Using Geographical Maps to Display Query Results
About Geographical Maps
A geographic information
system (GIS) is a tool for organizing and analyzing data that can
be referenced spatially (that is, data that can be tied to physical
locations). Many types of data have a spatial aspect, including demographics,
marketing surveys, and customer addresses. A GIS helps users analyze
data in the context of location.
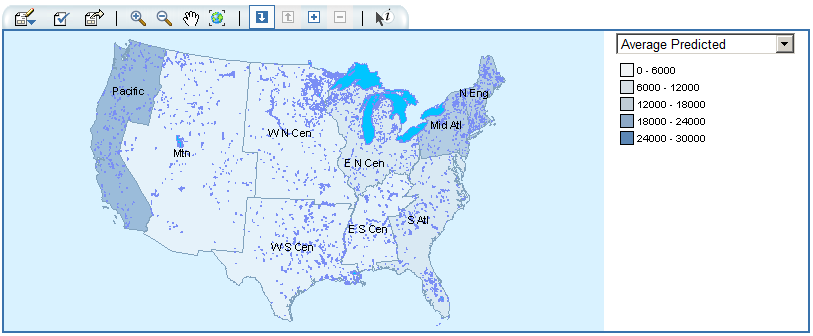
For example, if report
viewers need to evaluate population data for U.S. Census tracts, a
report author could render the information in a table. However, it
would be easier and more effective for viewers to see the information
in the context of the geography of the tracts. When evaluating information
that has a spatial component, viewers might find it easier to recognize
relationships and trends in the data if they see the information in
a spatial context.
Insert a Geographical Map
If the current report
section uses data items from a multidimensional data source that is
enabled for geographic mapping and that contains a geographic hierarchy,
then you can insert a geographical map into the layout.
Note: For more information about
how to position objects in the layout grid, see Overview of Positioning Report Objects.
You can also perform
one or more of these tasks:
-
Change the default measure assigned to the geographical map. For more information, see Select a Measure for a Geographical Map
-
Filter or rank geographical map values. For more information, see Filtering and Ranking a Geographical Map .
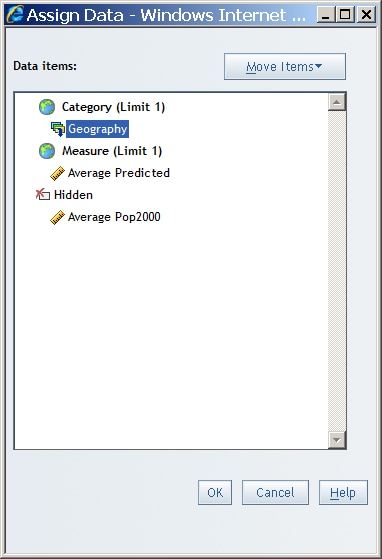
Select a Measure for a Geographical Map
Note: You can also complete this
task in View mode by selecting a measure from the drop-down list in
the geographical map legend.
By default, the first
measure selected from the data source is used for the geographical
map. To specify a different measure (if one is available), complete
these steps:
-
The following data assignments are available for geographical maps:HiddenData items that are assigned to Hidden do not appear in the geographical map but can be used in filtering. For more information, see Hiding Data Items.
Change the Measure Used in a Geographical Map
A report section can
contain a geographical map if the section query uses data items from
a data source that is enabled for geographic mapping. The geographical
map is rendered by using two data items from the data source: one
measure and the geographic hierarchy.
Zoom and Pan a Geographical Map
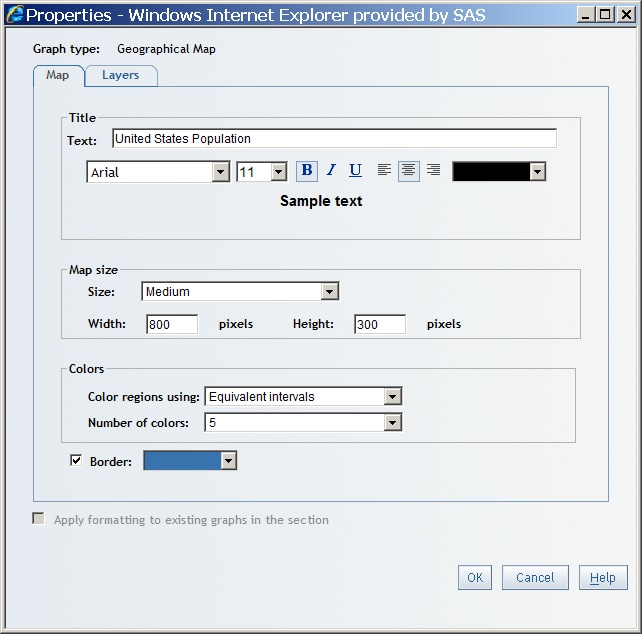
Specify Properties for a Geographical Map
To specify properties
for a geographical map, complete these steps:
-
-
Choose one of the following methods to color the regions of the geographical map:Equivalent intervalsEach color in the geographical map is defined by the range of the data divided by the number of colors.Natural breaksEach color in the geographical map is defined by natural breaks (or interruptions) in the data. The breaks are based on a histogram of data distributions.
-
Select the Border drop-down list to open the color palette. Then select a border color for the geographical map. You can customize a color using the Color value field. For more information, see Customizing Colors.