The OPTLP Procedure
- Overview
- Getting Started
-
Syntax

-
Details
 Data Input and OutputPresolvePricing Strategies for the Primal and Dual Simplex AlgorithmsWarm Start for the Primal and Dual Simplex AlgorithmsThe Network Simplex AlgorithmThe Interior Point AlgorithmIteration Log for the Primal and Dual Simplex AlgorithmsIteration Log for the Network Simplex AlgorithmIteration Log for the Interior Point AlgorithmIteration Log for the Crossover AlgorithmConcurrent LPParallel ProcessingODS TablesIrreducible Infeasible SetMacro Variable _OROPTLP_
Data Input and OutputPresolvePricing Strategies for the Primal and Dual Simplex AlgorithmsWarm Start for the Primal and Dual Simplex AlgorithmsThe Network Simplex AlgorithmThe Interior Point AlgorithmIteration Log for the Primal and Dual Simplex AlgorithmsIteration Log for the Network Simplex AlgorithmIteration Log for the Interior Point AlgorithmIteration Log for the Crossover AlgorithmConcurrent LPParallel ProcessingODS TablesIrreducible Infeasible SetMacro Variable _OROPTLP_ -
Examples

- References
You can specify the following options in the PROC OPTLP statement.
- DATA=SAS-data-set
-
specifies the input data set corresponding to the LP model. If this option is not specified, PROC OPTLP will use the most recently created SAS data set. See Chapter 17: The MPS-Format SAS Data Set, for more details about the input data set.
-
DUALIN=SAS-data-set
DIN=SAS-data-set -
specifies the input data set corresponding to the dual solution that is required for warm starting the primal and dual simplex algorithms. See the section Data Input and Output for details.
-
DUALOUT=SAS-data-set
DOUT=SAS-data-set -
specifies the output data set for the dual solution. This data set contains the dual solution information. See the section Data Input and Output for details.
- OBJSENSE=option
-
specifies whether the LP model is a minimization or a maximization problem. You specify OBJSENSE=MIN for a minimization problem and OBJSENSE=MAX for a maximization problem. Alternatively, you can specify the objective sense in the input data set; see the section ROWS Section for details. If for some reason the objective sense is specified differently in these two places, this option supersedes the objective sense specified in the input data set. If the objective sense is not specified anywhere, then PROC OPTLP interprets and solves the linear program as a minimization problem.
-
PRIMALIN=SAS-data-set
PIN=SAS-data-set -
specifies the input data set corresponding to the primal solution that is required for warm starting the primal and dual simplex algorithms. See the section Data Input and Output for details.
-
PRIMALOUT=SAS-data-set
POUT=SAS-data-set -
specifies the output data set for the primal solution. This data set contains the primal solution information. See the section Data Input and Output for details.
- SAVE_ONLY_IF_OPTIMAL
-
specifies that the PRIMALOUT= and DUALOUT= data sets be saved only if the final solution obtained by the solver at termination is optimal. If the PRIMALOUT= and DUALOUT= options are specified, then by default (that is, omitting the SAVE_ONLY_IF_OPTIMAL option), PROC OPTLP always saves the solutions obtained at termination, regardless of the final status. If the SAVE_ONLY_IF_OPTIMAL option is not specified, the output data sets can contain an intermediate solution, if one is available.
- IIS=number | string
-
specifies whether PROC OPTLP attempts to identify a set of constraints and variables that form an irreducible infeasible set (IIS). Table 12.2 describes the valid values of the IIS= option.
Table 12.2: Values for IIS= Option
number
string
Description
0
OFF
Disables IIS detection.
1
ON
Enables IIS detection.
If an IIS is found, information about infeasible constraints or variable bounds can be found in the DUALOUT= and PRIMALOUT= data sets. The default value of this option is OFF. See the section Irreducible Infeasible Set for details.
-
ALGORITHM=option
SOLVER=option
SOL=option -
specifies one of the following LP algorithms:
Option
Description
PRIMAL (PS)
Uses primal simplex algorithm.
DUAL (DS)
Uses dual simplex algorithm.
NETWORK (NS)
Uses network simplex algorithm.
INTERIORPOINT (IP)
Uses interior point algorithm.
CONCURRENT (CON)
Uses several different algorithms in parallel.
The valid abbreviated value for each option is indicated in parentheses. By default, the dual simplex algorithm is used.
-
ALGORITHM2=option
SOLVER2=option -
specifies one of the following LP algorithms if ALGORITHM= NS:
Option
Description
PRIMAL (PS)
Uses primal simplex algorithm (after network simplex).
DUAL (DS)
Uses dual simplex algorithm (after network simplex).
The valid abbreviated value for each option is indicated in parentheses. By default, the OPTLP procedure decides which algorithm is best to use after calling the network simplex algorithm on the extracted network.
-
PRESOLVER=number | string
PRESOL=number | string -
specifies one of the following presolve options:
number
string
Description
–1
AUTOMATIC
Applies presolver by using default settings.
0
NONE
Disables presolver.
1
BASIC
Performs basic presolve such as removing empty rows, columns, and fixed variables.
2
MODERATE
Performs basic presolve and applies other inexpensive presolve techniques.
3
AGGRESSIVE
Performs moderate presolve and applies other aggressive (but expensive) presolve techniques.
The default option is AUTOMATIC (–1), which is somewhere between the MODERATE and AGRESSIVE setting. See the section Presolve for details.
- DUALIZE=number | string
-
controls the dualization of the problem:
number
string
Description
–1
AUTOMATIC
The presolver uses a heuristic to decide whether to dualize the problem or not.
0
OFF
Disables dualization. The optimization problem is solved in the form that you specify.
1
ON
The presolver formulates the dual of the linear optimization problem.
Dualization is usually helpful for problems that have many more constraints than variables. You can use this option with all simplex algorithms in PROC OPTLP, but it is most effective with the primal and dual simplex algorithms.
The default option is AUTOMATIC.
-
FEASTOL=

-
specifies the feasibility tolerance
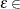 [1E–9, 1E–4] for determining the feasibility of a variable value. The default value is 1E–6.
[1E–9, 1E–4] for determining the feasibility of a variable value. The default value is 1E–6.
-
LOGFREQ=k
PRINTFREQ=k -
specifies that the printing of the solution progress to the iteration log is to occur after every k iterations. The print frequency, k, is an integer between zero and the largest four-byte signed integer, which is
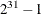 .
.
The value
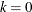 disables the printing of the progress of the solution.
disables the printing of the progress of the solution.
If the LOGFREQ= option is not specified, then PROC OPTLP displays the iteration log with a dynamic frequency according to the problem size if the primal or dual simplex algorithm is used, with frequency 10,000 if the network simplex algorithm is used, or with frequency 1 if the interior point algorithm is used.
-
LOGLEVEL=number | string
PRINTLEVEL2=number | string -
controls the amount of information displayed in the SAS log by the LP solver, from a short description of presolve information and summary to details at each iteration. Table 12.3 describes the valid values for this option.
Table 12.3: Values for LOGLEVEL= Option
number
string
Description
0
NONE
Turn off all solver-related messages in SAS log.
1
BASIC
Display a solver summary after stopping.
2
MODERATE
Print a solver summary and an iteration log by using the interval dictated by the LOGFREQ= option.
3
AGGRESSIVE
Print a detailed solver summary and an iteration log by using the interval dictated by the LOGFREQ= option.
The default value is MODERATE.
- MAXITER=k
-
specifies the maximum number of iterations. The value k can be any integer between one and the largest four-byte signed integer, which is
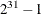 . If you do not specify this option, the procedure does not stop based on the number of iterations performed. For network
simplex, this iteration limit corresponds to the algorithm called after network simplex (either primal or dual simplex).
. If you do not specify this option, the procedure does not stop based on the number of iterations performed. For network
simplex, this iteration limit corresponds to the algorithm called after network simplex (either primal or dual simplex).
- MAXTIME=t
-
specifies an upper limit of t seconds of time for reading in the data and performing the optimization process. The value of the TIMETYPE= option determines the type of units used. If you do not specify this option, the procedure does not stop based on the amount of time elapsed. The value of t can be any positive number; the default value is the positive number that has the largest absolute value that can be represented in your operating environment.
-
OPTTOL=

-
specifies the optimality tolerance
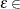 [1E–9, 1E–4] for declaring optimality. The default value is 1E–6.
[1E–9, 1E–4] for declaring optimality. The default value is 1E–6.
-
PRINTLEVEL=0
 1
1  2
2
-
specifies whether a summary of the problem and solution should be printed. If PRINTLEVEL=1, then the Output Delivery System (ODS) tables ProblemSummary, SolutionSummary, and PerformanceInfo are produced and printed. If PRINTLEVEL=2, then the same tables are produced and printed along with an additional table called ProblemStatistics. If PRINTLEVEL=0, then no ODS tables are produced or printed. The default value is 1.
For details about the ODS tables created by PROC OPTLP, see the section ODS Tables.
- TIMETYPE=number | string
-
specifies whether CPU time or real time is used for the MAXTIME= option and the _OROPTLP_ macro variable in a PROC OPTLP call. Table 12.4 describes the valid values of the TIMETYPE= option.
Table 12.4: Values for TIMETYPE= Option
number
string
Description
0
CPU
Specifies units of CPU time.
1
REAL
Specifies units of real time.
The default value of the TIMETYPE= option depends on the values of the NTHREADS= and NODES= options in the PERFORMANCE statement. See the section PERFORMANCE Statement in Chapter 4: Shared Concepts and Topics. for more information about the NTHREADS= and NODES= options.
If you specify a value greater than 1 for either the NTHREADS= or the NODES= option, the default value of the TIMETYPE= option is REAL. If you specify a value of 1 for both the NTHREADS= and NODES= options, the default value of the TIMETYPE= option is CPU.
- BASIS=number | string
-
specifies the following options for generating an initial basis:
number
string
Description
0
CRASH
Generate an initial basis by using crash techniques (Maros, 2003). The procedure creates a triangular basic matrix consisting of both decision variables and slack variables.
1
SLACK
Generate an initial basis by using all slack variables.
2
WARMSTART
Start the primal and dual simplex algorithms with a user-specified initial basis. The PRIMALIN= and DUALIN= data sets are required to specify an initial basis.
The default option is determined automatically based on the problem structure. For network simplex, this option has no effect.
- PRICETYPE=number | string
-
specifies one of the following pricing strategies for the primal and dual simplex algorithms:
number
string
Description
0
HYBRID
Use a hybrid of Devex and steepest-edge pricing strategies. Available for the primal simplex algorithm only.
1
PARTIAL
Use Dantzig’s rule on a queue of decision variables. Optionally, you can specify QUEUESIZE=. Available for the primal simplex algorithm only.
2
FULL
Use Dantzig’s rule on all decision variables.
3
DEVEX
Use Devex pricing strategy.
4
STEEPESTEDGE
Use steepest-edge pricing strategy.
The default option is determined automatically based on the problem structure. For the network simplex algorithm, this option applies only to the algorithm specified by the ALGORITHM2= option. See the section Pricing Strategies for the Primal and Dual Simplex Algorithms for details.
- QUEUESIZE=k
-
specifies the queue size
![$k\in [1, n]$](images/ormpug_optlp0019.png) , where n is the number of decision variables. This queue is used for finding an entering variable in the simplex iteration. The default
value is chosen adaptively based on the number of decision variables. This option is used only when PRICETYPE=PARTIAL.
, where n is the number of decision variables. This queue is used for finding an entering variable in the simplex iteration. The default
value is chosen adaptively based on the number of decision variables. This option is used only when PRICETYPE=PARTIAL.
- SCALE=number | string
-
specifies one of the following scaling options:
number
string
Description
0
NONE
Disable scaling.
–1
AUTOMATIC
Automatically apply scaling procedure if necessary.
The default option is AUTOMATIC.
- SEED=number
-
specifies the initial seed for the random number generator. Because the seed affects the perturbation in the simplex algorithms, the result might be a different optimal solution and a different solver path, but the effect is usually negligible. The value of number can be any positive integer up to the largest four-byte signed integer, which is
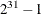 . By default, SEED=100.
. By default, SEED=100.
- CROSSOVER=number | string
-
specifies whether to convert the interior point solution to a basic simplex solution. If the interior point algorithm terminates with a solution, the crossover algorithm uses the interior point solution to create an initial basic solution. After performing primal fixing and dual fixing, the crossover algorithm calls a simplex algorithm to locate an optimal basic solution.
number
string
Description
0
OFF
Do not convert the interior point solution to a basic simplex solution.
1
ON
Convert the interior point solution to a basic simplex solution.
The default value of the CROSSOVER= option is ON.
-
STOP_DG=
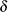
-
specifies the desired relative duality gap
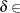 [1E–9, 1E–4]. This is the relative difference between the primal and dual objective function values and is the primary solution
quality parameter. The default value is 1E–6. See the section The Interior Point Algorithm for details.
[1E–9, 1E–4]. This is the relative difference between the primal and dual objective function values and is the primary solution
quality parameter. The default value is 1E–6. See the section The Interior Point Algorithm for details.
-
STOP_DI=
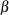
-
specifies the maximum allowed relative dual constraints violation
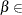 [1E–9, 1E–4]. The default value is 1E–6. See the section The Interior Point Algorithm for details.
[1E–9, 1E–4]. The default value is 1E–6. See the section The Interior Point Algorithm for details.
-
STOP_PI=

-
specifies the maximum allowed relative bound and primal constraints violation
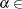 [1E–9, 1E–4]. The default value is 1E–6. See the section The Interior Point Algorithm for details.
[1E–9, 1E–4]. The default value is 1E–6. See the section The Interior Point Algorithm for details.