The REG Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 Missing ValuesInput Data SetsOutput Data SetsInteractive AnalysisModel-Selection MethodsCriteria Used in Model-Selection MethodsLimitations in Model-Selection MethodsParameter Estimates and Associated StatisticsPredicted and Residual ValuesModels of Less Than Full RankCollinearity DiagnosticsModel Fit and Diagnostic StatisticsInfluence StatisticsReweighting Observations in an AnalysisTesting for HeteroscedasticityTesting for Lack of FitMultivariate TestsAutocorrelation in Time Series DataComputations for Ridge Regression and IPC AnalysisConstruction of Q-Q and P-P PlotsComputational MethodsComputer Resources in Regression AnalysisDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics
Missing ValuesInput Data SetsOutput Data SetsInteractive AnalysisModel-Selection MethodsCriteria Used in Model-Selection MethodsLimitations in Model-Selection MethodsParameter Estimates and Associated StatisticsPredicted and Residual ValuesModels of Less Than Full RankCollinearity DiagnosticsModel Fit and Diagnostic StatisticsInfluence StatisticsReweighting Observations in an AnalysisTesting for HeteroscedasticityTesting for Lack of FitMultivariate TestsAutocorrelation in Time Series DataComputations for Ridge Regression and IPC AnalysisConstruction of Q-Q and P-P PlotsComputational MethodsComputer Resources in Regression AnalysisDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics -
Examples

- References
References
-
Akaike, H. (1969), “Fitting Autoregressive Models for Prediction,” Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 21, 243–247.
-
Allen, D. M. (1971), “Mean Square Error of Prediction as a Criterion for Selecting Variables,” Technometrics, 13, 469–475.
-
Allen, D. M. and Cady, F. B. (1982), Analyzing Experimental Data by Regression, Belmont, CA: Lifetime Learning Publications.
-
Amemiya, T. (1976), Selection of Regressors, Technical Report 225, Stanford University, Stanford, CA.
-
Belsley, D. A., Kuh, E., and Welsch, R. E. (1980), Regression Diagnostics: Identifying Influential Data and Sources of Collinearity, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Berk, K. N. (1977), “Tolerance and Condition in Regression Computations,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 72, 863–866.
-
Bock, R. D. (1975), Multivariate Statistical Methods in Behavioral Research, New York: McGraw-Hill.
-
Box, G. E. P. (1966), “The Use and Abuse of Regression,” Technometrics, 8, 625–629.
-
Cleveland, W. S. (1993), Visualizing Data, Summit, NJ: Hobart Press.
-
Cook, R. D. (1977), “Detection of Influential Observations in Linear Regression,” Technometrics, 19, 15–18.
-
Cook, R. D. (1979), “Influential Observations in Linear Regression,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 74, 169–174.
-
Daniel, C. and Wood, F. (1980), Fitting Equations to Data, Revised Edition, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Darlington, R. B. (1968), “Multiple Regression in Psychological Research and Practice,” Psychological Bulletin, 69, 161–182.
-
Draper, N. R. and Smith, H. (1981), Applied Regression Analysis, Second Edition, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Durbin, J. and Watson, G. S. (1951), “Testing for Serial Correlation in Least Squares Regression,” Biometrika, 37, 409–428.
-
Freund, R. J. and Littell, R. C. (1986), SAS System for Regression, 1986 Edition, Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
-
Furnival, G. M. and Wilson, R. W. (1974), “Regression by Leaps and Bounds,” Technometrics, 16, 499–511.
-
Goodnight, J. H. (1979), “A Tutorial on the Sweep Operator,” The American Statistician, 33, 149–158.
-
Hocking, R. R. (1976), “The Analysis and Selection of Variables in a Linear Regression,” Biometrics, 32, 1–50.
-
Johnston, J. (1972), Econometric Methods, Second Edition, New York: McGraw-Hill.
-
Judge, G. G., Griffiths, W. E., Hill, R. C., and Lee, T.-C. (1980), The Theory and Practice of Econometrics, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Judge, G. G., Griffiths, W. E., Hill, R. C., Lutkepohl, H., and Lee, T. C. (1985), The Theory and Practice of Econometrics, Second Edition, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Kennedy, W. J., Jr. and Gentle, J. E. (1980), Statistical Computing, New York: Marcel Dekker.
-
LaMotte, L. R. (1994), “A Note on the Role of Independence in t Statistics Constructed from Linear Statistics in Regression Models,” The American Statistician, 48, 238–240.
-
Lewis, T. and Taylor, L. R. (1967), Introduction to Experimental Ecology, New York: Academic Press.
-
Long, J. S. and Ervin, L. H. (2000), “Using Heteroscedasticity Consistent Standard Errors in the Linear Regression Model,” The American Statistician, 54, 217–224.
-
Lord, F. M. (1950), Efficiency of Prediction When a Progression Equation from One Sample Is Used in a New Sample, Research bulletin, Educational Testing Service., Princeton, NJ.
-
MacKinnon, J. G. and White, H. (1985), “Some Heteroskedasticity-Consistent Covariance Matrix Estimators with Improved Finite Sample Properties,” Journal of Econometrics, 29, 305–325.
-
Mallows, C. L. (1967), “Choosing a Subset Regression,” Bell Telephone Laboratories.
-
Mallows, C. L. (1973), “Some Comments on
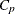 ,” Technometrics, 15, 661–675.
,” Technometrics, 15, 661–675.
-
Mardia, K. V., Kent, J. T., and Bibby, J. M. (1979), Multivariate Analysis, London: Academic Press.
-
Marquardt, D. W. and Snee, R. D. (1975), “Ridge Regression in Practice,” The American Statistician, 29, 3–20.
-
Morrison, D. F. (1976), Multivariate Statistical Methods, Second Edition, New York: McGraw-Hill.
-
Mosteller, F. and Tukey, J. W. (1977), Data Analysis and Regression, Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
-
Neter, J., Wasserman, W., and Kutner, M. H. (1990), Applied Linear Statistical Models, Third Edition, Homewood, IL: Irwin.
-
Nicholson, G. E., Jr. (1948), “The Application of a Regression Equation to a New Sample,” Unpublished Ph.D. dissertation, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
-
Pillai, K. C. S. (1960), Statistical Table for Tests of Multivariate Hypotheses, Manila: The Statistical Center, University of Philippines.
-
Pindyck, R. S. and Rubinfeld, D. L. (1981), Econometric Models and Econometric Forecasts, Second Edition, New York: McGraw-Hill.
-
Pringle, R. M. and Rayner, A. A. (1971), Generalized Inverse Matrices with Applications to Statistics, New York: Hafner Publishing.
-
Rao, C. R. (1973), Linear Statistical Inference and Its Applications, Second Edition, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Rawlings, J. O., Pantula, S. G., and Dickey, D. A. (1998), Applied Regression Analysis: A Research Tool, Springer Texts in Statistics, Second Edition, New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Reichler, J. L., ed. (1987), The 1987 Baseball Encyclopedia Update, New York: Macmillan.
-
Rothman, D. (1968), “letter to the editor,” Technometrics, 10, 432.
-
Sall, J. P. (1981), SAS Regression Applications, Revised Edition, SAS Technical Report A-102, Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
-
Sawa, T. (1978), “Information Criteria for Discriminating Among Alternative Regression Models,” Econometrica, 46, 1273–1282.
-
Schwarz, G. (1978), “Estimating the Dimension of a Model,” Annals of Statistics, 6, 461–464.
-
Stein, C. (1960), “Multiple Regression,” in I. Olkin, ed., Contributions to Probability and Statistics, Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
-
Time Inc. (1987), “What They Make,” Sports Illustrated, 54–81.
-
Timm, N. H. (1975), Multivariate Analysis with Applications in Education and Psychology, Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole.
-
Weisberg, S. (1980), Applied Linear Regression, New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
White, H. (1980), “A Heteroskedasticity-Consistent Covariance Matrix Estimator and a Direct Test for Heteroskedasticity,” Econometrica, 48, 817–838.