In the preceding syntax, variable is a variable whose values determine the groups to be tested. The values for variable can be formatted or unformatted. If variable is a character or numeric variable, then the groups are defined by the unique values of the TEST variable. You can specify
only one variable in the TEST statement.
When you are comparing more than two survival curves, a generalized log-rank test tells you whether the curves are significantly
different from each other, but it does not identify which pairs of curves are different. A multiple-comparison adjustment
of the p-values for the paired comparisons retains the same overall probability of a Type I error as the K-sample test. Two types of paired comparisons can be made: comparisons between all pairs of curves and comparisons between
a control curve and all other curves. You use the DIFF=
option to specify the comparison type, and you use the ADJUST=
option to select a method of multiple-comparison adjustments.
Compared with the TEST statement in the LIFETEST procedure, the TEST statement in PROC ICLIFETEST is designed for comparing
survival between predefined groups. Unlike the LIFETEST procedure, PROC ICLIFETEST does not support a similar test for detecting
association with multiple covariates.
Table 50.2 summarizes the options available in the TEST statement.
Table 50.2: Options Available in the TEST Statement
|
Option
|
Description
|
|
Homogeneity Tests
|
|
NOTEST
|
Suppresses all tests
|
|
TREND
|
Requests a trend test
|
|
WEIGHT=
|
Specifies tests that correspond to various weight functions
|
|
Multiple Comparisons
|
|
ADJUST=
|
Requests a multiple-comparison adjustment
|
|
DIFF=
|
Specifies the type of differences to consider
|
You can specify the following options in the TEST statement after a slash (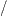 ).
).
-
ADJUST=method
-
specifies the multiple-comparison method to use for adjusting the p-values of the paired tests. For mathematical details, see the section Multiple-Comparison Adjustments; also see Westfall et al. (1999). You can specify the following adjustment methods:
-
BONFERRONI
BON
-
applies the Bonferroni correction to the raw p-values.
-
DUNNETT
-
performs Dunnett’s two-tailed comparisons of the control group to all other groups. PROC ICLIFETEST uses the factor-analytic
covariance approximation that is described in Hsu (1992) and identifies the adjustment in the results as "Dunnett-Hsu." ADJUST=DUNNETT is incompatible with DIFF=
ALL.
-
SCHEFFE
-
performs Scheffé’s multiple-comparison adjustment.
-
SIDAK
-
applies the Šidák correction to the raw p-values.
-
SMM
GTE
-
performs the paired comparisons based on the studentized maximum modulus test.
-
TUKEY
-
performs the paired comparisons based on Tukey’s studentized range test. PROC ICLIFETEST uses the approximation that is described
in Kramer (1956) and identifies the adjustment as "Tukey-Kramer" in the results. ADJUST=TUKEY is incompatible with DIFF=
CONTROL.
-
SIMULATE <(simulate-options)>
-
computes the adjusted p-values from the simulated distribution of the maximum or maximum absolute value of a multivariate normal random vector. The
simulation estimates q, the true 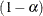 quantile, where
quantile, where  is the value of the ALPHA= simulate-option.
is the value of the ALPHA= simulate-option.
The number of samples for the simulation adjustment is set so that the tail area for the simulated q is within a certain accuracy radius 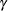 of
of 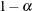 , with an accuracy confidence of
, with an accuracy confidence of 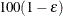 %. In equation form,
%. In equation form,
where 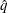 is the simulated q and F is the true distribution function of the maximum; for more information, see Edwards and Berry (1987). By default,
is the simulated q and F is the true distribution function of the maximum; for more information, see Edwards and Berry (1987). By default, 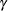 = 0.005 and
= 0.005 and  = 0.01, so the tail area of
= 0.01, so the tail area of 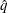 is within 0.005 of 0.95 with 99% confidence.
is within 0.005 of 0.95 with 99% confidence.
You can specify the following simulate-options:
-
ACC=value
-
specifies the target accuracy radius 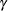 of a
of a 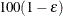 % confidence interval for the true probability content of the estimated
% confidence interval for the true probability content of the estimated 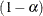 quantile. By default, ACC=0.005.
quantile. By default, ACC=0.005.
-
ALPHA=value
-
specifies the value  for estimating the
for estimating the 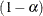 quantile. The default value is the ALPHA= value in the PROC ICLIFETEST statement, or 0.05 if that option is not specified.
quantile. The default value is the ALPHA= value in the PROC ICLIFETEST statement, or 0.05 if that option is not specified.
-
EPS=value
-
specifies the value  for a
for a 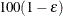 % confidence interval for the true probability content of the estimated
% confidence interval for the true probability content of the estimated 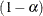 quantile. The default value for the accuracy confidence is 99%, corresponding to EPS=0.01.
quantile. The default value for the accuracy confidence is 99%, corresponding to EPS=0.01.
-
NSAMP=n
-
specifies the sample size for the simulation. By default, n is set based on the values of the target accuracy radius 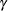 and accuracy confidence
and accuracy confidence 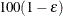 % for an interval for the true probability content of the estimated
% for an interval for the true probability content of the estimated 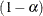 quantile. With the default values for
quantile. With the default values for 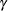 ,
,  , and
, and  (0.005, 0.01, and 0.05, respectively), by default NSAMP=12604.
(0.005, 0.01, and 0.05, respectively), by default NSAMP=12604.
-
REPORT
-
specifies that a report of the simulation be displayed, including a listing of the parameters, such as 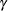 ,
,  , and
, and  , in addition to an analysis of various methods of estimating or approximating the quantile.
, in addition to an analysis of various methods of estimating or approximating the quantile.
-
SEED=number
-
specifies an integer used to start the pseudorandom number generator for the simulation. If you do not specify a seed, or
if you specify a value less than or equal to 0, the seed is generated by default from reading the time of day from the computer’s
clock.
-
DIFF=ALL | CONTROL<(’string’ <…, ’string’>)>
-
specifies which pairs of survival curves to consider for the multiple comparisons. You can specify the following values:
-
ALL
-
requests all paired comparisons.
-
CONTROL <(’string’ <…’string’>)>
-
requests comparisons of the control survival curve with all other survival curves. To specify the control curve, you specify
the quoted strings of formatted values that represent the curve in parentheses. For example, if CELL=LARGE identifies the
control group, you specify
DIFF=CONTROL('large')
If more than one variable is used to identify the curves (for example, if CELL=LARGE and SEX=F represent the control), you
specify
DIFF=CONTROL('large' 'F')
The order of the quoted strings should correspond to the order of the TEST variable. If no string is specified as the control, the first group value is used.
By default, DIFF=ALL unless you specify ADJUST=
DUNNETT, in which case DIFF=CONTROL.
-
NOTEST
-
suppresses the K-sample tests, stratified tests, and trend tests.
-
TREND
-
computes the trend test for the null hypothesis that the survival rates are the same for the groups versus an ordered alternative.
If the TEST variable is numeric, the unformatted values of the variable are used as the scores; otherwise, the scores are
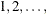 in the order of the strata. For more information, see the section Trend Tests.
in the order of the strata. For more information, see the section Trend Tests.
-
WEIGHT=test-request | (test-request <…test-request>)
-
requests weights to be applied to the generalized log-rank statistics to perform various tests. For more information about
the various weight functions that the ICLIFETEST procedure supports, see the section Generalized Log-Rank Statistic. You can specify the following test-requests:
- FAY
-
specifies the test that uses Fay’s weights (Fay, 1999).
- FINKELSTEIN
-
specifies the test that uses Finkelstein’s weights (Finkelstein, 1986).
- FLEMING(
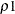 ,
, 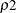 )
)
-
specifies the family of tests in Harrington and Fleming (1982), where 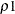 and
and 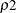 are nonnegative numbers. FLEMING(
are nonnegative numbers. FLEMING(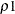 ,
,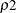 ) corresponds to the Fleming-Harrington
) corresponds to the Fleming-Harrington 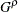 family (Fleming and Harrington, 1981) when
family (Fleming and Harrington, 1981) when 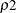 =0. Alternatively, you can specify a test in this family as FLEMING(
=0. Alternatively, you can specify a test in this family as FLEMING(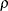 ) with one argument. When
) with one argument. When 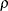 =0, the test becomes the log-rank test. When
=0, the test becomes the log-rank test. When 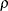 =1, the test should be very close to the Peto-Peto test.
=1, the test should be very close to the Peto-Peto test.
- NONE
-
suppresses all comparison tests. Specifying WEIGHT=NONE is equivalent to specifying NOTEST.
- SUN
-
specifies the test that uses Sun’s weights (Sun, 1996).
![]() ).
).
