The VARMAX Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 Missing ValuesVARMAX ModelDynamic Simultaneous Equations ModelingImpulse Response FunctionForecastingTentative Order SelectionVAR and VARX ModelingBayesian VAR and VARX ModelingVARMA and VARMAX ModelingModel Diagnostic ChecksCointegrationVector Error Correction ModelingI(2) ModelMultivariate GARCH ModelingOutput Data SetsOUT= Data SetOUTEST= Data SetOUTHT= Data SetOUTSTAT= Data SetPrinted OutputODS Table NamesODS GraphicsComputational Issues
Missing ValuesVARMAX ModelDynamic Simultaneous Equations ModelingImpulse Response FunctionForecastingTentative Order SelectionVAR and VARX ModelingBayesian VAR and VARX ModelingVARMA and VARMAX ModelingModel Diagnostic ChecksCointegrationVector Error Correction ModelingI(2) ModelMultivariate GARCH ModelingOutput Data SetsOUT= Data SetOUTEST= Data SetOUTHT= Data SetOUTSTAT= Data SetPrinted OutputODS Table NamesODS GraphicsComputational Issues -
Examples

- References
The OUTEST= data set contains estimation results of the fitted model produced by the VARMAX statement. The following output variables can be created:
-
BY variables
-
NAME, a character variable that contains the name of the endogenous (dependent) variables or the name of the parameters for the covariance of the matrix of the parameter estimates if you specify the OUTCOV option
-
TYPE, a character variable that contains the value EST for parameter estimates, the value STD for standard error of parameter estimates, and the value COV for the covariance of the matrix of the parameter estimates if you specify the OUTCOV option
-
CONST, a numeric variable that contains the estimates of constant parameters and their standard errors
-
SEASON
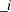 , a numeric variable that contains the estimates of seasonal dummy parameters and their standard errors, where
, a numeric variable that contains the estimates of seasonal dummy parameters and their standard errors, where 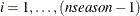 , and
, and 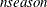 is based on the NSEASON= option
is based on the NSEASON= option
-
LTREND, a numeric variable that contains the estimates of linear trend parameters and their standard errors
-
QTREND, a numeric variable that contains the estimates of quadratic trend parameters and their standard errors
-
XL
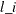 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of exogenous parameters and their standard errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of exogenous parameters and their standard errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and 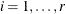 , where r is the number of exogenous variables
, where r is the number of exogenous variables
-
AR
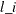 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of autoregressive parameters and their standard errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of autoregressive parameters and their standard errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and 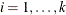 , where k is the number of endogenous variables
, where k is the number of endogenous variables
-
MA
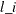 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of moving-average parameters and their standard errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of moving-average parameters and their standard errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and 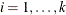 , where k is the number of endogenous variables
, where k is the number of endogenous variables
-
COV
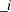 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of the covariance of innovations parameters when the maximum likelihood method
is applied, where
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of the covariance of innovations parameters when the maximum likelihood method
is applied, where 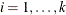
-
DCCAB, a numeric variable that contains the estimates of
 or
or 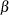 in the correlation equation for DCC representation and their standard errors
in the correlation equation for DCC representation and their standard errors
-
CCC
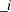 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of the conditional constant correlation parameters for CCC representation,
where
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of the conditional constant correlation parameters for CCC representation,
where 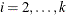
-
DCCS
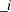 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of the unconditional correlation parameters for DCC representation, where
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of the unconditional correlation parameters for DCC representation, where 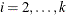
-
GCHC
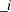 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of the constant parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard errors,
where
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of the constant parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard errors,
where 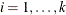 for BEKK representation, k is the number of endogenous variables, and
for BEKK representation, k is the number of endogenous variables, and 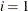 for CCC and DCC representations
for CCC and DCC representations
-
ACH
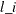 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of the ARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard errors,
where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of the ARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard errors,
where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and 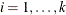 for BEKK, CCC, and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
for BEKK, CCC, and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
-
EACH
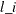 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of the exponential ARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard
errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of the exponential ARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard
errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and 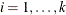 for CCC and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
for CCC and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
-
PACH
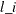 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of the power ARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard errors,
where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of the power ARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard errors,
where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and 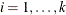 for CCC and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
for CCC and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
-
QACH
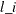 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of the quadratic ARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard
errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of the quadratic ARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard
errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and 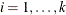 for CCC and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
for CCC and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
-
TACH
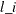 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of the threshold ARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard
errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of the threshold ARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard
errors, where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and 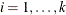 for CCC and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
for CCC and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
-
GCH
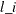 , numeric variables that contain the estimates of the GARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard errors,
where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and
, numeric variables that contain the estimates of the GARCH parameters of the covariance matrix and their standard errors,
where l is the lag lth coefficient matrix and 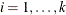 for BEKK, CCC, and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
for BEKK, CCC, and DCC representations, where k is the number of endogenous variables
-
LAMBDA, a numeric variable that contains the estimates of power parameters in the PGARCH model for CCC and DCC representations and their standard errors
The OUTEST= data set contains the values shown in Table 35.9 for a bivariate case.
Table 35.9: OUTEST= Data Set
|
Obs |
NAME |
TYPE |
CONST |
AR1_1 |
AR1_2 |
AR2_1 |
AR2_2 |
|
1 |
y1 |
EST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
STD |
se( |
se( |
se( |
se( |
se( |
|
|
3 |
y2 |
EST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
STD |
se( |
se( |
se( |
se( |
se( |
Consider the following example:
proc varmax data=simul2 outest=est;
model y1 y2 / p=2 noint
ecm=(rank=1 normalize=y1)
noprint;
run;
proc print data=est;
run;
The output in Figure 35.67 shows the results of the OUTEST= data set.