The MODECLUS Procedure
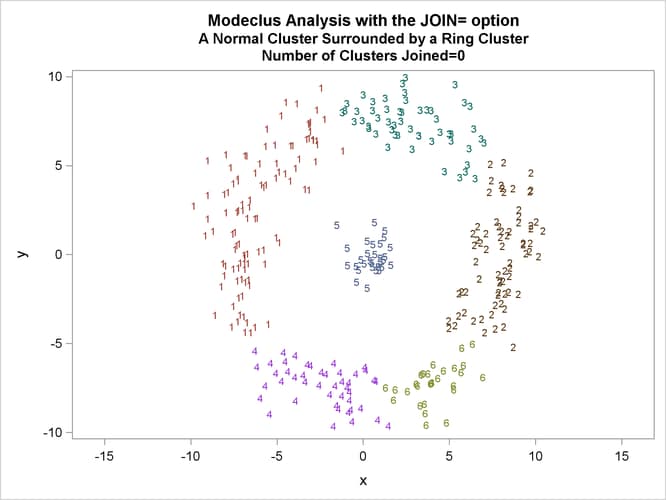
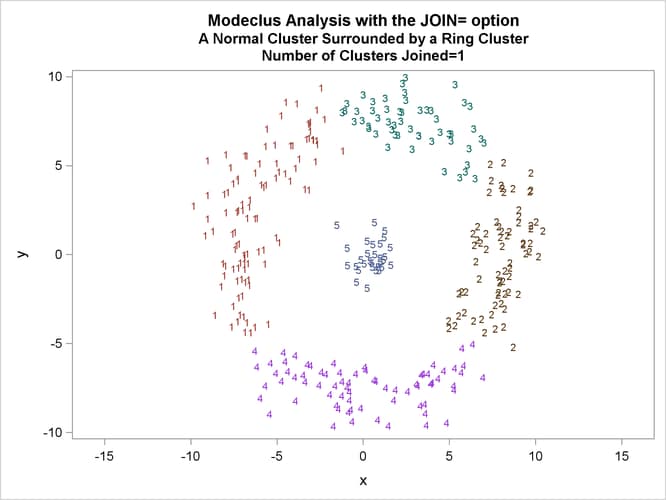
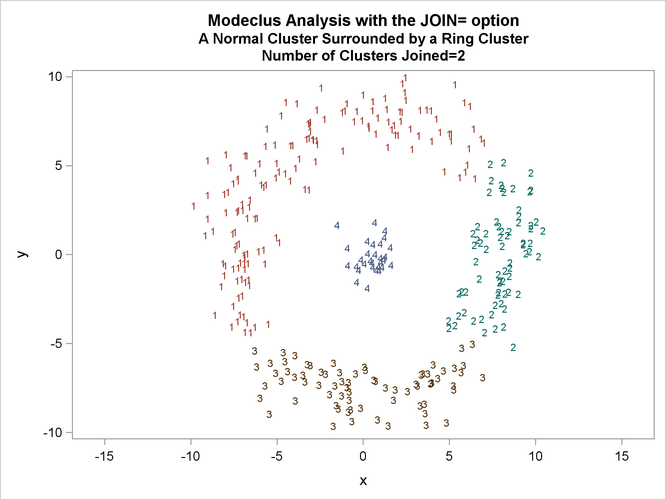
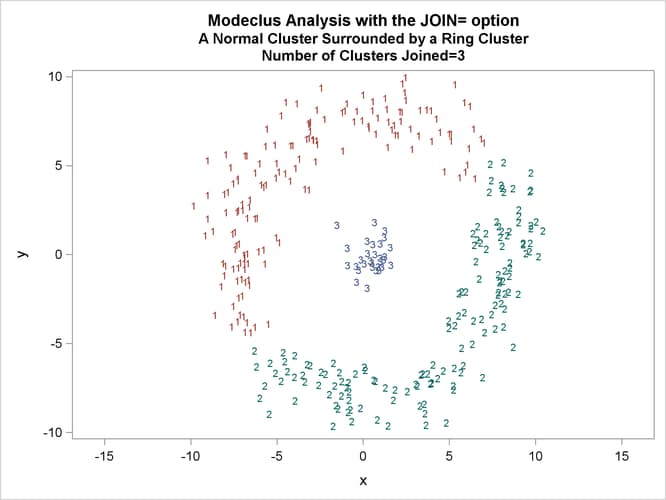
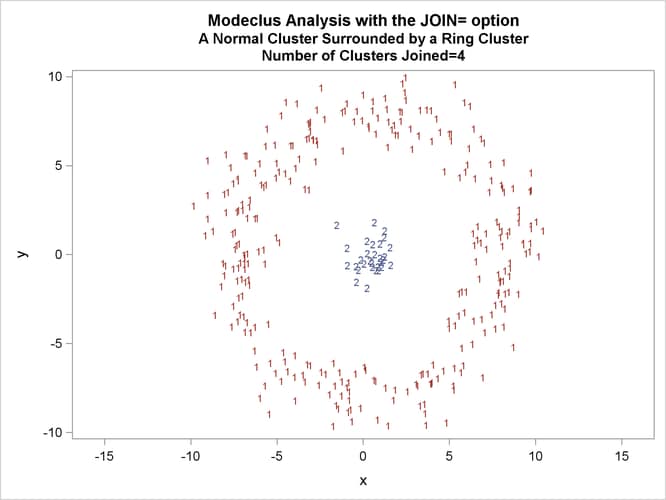
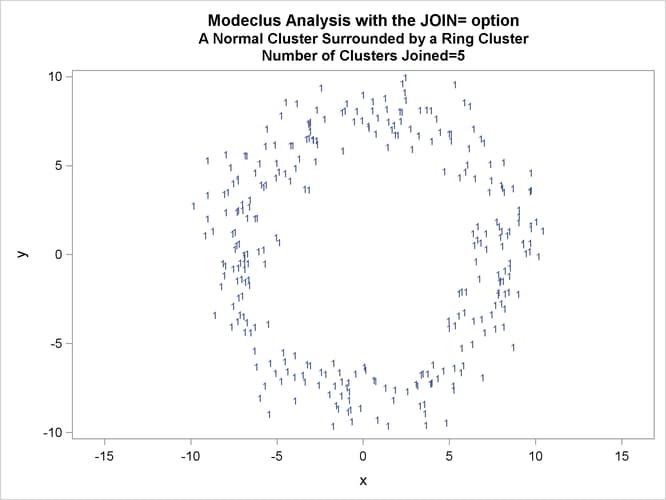
This example uses artificial data containing two clusters. One cluster is from a circular bivariate normal distribution. The other is a ring-shaped cluster that completely surrounds the first cluster. Without significance tests, the ring is divided into several sample clusters for any degree of smoothing that yields reasonable density estimates. The JOIN= option puts the ring back together. Output 66.3.1 displays a short summary generated from the first PROC MODECLUS statement. Output 66.3.2 contains a series of tables produced from the second PROC MODECLUS statement. The lack of p-value in the JOIN= option makes joining continue until only one cluster remains (see the description of the JOIN= option). The cluster memberships are then plotted as displayed in Output 66.3.1 through Output 66.3.8.
The following statements produce Output 66.3.1 through Output 66.3.8:
title 'Modeclus Analysis with the JOIN= option';
title2 'A Normal Cluster Surrounded by a Ring Cluster';
data circle; keep x y;
c=1;
do n=1 to 30;
x=rannor(5);
y=rannor(5);
output;
end;
c=2;
do n=1 to 300;
x=rannor(5);
y=rannor(5);
z=rannor(5)+8;
l=z/sqrt(x**2+y**2);
x=x*l;
y=y*l;
output;
end;
run;
proc modeclus data=circle m=1 r=1 to 3.5 by .25 join=20 short; run;
proc modeclus data=circle m=1 r=2.5 join out=out; run;
proc sgplot data=out noautolegend; yaxis values=(-10 to 10 by 5); xaxis values=(-15 to 15 by 5); scatter y=y x=x / group=cluster Markerchar=cluster; by _NJOIN_; run;
Output 66.3.1: Significance Tests with the JOIN=20 and SHORT Options
| Modeclus Analysis with the JOIN= option |
| A Normal Cluster Surrounded by a Ring Cluster |
| Cluster Summary | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Number of Clusters Joined |
Maximum P-value |
Number of Clusters |
Frequency of Unclassified Objects |
| 1 | 36 | 0.9339 | 1 | 301 |
| 1.25 | 20 | 0.7131 | 1 | 301 |
| 1.5 | 10 | 0.3296 | 1 | 300 |
| 1.75 | 5 | 0.1990 | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | 5 | 0.0683 | 2 | 0 |
| 2.25 | 3 | 0.0504 | 2 | 0 |
| 2.5 | 4 | 0.0301 | 2 | 0 |
| 2.75 | 3 | 0.0585 | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | 5 | 0.0003 | 1 | 0 |
| 3.25 | 4 | 0.1923 | 2 | 0 |
| 3.5 | 4 | 0.0000 | 1 | 0 |
Output 66.3.2: Significance Tests with the JOIN Option
| Modeclus Analysis with the JOIN= option |
| A Normal Cluster Surrounded by a Ring Cluster |
| Cluster Statistics | -Saddle Test: Version 92.7- | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | Frequency | Maximum Estimated Density |
Boundary Frequency |
Estimated Saddle Density |
Mode Count |
Saddle Count |
Overlap Count |
Z | Approx P-value |
| 1 | 103 | 0.00617328 | 22 | 0.00308664 | 39 | 19 | 0 | 2.495 | 0.5055 |
| 2 | 71 | 0.00571029 | 20 | 0.0043213 | 36 | 27 | 9 | 1.193 | 0.999 |
| 3 | 53 | 0.00509296 | 18 | 0.00401263 | 32 | 25 | 10 | 0.986 | 0.9999 |
| 4 | 45 | 0.00478429 | 19 | 0.00354964 | 30 | 22 | 14 | 1.429 | 0.9924 |
| 5 | 30 | 0.00462996 | 0 | . | 29 | 0 | . | 3.611 | 0.0301 |
| 6 | 28 | 0.00370397 | 17 | 0.00354964 | 23 | 22 | 9 | 0.000 | 1 |
| Cluster 6 with P-value 1.0000 will be joined to cluster 4. |
| Cluster Statistics | -Saddle Test: Version 92.7- | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | Frequency | Maximum Estimated Density |
Boundary Frequency |
Estimated Saddle Density |
Mode Count |
Saddle Count |
Overlap Count |
Z | Approx P-value |
| 1 | 103 | 0.00617328 | 22 | 0.00308664 | 39 | 19 | 0 | 2.495 | 0.5055 |
| 2 | 71 | 0.00571029 | 20 | 0.0043213 | 36 | 27 | 9 | 1.193 | 0.999 |
| 3 | 53 | 0.00509296 | 18 | 0.00401263 | 32 | 25 | 10 | 0.986 | 0.9999 |
| 4 | 73 | 0.00478429 | 13 | 0.00293231 | 30 | 18 | 0 | 1.588 | 0.9778 |
| 5 | 30 | 0.00462996 | 0 | . | 29 | 0 | . | 3.611 | 0.0301 |
| Cluster 3 with P-value 0.9999 will be joined to cluster 1. |
| Cluster Statistics | -Saddle Test: Version 92.7- | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | Frequency | Maximum Estimated Density |
Boundary Frequency |
Estimated Saddle Density |
Mode Count |
Saddle Count |
Overlap Count |
Z | Approx P-value |
| 1 | 156 | 0.00617328 | 17 | 0.00246931 | 39 | 15 | 0 | 3.130 | 0.1318 |
| 2 | 71 | 0.00571029 | 20 | 0.0043213 | 36 | 27 | 9 | 1.193 | 0.999 |
| 3 | 73 | 0.00478429 | 13 | 0.00293231 | 30 | 18 | 0 | 1.588 | 0.9778 |
| 4 | 30 | 0.00462996 | 0 | . | 29 | 0 | . | 3.611 | 0.0301 |
| Cluster 2 with P-value 0.9990 will be joined to cluster 3. |
| Cluster Statistics | -Saddle Test: Version 92.7- | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | Frequency | Maximum Estimated Density |
Boundary Frequency |
Estimated Saddle Density |
Mode Count |
Saddle Count |
Overlap Count |
Z | Approx P-value |
| 1 | 156 | 0.00617328 | 17 | 0.00246931 | 39 | 15 | 0 | 3.130 | 0.1318 |
| 2 | 144 | 0.00571029 | 14 | 0.00293231 | 36 | 18 | 0 | 2.313 | 0.6447 |
| 3 | 30 | 0.00462996 | 0 | . | 29 | 0 | . | 3.611 | 0.0301 |
| Cluster 2 with P-value 0.6447 will be joined to cluster 1. |
| Cluster Statistics | -Saddle Test: Version 92.7- | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | Frequency | Maximum Estimated Density |
Boundary Frequency |
Estimated Saddle Density |
Mode Count |
Saddle Count |
Overlap Count |
Z | Approx P-value |
| 1 | 300 | 0.00617328 | 0 | . | 39 | 0 | . | 4.246 | 0.0026 |
| 2 | 30 | 0.00462996 | 0 | . | 29 | 0 | . | 3.611 | 0.0301 |
| 30 observations were unassigned. |
| Cluster 1 with P-value 0.0026 will be dissolved. |
| Modeclus Analysis with the JOIN= option |
| A Normal Cluster Surrounded by a Ring Cluster |
| Cluster Summary | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Number of Clusters Joined |
Maximum P-value |
Number of Clusters |
Frequency of Unclassified Objects |
| 2.5 | 0 | 1.0000 | 6 | 0 |
| 2.5 | 1 | 0.9999 | 5 | 0 |
| 2.5 | 2 | 0.9990 | 4 | 0 |
| 2.5 | 3 | 0.6447 | 3 | 0 |
| 2.5 | 4 | 0.0301 | 2 | 0 |
| 2.5 | 5 | 0.0026 | 1 | 30 |