The STDIZE Procedure
Formulas for statistics of METHOD=MEAN, METHOD=MEDIAN, METHOD=SUM, METHOD=USTD, METHOD=STD, METHOD=RANGE, and METHOD=IQR are given in the chapter “Elementary Statistics Procedures” ( Base SAS Procedures Guide).
Note that the computations of median and upper and lower quartiles depend on the PCTLMTD= option.
The other statistics listed in Table 91.2, except for METHOD=IN, are described as follows:
- EUCLEN
-
Euclidean length.
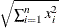 , where
, where 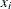 is the ith observation and n is the total number of observations in the sample.
is the ith observation and n is the total number of observations in the sample.
- L(p)
-
Minkowski metric. This metric is documented as the LEAST=p option in the PROC FASTCLUS statement of the FASTCLUS procedure (see Chapter 38: The FASTCLUS Procedure).
If you specify METHOD=L(p) in the PROC STDIZE statement, your results are similar to those obtained from PROC FASTCLUS if you specify the LEAST=p option with MAXCLUS=1 (and use the default values of the MAXITER= option). The difference between the two types of calculations concerns the maximum number of iterations. In PROC STDIZE, it is a criterion for convergence on all variables; in PROC FASTCLUS, it is a criterion for convergence on a single variable.
The location and scale measures for L(p) are output to the OUTSEED= data set in PROC FASTCLUS.
- MIDRANGE
-
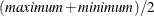
- ABW(c)
-
Tukey’s biweight. See Goodall (1983, pp. 376–378, p. 385) for the biweight one-step M-estimate. Also see Iglewicz (1983, pp. 416-418) for the biweight A-estimate.
- AHUBER(c)
-
Hubers. See Goodall (1983, pp. 371–374) for the Huber one-step M-estimate. Also see Iglewicz (1983, pp. 416-418) for the Huber A-estimate of scale.
- AWAVE(c)
-
Andrews’ wave. See Goodall (1983, p. 376) for the Wave one-step M-estimate. Also see Iglewicz (1983, pp. 416-418) for the Wave A-estimate of scale.
- AGK(p)
-
The noniterative univariate form of the estimator described by Art, Gnanadesikan, and Kettenring (1982).
The AGK estimate is documented in the section on the METHOD= option in the PROC ACECLUS statement of the ACECLUS procedure (also see the section Background in Chapter 24: The ACECLUS Procedure). Specifying METHOD=AGK(p) in the PROC STDIZE statement is the same as specifying METHOD=COUNT and P=p in the PROC ACECLUS statement.
- SPACING(p)
-
The absolute difference between two data values. The minimum spacing for a proportion p is the minimum absolute difference between two data values that contain a proportion p of the data between them. The mid-minimum spacing is the mean of these two data values.
