The TPSPLINE Procedure
This example continues the analysis of the data set Measure to illustrate how you can use PROC TPSPLINE to fit a spline model with a higher-order penalty term. Spline models with high-order
penalty terms move low-order polynomial terms into the polynomial space. Hence, there is no penalty for these terms, and they
can vary without constraint.
As shown in the previous analyses, the final model for the data set Measure must include quadratic terms for both ![]() and
and ![]() . This example fits the following model:
. This example fits the following model:
The model includes quadratic terms for both variables, although it differs from the usual linear model. The nonparametric
term ![]() explains the variation of the data that is unaccounted for by a simple quadratic surface.
explains the variation of the data that is unaccounted for by a simple quadratic surface.
To modify the order of the derivative in the penalty term, specify the M= option. The following statements specify the option M=3 in order to include the quadratic terms in the polynomial space:
data Measure; set Measure; x1sq = x1*x1; x2sq = x2*x2; x1x2 = x1*x2; run; proc tpspline data= Measure; model y = (x1 x2) / m=3; score data = pred out = predy; run;
Output 100.2.1 displays the results from these statements.
Output 100.2.1: Output from PROC TPSPLINE with M=3
| Raw Data |
| Summary of Input Data Set | |
|---|---|
| Number of Non-Missing Observations | 50 |
| Number of Missing Observations | 0 |
| Unique Smoothing Design Points | 25 |
| Summary of Final Model | |
|---|---|
| Number of Regression Variables | 0 |
| Number of Smoothing Variables | 2 |
| Order of Derivative in the Penalty | 3 |
| Dimension of Polynomial Space | 6 |
| Summary Statistics of Final Estimation | |
|---|---|
| log10(n*Lambda) | -3.7831 |
| Smoothing Penalty | 2092.4495 |
| Residual SS | 0.2731 |
| Tr(I-A) | 29.1716 |
| Model DF | 20.8284 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.0968 |
| GCV | 0.0160 |
The model contains six terms in the polynomial space is the number of columns in (![]() ). Compare Output 100.2.1 with Output 100.1.1: the
). Compare Output 100.2.1 with Output 100.1.1: the ![]() value and the smoothing penalty differ significantly. In general, these terms are not directly comparable for different models.
The final estimate based on this model is close to the estimate based on the model by using the default, M=2.
value and the smoothing penalty differ significantly. In general, these terms are not directly comparable for different models.
The final estimate based on this model is close to the estimate based on the model by using the default, M=2.
In the following statements, the REG procedure fits a quadratic surface model to the data set Measure:
proc reg data= Measure; model y = x1 x1sq x2 x2sq x1x2; run;
The results are displayed in Output 100.2.2.
Output 100.2.2: Quadratic Surface Model: The REG Procedure
| Raw Data |
| Analysis of Variance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares |
Mean Square |
F Value | Pr > F |
| Model | 5 | 443.20502 | 88.64100 | 436.33 | <.0001 |
| Error | 44 | 8.93874 | 0.20315 | ||
| Corrected Total | 49 | 452.14376 | |||
| Root MSE | 0.45073 | R-Square | 0.9802 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Mean | 15.08548 | Adj R-Sq | 0.9780 |
| Coeff Var | 2.98781 |
| Parameter Estimates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | DF | Parameter Estimate |
Standard Error |
t Value | Pr > |t| |
| Intercept | 1 | 14.90834 | 0.12519 | 119.09 | <.0001 |
| x1 | 1 | 0.01292 | 0.09015 | 0.14 | 0.8867 |
| x1sq | 1 | -4.85194 | 0.15237 | -31.84 | <.0001 |
| x2 | 1 | 0.02618 | 0.09015 | 0.29 | 0.7729 |
| x2sq | 1 | 5.20624 | 0.15237 | 34.17 | <.0001 |
| x1x2 | 1 | -0.04814 | 0.12748 | -0.38 | 0.7076 |
The REG procedure produces slightly different results. To fit a similar model with PROC TPSPLINE, you can use a MODEL statement that specifies the degrees of freedom with the DF= option. You can also use a large value for the LOGNLAMBDA0= option to force a parametric model fit.
Because there is one degree of freedom for each of the terms intercept, x1, x2, x1sq, x2sq, and x1x2, the DF=6 option is used as follows:
proc tpspline data=measure;
model y=(x1 x2) /m=3 df=6 lognlambda=(-4 to 1 by 0.5);
score data = pred
out = predy;
run;
The fit statistics are displayed in Output 100.2.3.
Output 100.2.3: Output from PROC TPSPLINE Using M=3 and DF=6
| Raw Data |
| Summary of Final Model | |
|---|---|
| Number of Regression Variables | 0 |
| Number of Smoothing Variables | 2 |
| Order of Derivative in the Penalty | 3 |
| Dimension of Polynomial Space | 6 |
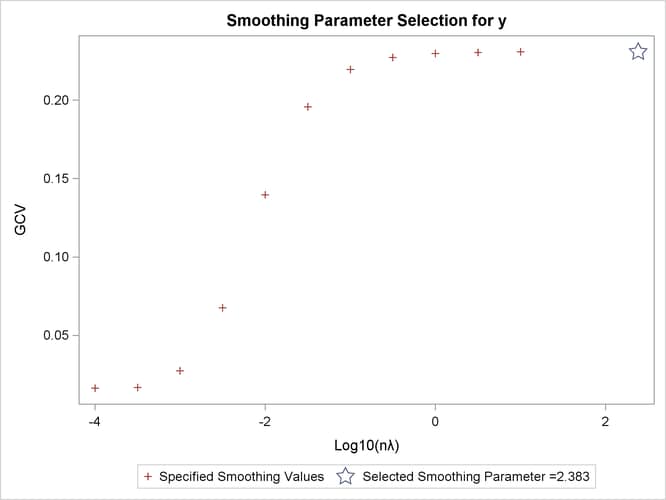
| GCV Function | ||
|---|---|---|
| log10(n*Lambda) | GCV | |
| -4.000000 | 0.016330 | * |
| -3.500000 | 0.016889 | |
| -3.000000 | 0.027496 | |
| -2.500000 | 0.067672 | |
| -2.000000 | 0.139642 | |
| -1.500000 | 0.195727 | |
| -1.000000 | 0.219512 | |
| -0.500000 | 0.227306 | |
| 0 | 0.229740 | |
| 0.500000 | 0.230504 | |
| 1.000000 | 0.230745 | |
| Note: * indicates minimum GCV value. |
| Summary Statistics of Final Estimation | |
|---|---|
| log10(n*Lambda) | 2.3830 |
| Smoothing Penalty | 0.0000 |
| Residual SS | 8.9384 |
| Tr(I-A) | 43.9997 |
| Model DF | 6.0003 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.4507 |
| GCV | 0.2309 |
Output 100.2.4 shows the GCV values for the list of supplied ![]() values in addition to the fitted model with fixed degrees of freedom 6. The fitted model has a larger GCV value than all
other examined models.
values in addition to the fitted model with fixed degrees of freedom 6. The fitted model has a larger GCV value than all
other examined models.
The final estimate is based on 6.000330 degrees of freedom because there are already 6 degrees of freedom in the polynomial
space and the search range for ![]() is not large enough (in this case, setting DF=6 is equivalent to setting
is not large enough (in this case, setting DF=6 is equivalent to setting ![]() ).
).
The standard deviation and RSS (Output 100.2.3) are close to the sum of squares for the error term and the root MSE from the linear regression model (Output 100.2.2), respectively.
For this model, the optimal ![]() is around –3.8, which produces a standard deviation estimate of 0.096765 (see Output 100.2.1) and a GCV value of 0.016051, while the model that specifies DF=6 results in a
is around –3.8, which produces a standard deviation estimate of 0.096765 (see Output 100.2.1) and a GCV value of 0.016051, while the model that specifies DF=6 results in a ![]() larger than 1 and a GCV value larger than 0.23074. The nonparametric model, based on the GCV, should provide better prediction,
but the linear regression model can be more easily interpreted.
larger than 1 and a GCV value larger than 0.23074. The nonparametric model, based on the GCV, should provide better prediction,
but the linear regression model can be more easily interpreted.