The GLIMMIX Procedure
-
Overview

-
Getting Started

-
Syntax
 PROC GLIMMIX StatementBY StatementCLASS StatementCODE StatementCONTRAST StatementCOVTEST StatementEFFECT StatementESTIMATE StatementFREQ StatementID StatementLSMEANS StatementLSMESTIMATE StatementMODEL StatementNLOPTIONS StatementOUTPUT StatementPARMS StatementRANDOM StatementSLICE StatementSTORE StatementWEIGHT StatementProgramming StatementsUser-Defined Link or Variance Function
PROC GLIMMIX StatementBY StatementCLASS StatementCODE StatementCONTRAST StatementCOVTEST StatementEFFECT StatementESTIMATE StatementFREQ StatementID StatementLSMEANS StatementLSMESTIMATE StatementMODEL StatementNLOPTIONS StatementOUTPUT StatementPARMS StatementRANDOM StatementSLICE StatementSTORE StatementWEIGHT StatementProgramming StatementsUser-Defined Link or Variance Function -
Details
 Generalized Linear Models TheoryGeneralized Linear Mixed Models TheoryGLM Mode or GLMM ModeStatistical Inference for Covariance ParametersDegrees of Freedom MethodsEmpirical Covariance (Sandwich) EstimatorsExploring and Comparing Covariance MatricesProcessing by SubjectsRadial Smoothing Based on Mixed ModelsOdds and Odds Ratio EstimationParameterization of Generalized Linear Mixed ModelsResponse-Level Ordering and ReferencingComparing the GLIMMIX and MIXED ProceduresSingly or Doubly Iterative FittingDefault Estimation TechniquesDefault OutputNotes on Output StatisticsODS Table NamesODS Graphics
Generalized Linear Models TheoryGeneralized Linear Mixed Models TheoryGLM Mode or GLMM ModeStatistical Inference for Covariance ParametersDegrees of Freedom MethodsEmpirical Covariance (Sandwich) EstimatorsExploring and Comparing Covariance MatricesProcessing by SubjectsRadial Smoothing Based on Mixed ModelsOdds and Odds Ratio EstimationParameterization of Generalized Linear Mixed ModelsResponse-Level Ordering and ReferencingComparing the GLIMMIX and MIXED ProceduresSingly or Doubly Iterative FittingDefault Estimation TechniquesDefault OutputNotes on Output StatisticsODS Table NamesODS Graphics -
Examples
 Binomial Counts in Randomized BlocksMating Experiment with Crossed Random EffectsSmoothing Disease Rates; Standardized Mortality RatiosQuasi-likelihood Estimation for Proportions with Unknown DistributionJoint Modeling of Binary and Count DataRadial Smoothing of Repeated Measures DataIsotonic Contrasts for Ordered AlternativesAdjusted Covariance Matrices of Fixed EffectsTesting Equality of Covariance and Correlation MatricesMultiple Trends Correspond to Multiple Extrema in Profile LikelihoodsMaximum Likelihood in Proportional Odds Model with Random EffectsFitting a Marginal (GEE-Type) ModelResponse Surface Comparisons with Multiplicity AdjustmentsGeneralized Poisson Mixed Model for Overdispersed Count DataComparing Multiple B-SplinesDiallel Experiment with Multimember Random EffectsLinear Inference Based on Summary Data
Binomial Counts in Randomized BlocksMating Experiment with Crossed Random EffectsSmoothing Disease Rates; Standardized Mortality RatiosQuasi-likelihood Estimation for Proportions with Unknown DistributionJoint Modeling of Binary and Count DataRadial Smoothing of Repeated Measures DataIsotonic Contrasts for Ordered AlternativesAdjusted Covariance Matrices of Fixed EffectsTesting Equality of Covariance and Correlation MatricesMultiple Trends Correspond to Multiple Extrema in Profile LikelihoodsMaximum Likelihood in Proportional Odds Model with Random EffectsFitting a Marginal (GEE-Type) ModelResponse Surface Comparisons with Multiplicity AdjustmentsGeneralized Poisson Mixed Model for Overdispersed Count DataComparing Multiple B-SplinesDiallel Experiment with Multimember Random EffectsLinear Inference Based on Summary Data - References
References
-
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, I. A. (1972), Handbook of Mathematical Functions, New York: Dover Publications.
-
Akaike, H. (1974), “A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification,” IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control, AC-19, 716–723.
-
Bahadur, R. R. (1961), Studies in Item Analysis and Prediction, chapter A Representation of the Joint Distribution of Responses to n Dichotomous Items, Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
-
Beale, E. M. L. (1972), “A Derivation of Conjugate Gradients,” in F. A. Lootsma, ed., Numerical Methods for Nonlinear Optimization, London: Academic Press.
-
Bell, R. M. and McCaffrey, D. F. (2002), “Bias Reduction in Standard Errors for Linear Regression with Multi-Stage Samples,” Survey Methodology, 28, 169–181.
-
Bickel, P. J. and Doksum, K. A. (1977), Mathematical Statistics, San Francisco: Holden-Day.
-
Booth, J. G. and Hobert, J. P. (1998), “Standard Errors of Prediction in Generalized Linear Mixed Models,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 93, 262–272.
-
Bozdogan, H. (1987), “Model Selection and Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC): The General Theory and Its Analytical Extensions,” Psychometrika, 52, 345–370.
-
Breslow, N. E. and Clayton, D. G. (1993), “Approximate Inference in Generalized Linear Mixed Models,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 88, 9–25.
-
Breslow, N. E. and Lin, X. (1995), “Bias Correction in Generalised Linear Mixed Models with a Single Component of Dispersion,” Biometrika, 81, 81–91.
-
Brinkman, N. D. (1981), “Ethanol Fuel—A Single-Cylinder Engine Study of Efficiency and Exhaust Emissions,” Society of Automotive Engineers Transactions, 90, 1410–1424.
-
Brown, H. and Prescott, R. (1999), Applied Mixed Models in Medicine, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Burdick, R. K. and Graybill, F. A. (1992), Confidence Intervals on Variance Components, New York: Marcel Dekker.
-
Burnham, K. P. and Anderson, D. R. (1998), Model Selection and Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Cameron, A. C. and Trivedi, P. K. (1998), Regression Analysis of Count Data, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
-
Clayton, D. and Kaldor, J. (1987), “Empirical Bayes Estimates of Age-Standardized Relative Risks for Use in Disease Mapping,” Biometrics, 43, 671–681.
-
Cleveland, W. S. and Grosse, E. (1991), “Computational Methods for Local Regression,” Statistics and Computing, 1, 47–62.
-
Cockerham, C. C. and Weir, B. S. (1977), “Quadratic Analyses of Reciprocal Crosses,” Biometrics, 33, 187–203.
-
Davis, A. W. (1977), “A Differential Equation Approach to Linear Combinations of Independent Chi-Squares,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 72, 212–214.
-
de Boor, C. (2001), A Practical Guide to Splines, Revised Edition, New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Dennis, J. E., Gay, D. M., and Welsch, R. E. (1981), “An Adaptive Nonlinear Least-Squares Algorithm,” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 7, 348–368.
-
Dennis, J. E. and Mei, H. H. W. (1979), “Two New Unconstrained Optimization Algorithms Which Use Function and Gradient Values,” Journal of Optimization Theory Applications, 28, 453–482.
-
Dennis, J. E. and Schnabel, R. B. (1983), Numerical Methods for Unconstrained Optimization and Nonlinear Equations, Englewood, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
-
Diggle, P. J., Liang, K.-Y., and Zeger, S. L. (1994), Analysis of Longitudinal Data, Oxford: Clarendon Press.
-
Dunnett, C. W. (1980), “Pairwise Multiple Comparisons in the Unequal Variance Case,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 75, 796–800.
-
Edwards, D. and Berry, J. J. (1987), “The Efficiency of Simulation-Based Multiple Comparisons,” Biometrics, 43, 913–928.
-
Eilers, P. H. C. and Marx, B. D. (1996), “Flexible Smoothing with B-Splines and Penalties,” Statistical Science, 11, 89–121, with discussion.
-
Eskow, E. and Schnabel, R. B. (1991), “Algorithm 695: Software for a New Modified Cholesky Factorization,” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 17, 306–312.
-
Evans, G. (1993), Practical Numerical Integration, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Fai, A. H. T. and Cornelius, P. L. (1996), “Approximate F-Tests of Multiple Degree of Freedom Hypotheses in Generalized Least Squares Analyses of Unbalanced Split-Plot Experiments,” Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 54, 363–378.
-
Fay, M. P. and Graubard, B. I. (2001), “Small-Sample Adjustments for Wald-Type Tests Using Sandwich Estimators,” Biometrics, 57, 1198–1206.
-
Ferrari, S. L. P. and Cribari-Neto, F. (2004), “Beta Regression for Modelling Rates and Proportions,” Journal of Applied Statistics, 31, 799–815.
-
Fisher, R. A. (1936), “The Use of Multiple Measurements in Taxonomic Problems,” Annals of Eugenics, 7, 179–188.
-
Fletcher, R. (1987), Practical Methods of Optimization, Second Edition, Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Friedman, J. H., Bentley, J. L., and Finkel, R. A. (1977), “An Algorithm for Finding Best Matches in Logarithmic Expected Time,” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 3, 209–226.
-
Fuller, W. A. (1976), Introduction to Statistical Time Series, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Games, P. A. and Howell, J. F. (1976), “Pairwise Multiple Comparison Procedures with Unequal n’s and/or Variances: A Monte Carlo Study,” Journal of Educational Statistics, 1, 113–125.
-
Gay, D. M. (1983), “Subroutines for Unconstrained Minimization,” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 9, 503–524.
-
Giesbrecht, F. G. and Burns, J. C. (1985), “Two-Stage Analysis Based on a Mixed Model: Large-Sample Asymptotic Theory and Small-Sample Simulation Results,” Biometrics, 41, 477–486.
-
Gilliland, D. and Schabenberger, O. (2001), “Limits on Pairwise Association for Equi-Correlated Binary Variables,” Journal of Applied Statistical Sciences, 10, 279–285.
-
Gilmour, A. R., Anderson, R. D., and Rae, A. L. (1987), “Variance Components on an Underlying Scale for Ordered Multiple Threshold Categorical Data Using a Generalized Linear Mixed Model,” Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics, 104, 149–155.
-
Golub, G. H. and Welsch, J. H. (1969), “Calculation of Gaussian Quadrature Rules,” Mathematical Computing, 23, 221–230.
-
Goodnight, J. H. (1978a), Computing MIVQUE0 Estimates of Variance Components, Technical report, SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC, SAS Technical Report R-105 Edition.
-
Goodnight, J. H. (1978b), Tests of Hypotheses in Fixed-Effects Linear Models, Technical Report R-101, SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC.
-
Goodnight, J. H. (1979), “A Tutorial on the Sweep Operator,” The American Statistician, 33, 149–158.
-
Goodnight, J. H. and Hemmerle, W. J. (1979), “A Simplified Algorithm for the W-Transformation in Variance Component Estimation,” Technometrics, 21, 265–268.
-
Gotway, C. A. and Stroup, W. W. (1997), “A Generalized Linear Model Approach to Spatial Data and Prediction,” Journal of Agricultural, Biological, and Environmental Statistics, 2, 157–187.
-
Guirguis, G. and Tobias, R. D. (2004), “On the Computation of the Distribution for the Analysis of Means,” Communications in Statistics: Simulation and Computation, 33, 861–888.
-
Hand, D. J., Daly, F., Lunn, A. D., McConway, K. J., and Ostrowski, E. (1994), A Handbook of Small Data Sets, London: Chapman & Hall.
-
Handcock, M. S. and Stein, M. L. (1993), “A Bayesian Analysis of Kriging,” Technometrics, 35, 403–410.
-
Handcock, M. S. and Wallis, J. R. (1994), “An Approach to Statistical Spatial-Temporal Modeling of Meteorological Fields (with Discussion),” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 89, 368–390.
-
Hannan, E. J. and Quinn, B. G. (1979), “The Determination of the Order of an Autoregression,” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 41, 190–195.
-
Harville, D. A. and Jeske, D. R. (1992), “Mean Squared Error of Estimation or Prediction under a General Linear Model,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 87, 724–731.
-
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., and Friedman, J. (2001), The Elements of Statistical Learning, New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Hemmerle, W. J. and Hartley, H. O. (1973), “Computing Maximum Likelihood Estimates for the Mixed AOV Model Using the W-Transformation,” Technometrics, 15, 819–831.
-
Henderson, C. R. (1984), Applications of Linear Models in Animal Breeding, Guelph, ON: University of Guelph.
-
Hinkley, D. V. (1977), “Jackknifing in Unbalanced Situations,” Technometrics, 19, 285–292.
-
Hirotsu, C. and Srivastava, M. (2000), “Simultaneous Confidence Intervals Based on One-Sided Max t Test,” Statistics and Probability Letters, 49, 25–37.
-
Holm, S. (1979), “A Simple Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test Procedure,” Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 6, 65–70.
-
Hsu, J. C. (1992), “The Factor Analytic Approach to Simultaneous Inference in the General Linear Model,” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 1, 151–168.
-
Hsu, J. C. (1996), Multiple Comparisons: Theory and Methods, London: Chapman & Hall.
-
Hsu, J. C. and Peruggia, M. (1994), “Graphical Representation of Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Method,” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 3, 143–161.
-
Huber, P. J. (1967), “The Behavior of Maximum Likelihood Estimates under Nonstandard Conditions,” Proc. Fifth Berkeley Symp. Math. Statist. Prob., 1, 221–233.
-
Hurvich, C. M. and Tsai, C.-L. (1989), “Regression and Time Series Model Selection in Small Samples,” Biometrika, 76, 297–307.
-
Huynh, H. and Feldt, L. S. (1970), “Conditions Under Which Mean Square Ratios in Repeated Measurements Designs Have Exact F-Distributions,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 65, 1582–1589.
-
Jennrich, R. I. and Schluchter, M. D. (1986), “Unbalanced Repeated-Measures Models with Structured Covariance Matrices,” Biometrics, 42, 805–820.
-
Joe, H. and Zhu, R. (2005), “Generalized Poisson Distribution: The Property of Mixture of Poisson and Comparison with Negative Binomial Distribution,” Biometrical Journal, 47, 219–229.
-
Johnson, N. L., Kotz, S., and Balakrishnan, N. (1994), Continuous Univariate Distributions, volume 1, Second Edition, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Kackar, R. N. and Harville, D. A. (1984), “Approximations for Standard Errors of Estimators of Fixed and Random Effects in Mixed Linear Models,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 79, 853–862.
-
Kahaner, D., Moler, C., and Nash, S. (1989), Numerical Methods and Software, Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
-
Karim, M. Z. and Zeger, S. L. (1992), “Generalized Linear Models with Random Effects; Salamander Mating Revisited,” Biometrics, 48, 631–644.
-
Kass, R. E. and Steffey, D. (1989), “Approximate Bayesian Inference in Conditionally Independent Hierarchical Models (Parametric Empirical Bayes Models),” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 84, 717–726.
-
Kauermann, G. and Carroll, R. J. (2001), “A Note on the Efficiency of Sandwich Covariance Estimation,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 96, 1387–1396.
-
Kenward, M. G. (1987), “A Method for Comparing Profiles of Repeated Measurements,” Applied Statistics, 36, 296–308.
-
Kenward, M. G. and Roger, J. H. (1997), “Small Sample Inference for Fixed Effects from Restricted Maximum Likelihood,” Biometrics, 53, 983–997.
-
Kenward, M. G. and Roger, J. H. (2009), “An Improved Approximation to the Precision of Fixed Effects from Restricted Maximum Likelihood,” Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 53, 2583–2595.
-
Koch, G. G., Carr, G. J., Amara, I. A., Stokes, M. E., and Uryniak, T. J. (1990), Statistical Methodology in the Pharmaceutical Sciences, chapter Categorical Data Analysis, New York: Marcel Dekker.
-
Kramer, C. Y. (1956), “Extension of Multiple Range Tests to Group Means with Unequal Numbers of Replications,” Biometrics, 12, 307–310.
-
Lange, K. (1999), Numerical Analysis for Statisticians, New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Liang, K.-Y. and Zeger, S. L. (1986), “Longitudinal Data Analysis Using Generalized Linear Models,” Biometrika, 73, 13–22.
-
Lin, X. and Breslow, N. E. (1996), “Bias Correction in Generalized Linear Mixed Models with Multiple Components of Dispersion,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 91, 1007–1016.
-
Littell, R. C., Milliken, G. A., Stroup, W. W., Wolfinger, R. D., and Schabenberger, O. (2006), SAS for Mixed Models, Second Edition, Cary, NC: SAS Press.
-
Long, J. S. and Ervin, L. H. (2000), “Using Heteroscedasticity Consistent Standard Errors in the Linear Regression Model,” The American Statistician, 54, 217–224.
-
Macchiavelli, R. E. and Arnold, S. F. (1994), “Variable Order Ante-dependence Models,” Communications in Statistics—Theory and Methods, 23, 2683–2699.
-
MacKinnon, J. G. and White, H. (1985), “Some Heteroskedasticity-Consistent Covariance Matrix Estimators with Improved Finite Sample Properties,” Journal of Econometrics, 29, 305–325.
-
Mancl, L. A. and DeRouen, T. A. (2001), “A Covariance Estimator for GEE with Improved Small-Sample Properties,” Biometrics, 57, 126–134.
-
Matérn, B. (1986), Spatial Variation, Second Edition, New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
McCullagh, P. (1980), “Regression Models for Ordinal Data,” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 42, 109–142.
-
McCullagh, P. and Nelder, J. A. (1989), Generalized Linear Models, Second Edition, London: Chapman & Hall.
-
McLean, R. A. and Sanders, W. L. (1988), “Approximating Degrees of Freedom for Standard Errors in Mixed Linear Models,” Proceedings of the Statistical Computing Section.
-
McLean, R. A., Sanders, W. L., and Stroup, W. W. (1991), “A Unified Approach to Mixed Linear Models,” The American Statistician, 45, 54–64.
-
Milliken, G. A. and Johnson, D. E. (1992), Analysis of Messy Data, Volume 1: Designed Experiments, New York: Chapman & Hall.
-
Moré, J. J. (1978), “The Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm: Implementation and Theory,” in G. A. Watson, ed., Lecture Notes in Mathematics, volume 30, 105–116, Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
-
Moré, J. J. and Sorensen, D. C. (1983), “Computing a Trust-Region Step,” SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing, 4, 553–572.
-
Morel, J. G. (1989), “Logistic Regression under Complex Survey Designs,” Survey Methodology, 15, 203–223.
-
Morel, J. G., Bokossa, M. C., and Neerchal, N. K. (2003), “Small Sample Correction for the Variance of GEE Estimators,” Biometrical Journal, 4, 395–409.
-
Moriguchi, S., ed. (1976), Statistical Method for Quality Control, (in Japanese), Tokyo: Japan Standards Association.
-
Mosteller, F. and Tukey, J. W. (1977), Data Analysis and Regression, Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
-
Murray, D. M., Varnell, S. P., and Blitstein, J. L. (2004), “Design and Analysis of Group-Randomized Trials: A Review of Recent Methodological Developments,” American Journal of Public Health, 94, 423–432.
-
National Institute of Standards and Technology (1998), “Statistical Reference Data Sets,” http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/strd/general/dataarchive.html, last accessed June 6, 2011.
-
Nelder, J. A. and Wedderburn, R. W. M. (1972), “Generalized Linear Models,” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A, 135, 370–384.
-
Nelson, P. R. (1982), “Exact Critical Points for the Analysis of Means,” Communications in Statistics, Part A: Theory and Methods, 699–709.
-
Nelson, P. R. (1991), “Numerical Evaluation of Multivariate Normal Integrals with Correlations
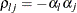 ,” Frontiers of Statistical Scientific Theory and Industrial Applications, 97–114.
,” Frontiers of Statistical Scientific Theory and Industrial Applications, 97–114.
-
Nelson, P. R. (1993), “Additional Uses for the Analysis of Means and Extended Tables of Critical Values,” Technometrics, 35, 61–71.
-
Ott, E. R. (1967), “Analysis of Means—A Graphical Procedure,” Industrial Quality Control, 24, 101–109. Reprinted in Journal of Quality Technology, 15 (1983), 10–18.
-
Patel, H. I. (1991), “Analysis of Incomplete Data from a Clinical Trial with Repeated Measurements,” Biometrika, 78, 609–619.
-
Pawitan, Y. (2001), In All Likelihood: Statistical Modelling and Inference Using Likelihood, Oxford: Clarendon Press.
-
Pinheiro, J. C. and Bates, D. M. (1995), “Approximations to the Log-Likelihood Function in the Nonlinear Mixed-Effects Model,” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 4, 12–35.
-
Pinheiro, J. C. and Chao, E. C. (2006), “Efficient Laplacian and Adaptive Gaussian Quadrature Algorithms for Multilevel Generalized Linear Mixed Models,” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 15, 58–81.
-
Polak, E. (1971), Computational Methods in Optimization, New York: Academic Press.
-
Pothoff, R. F. and Roy, S. N. (1964), “A Generalized Multivariate Analysis of Variance Model Useful Especially for Growth Curve Problems,” Biometrika, 51, 313–326.
-
Powell, M. J. D. (1977), “Restart Procedures for the Conjugate Gradient Method,” Mathematical Programming, 12, 241–254.
-
Prasad, N. G. N. and Rao, J. N. K. (1990), “The Estimation of Mean Squared Error of Small-Area Estimators,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 85, 163–171.
-
Pringle, R. M. and Rayner, A. A. (1971), Generalized Inverse Matrices with Applications to Statistics, New York: Hafner Publishing.
-
Raudenbush, S. M., Yang, M.-L., and Yosef, M. (2000), “Maximum Likelihood for Generalized Linear Models with Nested Random Effects via Higher-Order, Multivariate Laplace Approximation,” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 9, 141–157.
-
Royen, T. (1989), “Generalized Maximum Range Tests for Pairwise Comparisons of Several Populations,” Biometrical Journal, 31, 905–929.
-
Ruppert, D., Wand, M. P., and Carroll, R. J. (2003), Semiparametric Regression, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
-
Saxton, A., ed. (2004), Genetic Analysis of Complex Traits Using SAS, Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
-
Schabenberger, O. and Gregoire, T. G. (1996), “Population-Averaged and Subject-Specific Approaches for Clustered Categorical Data,” Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 54, 231–253.
-
Schabenberger, O., Gregoire, T. G., and Kong, F. (2000), “Collections of Simple Effects and Their Relationship to Main Effects and Interactions in Factorials,” The American Statistician, 54, 210–214.
-
Schabenberger, O. and Pierce, F. J. (2002), Contemporary Statistical Models for the Plant and Soil Sciences, Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
-
Schall, R. (1991), “Estimation in Generalized Linear Models with Random Effects,” Biometrika, 78, 719–727.
-
Schluchter, M. D. and Elashoff, J. D. (1990), “Small-Sample Adjustments to Tests with Unbalanced Repeated Measures Assuming Several Covariance Structures,” Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 37, 69–87.
-
Schwarz, G. (1978), “Estimating the Dimension of a Model,” Annals of Statistics, 6, 461–464.
-
Searle, S. R. (1971), Linear Models, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Self, S. G. and Liang, K.-Y. (1987), “Asymptotic Properties of Maximum Likelihood Estimators and Likelihood Ratio Tests under Nonstandard Conditions,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 82, 605–610.
-
Shaffer, J. P. (1986), “Modified Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test Procedures,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 81, 826–831.
-
Shapiro, A. (1988), “Towards a Unified Theory of Inequality Constrained Testing in Multivariate Analysis,” International Statistical Review, 56, 49–62.
-
Shun, Z. (1997), “Another Look at the Salamander Mating Data: A Modified Laplace Approximation Approach,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 92, 341–349.
-
Shun, Z. and McCullagh, P. (1995), “Laplace Approximation of High Dimensional Integrals,” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 57, 749–760.
-
Silvapulle, M. J. and Sen, P. K. (2004), Constrained Statistical Inference: Order, Inequality, and Shape Constraints, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Silvapulle, M. J. and Silvapulle, P. (1995), “A Score Test against One-Sided Alternatives,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 429, 342–349.
-
Stenstrom, F. H. (1940), The Growth of Snapdragons, Stocks, Cinerarias and Carnations on Six Iowa Soils, Master’s thesis, Iowa State College.
-
Stram, D. O. and Lee, J. W. (1994), “Variance Components Testing in the Longitudinal Mixed Effects Model,” Biometrics, 50, 1171–1177.
-
Stram, D. O. and Lee, J. W. (1995), “Correction to 'Variance Components Testing in the Longitudinal Mixed Effects Model',” Biometrics, 51, 1196.
-
Tamhane, A. C. (1979), “A Comparison of Procedures for Multiple Comparisons of Means with Unequal Variances,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 74, 471–480.
-
Thall, P. F. and Vail, S. C. (1990), “Some Covariance Models for Longitudinal Count Data with Overdispersion,” Biometrics, 46, 657–671.
-
Verbeke, G. and Molenberghs, G. (2000), Linear Mixed Models for Longitudinal Data, New York: Springer.
-
Verbeke, G. and Molenberghs, G. (2003), “The Use of Score Tests for Inference on Variance Components,” Biometrics, 59, 254–262.
-
Vonesh, E. F. (1996), “A Note on Laplace’s Approximation for Nonlinear Mixed-Effects Models,” Biometrika, 83, 447–452.
-
Vonesh, E. F. and Chinchilli, V. M. (1997), Linear and Nonlinear Models for the Analysis of Repeated Measurements, New York: Marcel Dekker.
-
Vonesh, E. F., Chinchilli, V. M., and Pu, K. (1996), “Goodness-of-Fit in Generalized Nonlinear Mixed-Effects Models,” Biometrics, 52, 572–587.
-
Wedderburn, R. W. M. (1974), “Quasilikelihood Functions, Generalized Linear Models, and the Gauss-Newton Method,” Biometrika, 61, 439–447.
-
Westfall, P. H. (1997), “Multiple Testing of General Contrasts Using Logical Constraints and Correlations,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 92, 299–306.
-
Westfall, P. H. and Tobias, R. D. (2007), “Multiple Testing of General Contrasts: Truncated Closure and the Extended Shaffer-Royen Method,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 478, 487–494.
-
Westfall, P. H., Tobias, R. D., Rom, D., Wolfinger, R. D., and Hochberg, Y. (1999), Multiple Comparisons and Multiple Tests Using the SAS System, Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
-
Westfall, P. J. and Young, S. S. (1993), Resampling-Based Multiple Testing, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
White, H. (1980), “A Heteroskedasticity-Consistent Covariance Matrix Estimator and a Direct Test for Heteroskedasticity,” Econometrica, 48, 817–838.
-
White, H. (1982), “Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Misspecified Models,” Econometrica, 50, 1–25.
-
Whittle, P. (1954), “On Stationary Processes in the Plane,” Biometrika, 41, 434–449.
-
Winer, B. J. (1971), Statistical Principles in Experimental Design, Second Edition, New York: McGraw-Hill.
-
Wolfinger, R. D. (1993), “Laplace’s Approximation for Nonlinear Mixed Models,” Biometrika, 80, 791–795.
-
Wolfinger, R. D. and O’Connell, M. (1993), “Generalized Linear Mixed Models: A Pseudo-likelihood Approach,” Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 48, 233–243.
-
Wolfinger, R. D., Tobias, R. D., and Sall, J. (1994), “Computing Gaussian Likelihoods and Their Derivatives for General Linear Mixed Models,” SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 15, 1294–1310.
-
Zeger, S. L. and Liang, K.-Y. (1986), “Longitudinal Data Analysis for Discrete and Continuous Outcomes,” Biometrics, 42, 121–130.