS= suboption for details. The PLOTS= suboption of the FITPLOT option overrides the global PLOTS= suboption.
- OBSERVEDBYPREDICTED <(LABEL)>
-
plots dependent variable values by the predicted values. If you specify the LABEL option, then points deemed as outliers or influential (see the RSTUDENTBYLEVERAGE option for details) are labeled.
- NONE
-
suppresses all plots.
- PARTIAL <(UNPACK)>
-
produces panels of partial regression plots for each regressor with at most six regressors per panel. If you specify the UNPACK option, then all partial plot panels are unpacked.
- PREDICTIONS (X=numeric-variable <prediction-options>)
-
produces a panel of two plots whose horizontal axis is the variable you specify in the required X= suboption. The upper plot in the panel is a scatter plot of the residuals. The lower plot shows the data overlaid with the regression line, confidence band, and prediction band. This plot is appropriate for models where all regressors are known to be functions of the single variable that you specify in the X= suboption.
You can specify the following prediction-options:
- NOCLI
-
suppresses the prediction limits.
- NOCLM
-
suppresses the confidence limits
- NOLIMITS
-
suppresses the confidence and prediction limits
- SMOOTH
-
requests a nonparametric smoothing of the residuals as a function of the variable you specify in the X= suboption. This nonparametric fit is a loess fit that uses local linear polynomials, linear interpolation, and a smoothing parameter that is selected to yield a local minimum of the corrected Akaike’s information criterion (AICC). See Chapter 57: The LOESS Procedure, for details. The SMOOTH option is not supported when a FREQ statement is used.
- UNPACK
-
suppresses paneling.
- QQPLOT | QQ
-
produces a normal quantile plot of the residuals.
- RESIDUALBOXPLOT | BOXPLOT <(LABEL)>
-
produces a box plot consisting of the residuals. If you specify label option, points deemed far-outliers are labeled. If you do not specify an ID variable, the observation number within the current BY group is used as the label. If you specify one or more ID variables in one or more ID statements, then the first ID variable you specify is used for the labeling.
- RESIDUALBYPREDICTED <(LABEL)>
-
plots residuals by predicted values. If you specify the LABEL option, then points deemed as outliers or influential (see the RSTUDENTBYLEVERAGE option for details) are labeled.
- RESIDUALS <(residual-options)>
-
produces panels of the residuals versus the regressors in the model. Each panel contains at most six plots, and multiple panels are used when the model contains more than six regressors (including the intercept). When the number of points exceeds the MAXPOINTS=max value, a heat map is displayed instead of a scatter plot. By default, heat maps are not displayed if the number of observations times the number of independent variables is greater than 150,000. See the MAXPOINTS= option. You can specify the following residual-options:
- SMOOTH
-
requests a nonparametric smoothing of the residuals for each regressor. Each nonparametric fit is a loess fit that uses local linear polynomials, linear interpolation, and a smoothing parameter that is selected to yield a local minimum of the corrected Akaike’s information criterion (AICC). See Chapter 57: The LOESS Procedure, for details. The SMOOTH option is not supported when a FREQ statement is used.
- UNPACK
-
suppresses paneling.
- RESIDUALHISTOGRAM
-
produces a histogram of the residuals.
- RFPLOT | RF
-
produces a “Residual-Fit” (or RF) plot consisting of side-by-side quantile plots of the centered fit and the residuals. This plot “shows how much variation in the data is explained by the fit and how much remains in the residuals” (Cleveland, 1993).
- RIDGE | RIDGEPANEL | RIDGEPLOT <(ridge-options)>
-
creates panels of VIF values and standardized ridge estimates by ridge values for each coefficient. The VIF values for each coefficient are connected by lines and are displayed in the upper plot in each panel. The points corresponding to the standardized estimates of each coefficient are connected by lines and are displayed in the lower plot in each panel. By default, at most 10 coefficients are represented in a panel and multiple panels are produced for models with more than 10 regressors. For ridge estimates to be computed and plotted, the OUTEST= option must be specified in the PROC REG statement, and the RIDGE= list must be specified in either the PROC REG or the MODEL statement. (See Example 83.5.)
The following ridge-options are available:
- COMMONAXES
-
specifies that the same VIF axis and the same standardized estimate axis are used in all panels when multiple panels are needed. By default, these axes are chosen independently for the regressors shown in each panel.
- RIDGEAXIS=LINEAR | LOG
-
specifies the axis type used to display the ridge parameters. The default is RIDGEAXIS=LINEAR. Note that the point with the ridge parameter equal to zero is not displayed if you specify RIDGEAXIS=LOG.
- UNPACK
-
suppresses paneling. The traces of the VIF statistics and standardized estimates are shown in separate plots.
-
VARSPERPLOT=ALL
VARSPERPLOT=number -
specifies the maximum number of regressors displayed in each panel or in each plot if you additionally specify the UNPACK option. If you specify VARSPERPLOT=ALL, then the VIF values and ridge traces for all regressors are displayed in a single panel.
- VIFAXIS=LINEAR | LOG
-
specifies the axis type used to display the VIF statistics. The default is VIFAXIS=LINEAR.
- RSQUARE <(rsquare-options)>
-
displays the R-square values for the models examined when you request variable selection with the SELECTION= option in the MODEL statement.
The following rsquare-options are available for models where you request the RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, or CP selection method:
- LABEL
-
requests that the model number corresponding to the one displayed in the “Subset Selection Summary” table be used to label the model with the largest R-square statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- LABELVARS
-
requests that the list (excluding the intercept) of the regressors in the relevant model be used to label the model with the largest R-square statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- RSTUDENTBYLEVERAGE <(LABEL)>
-
plots studentized residuals by leverage. Observations whose studentized residuals lie outside the band between the reference lines
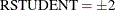 are deemed outliers. Observations whose leverage values are greater than the vertical reference
are deemed outliers. Observations whose leverage values are greater than the vertical reference 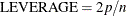 , where p is the number of parameters including the intercept and n is the number of observations used, are deemed influential (Rawlings, Pantula, and Dickey, 1998). If you specify the LABEL option, then points deemed as outliers or influential are labeled. If you do not specify an ID
variable, the observation number within the current BY group is used as the label. If you specify one or more ID variables
in one or more ID statements, then the first ID variable you specify is used for the labeling.
, where p is the number of parameters including the intercept and n is the number of observations used, are deemed influential (Rawlings, Pantula, and Dickey, 1998). If you specify the LABEL option, then points deemed as outliers or influential are labeled. If you do not specify an ID
variable, the observation number within the current BY group is used as the label. If you specify one or more ID variables
in one or more ID statements, then the first ID variable you specify is used for the labeling.
- RSTUDENTBYPREDICTED <(LABEL)>
-
plots studentized residuals by predicted values. If you specify the LABEL option, then points deemed as outliers or influential (see the RSTUDENTBYLEVERAGE option for details) are labeled.
- SBC <(sbc-options)>
-
displays Schwarz’s Bayesian information criterion (SBC) for the models examined when you request variable selection with the SELECTION= option in the MODEL statement.
The following sbc-options are available for models where you request the RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, or CP selection method:
- LABEL
-
requests that the model number corresponding to the one displayed in the “Subset Selection Summary” table be used to label the model with the smallest SBC statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- LABELVARS
-
requests that the list (excluding the intercept) of the regressors in the relevant model be used to label the model with the smallest SBC statistic at each value of the number of parameters.
- PRESS
-
outputs the PRESS statistic to the OUTEST= data set. The values of this statistic are saved in the variable
_PRESS_. This option is available for all model selection methods except RSQUARE, ADJRSQ, and CP. - RIDGE=list
-
requests a ridge regression analysis and specifies the values of the ridge constant k (see the section Computations for Ridge Regression and IPC Analysis). Each value of k produces a set of ridge regression estimates that are placed in the OUTEST= data set. The values of k are saved by the variable
_RIDGE_, and the value of the variable_TYPE_is set to RIDGE to identify the estimates.Only nonnegative numbers can be specified with the RIDGE= option. Example 83.5 illustrates this option.
If ODS Graphics is enabled (see the section ODS Graphics), then ridge regression plots are automatically produced. These plots consist of panels containing ridge traces for the regressors, with at most eight ridge traces per panel.
If you specify the RIDGE= option, RESTRICT statements are ignored.
- RSQUARE
-
has the same effect as the EDF option.
- SIMPLE
-
displays the sum, mean, variance, standard deviation, and uncorrected sum of squares for each variable used in PROC REG.
- SINGULAR=n
-
tunes the mechanism used to check for singularities. The default value is machine dependent but is approximately 1E–7 on most machines. This option is rarely needed.
Singularity checking is described in the section Computational Methods.
- TABLEOUT
-
outputs the standard errors and
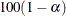 % confidence
limits for the parameter estimates, the t statistics for testing if the estimates are zero, and the associated p-values to the OUTEST= data set. The
% confidence
limits for the parameter estimates, the t statistics for testing if the estimates are zero, and the associated p-values to the OUTEST= data set. The _TYPE_variable values STDERR, LnB, UnB, T, and PVALUE, where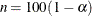 , identify these rows in the OUTEST= data set. The
, identify these rows in the OUTEST= data set. The  level can be set with the ALPHA= option in the PROC REG or MODEL statement. The OUTEST= option must be specified in the PROC REG statement for this option to take effect.
level can be set with the ALPHA= option in the PROC REG or MODEL statement. The OUTEST= option must be specified in the PROC REG statement for this option to take effect.
- USSCP
-
displays the uncorrected sums-of-squares and crossproducts matrix for all variables used in the procedure.