The GLIMMIX Procedure
-
Overview

-
Getting Started

-
Syntax
 PROC GLIMMIX StatementBY StatementCLASS StatementCODE StatementCONTRAST StatementCOVTEST StatementEFFECT StatementESTIMATE StatementFREQ StatementID StatementLSMEANS StatementLSMESTIMATE StatementMODEL StatementNLOPTIONS StatementOUTPUT StatementPARMS StatementRANDOM StatementSLICE StatementSTORE StatementWEIGHT StatementProgramming StatementsUser-Defined Link or Variance Function
PROC GLIMMIX StatementBY StatementCLASS StatementCODE StatementCONTRAST StatementCOVTEST StatementEFFECT StatementESTIMATE StatementFREQ StatementID StatementLSMEANS StatementLSMESTIMATE StatementMODEL StatementNLOPTIONS StatementOUTPUT StatementPARMS StatementRANDOM StatementSLICE StatementSTORE StatementWEIGHT StatementProgramming StatementsUser-Defined Link or Variance Function -
Details
 Generalized Linear Models TheoryGeneralized Linear Mixed Models TheoryGLM Mode or GLMM ModeStatistical Inference for Covariance ParametersDegrees of Freedom MethodsEmpirical Covariance ("Sandwich") EstimatorsExploring and Comparing Covariance MatricesProcessing by SubjectsRadial Smoothing Based on Mixed ModelsOdds and Odds Ratio EstimationParameterization of Generalized Linear Mixed ModelsResponse-Level Ordering and ReferencingComparing the GLIMMIX and MIXED ProceduresSingly or Doubly Iterative FittingDefault Estimation TechniquesDefault OutputNotes on Output StatisticsODS Table NamesODS Graphics
Generalized Linear Models TheoryGeneralized Linear Mixed Models TheoryGLM Mode or GLMM ModeStatistical Inference for Covariance ParametersDegrees of Freedom MethodsEmpirical Covariance ("Sandwich") EstimatorsExploring and Comparing Covariance MatricesProcessing by SubjectsRadial Smoothing Based on Mixed ModelsOdds and Odds Ratio EstimationParameterization of Generalized Linear Mixed ModelsResponse-Level Ordering and ReferencingComparing the GLIMMIX and MIXED ProceduresSingly or Doubly Iterative FittingDefault Estimation TechniquesDefault OutputNotes on Output StatisticsODS Table NamesODS Graphics -
Examples
 Binomial Counts in Randomized BlocksMating Experiment with Crossed Random EffectsSmoothing Disease Rates; Standardized Mortality RatiosQuasi-likelihood Estimation for Proportions with Unknown DistributionJoint Modeling of Binary and Count DataRadial Smoothing of Repeated Measures DataIsotonic Contrasts for Ordered AlternativesAdjusted Covariance Matrices of Fixed EffectsTesting Equality of Covariance and Correlation MatricesMultiple Trends Correspond to Multiple Extrema in Profile LikelihoodsMaximum Likelihood in Proportional Odds Model with Random EffectsFitting a Marginal (GEE-Type) ModelResponse Surface Comparisons with Multiplicity AdjustmentsGeneralized Poisson Mixed Model for Overdispersed Count DataComparing Multiple B-SplinesDiallel Experiment with Multimember Random EffectsLinear Inference Based on Summary DataWeighted Multilevel Model for Survey Data
Binomial Counts in Randomized BlocksMating Experiment with Crossed Random EffectsSmoothing Disease Rates; Standardized Mortality RatiosQuasi-likelihood Estimation for Proportions with Unknown DistributionJoint Modeling of Binary and Count DataRadial Smoothing of Repeated Measures DataIsotonic Contrasts for Ordered AlternativesAdjusted Covariance Matrices of Fixed EffectsTesting Equality of Covariance and Correlation MatricesMultiple Trends Correspond to Multiple Extrema in Profile LikelihoodsMaximum Likelihood in Proportional Odds Model with Random EffectsFitting a Marginal (GEE-Type) ModelResponse Surface Comparisons with Multiplicity AdjustmentsGeneralized Poisson Mixed Model for Overdispersed Count DataComparing Multiple B-SplinesDiallel Experiment with Multimember Random EffectsLinear Inference Based on Summary DataWeighted Multilevel Model for Survey Data - References
-
OUTPUT <OUT=SAS-data-set>
<keyword<(keyword-options)> <=name>> …
<keyword<(keyword-options)> <=name>> </ options>;
The OUTPUT statement creates a data set that contains predicted values and residual diagnostics, computed after fitting the model. By default, all variables in the original data set are included in the output data set.
You can use the ID statement to select a subset of the variables from the input data set as well as computed variables for adding to the output data set. If you reassign a data set variable through programming statements, the value of the variable from the input data set supersedes the recomputed value when observations are written to the output data set. If you list the variable in the ID statement, however, PROC GLIMMIX saves the current value of the variable after the programming statements have been executed.
For example, suppose that data set Scores contains the variables score, machine, and person. The following statements fit a model with fixed machine and random person effects. The variable score divided by 100 is
assumed to follow an inverse Gaussian distribution. The (conditional) mean and residuals are saved to the data set igausout. Because no ID
statement is given, the variable score in the output data set contains the values from the input data set.
proc glimmix; class machine person; score = score/100; p = 4*_linp_; model score = machine / dist=invgauss; random int / sub=person; output out=igausout pred=p resid=r; run;
On the contrary, the following statements list explicitly which variables to save to the OUTPUT data set. Because the variable
score is listed in the ID
statement, and is (re-)assigned through programming statements, the values of score saved to the OUTPUT data set are the input values divided by 100.
proc glimmix; class machine person; score = score / 100; model score = machine / dist=invgauss; random int / sub=person; output out=igausout pred=p resid=r; id machine score _xbeta_ _zgamma_; run;
You can specify the following syntax elements in the OUTPUT statement before the slash (/).
- OUT=SAS-data-set
-
specifies the name of the output data set. If the OUT= option is omitted, the procedure uses the
DATAnconvention to name the output data set. - keyword<(keyword-options)> <=name>
-
specifies a statistic to include in the output data set and optionally assigns the variable the name name. You can use the keyword-options to control which type of a particular statistic to compute. The keyword-options can take on the following values:
- BLUP
-
uses the predictors of the random effects in computing the statistic.
- ILINK
-
computes the statistic on the scale of the data.
- NOBLUP
-
does not use the predictors of the random effects in computing the statistic.
- NOILINK
-
computes the statistic on the scale of the link function.
The default is to compute statistics by using BLUPs on the scale of the link function (the linearized scale). For example, the following OUTPUT statements are equivalent:
output out=out1 pred=predicted lcl=lower;
output out=out1 pred(blup noilink)=predicted lcl (blup noilink)=lower;If a particular combination of keyword and keyword options is not supported, the statistic is not computed and a message is produced in the SAS log.
A keyword can appear multiple times in the OUTPUT statement. Table 44.15 lists the keywords and the default names assigned by the GLIMMIX procedure if you do not specify a name. In this table, y denotes the observed response, and p denotes the linearized pseudo-data. See the section Pseudo-likelihood Estimation Based on Linearization for details on notation and the section Notes on Output Statistics for further details regarding the output statistics.
Table 44.15: Keywords for Output Statistics
Keyword
Options
Description
Expression
Name
PREDICTED
Default
Linear predictor
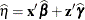
Pred
NOBLUP
Marginal linear predictor
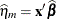
PredPA
ILINK
Predicted mean
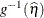
PredMu
NOBLUP ILINK
Marginal mean
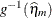
PredMuPA
STDERR
Default
Standard deviation of linear predictor
![$\sqrt {\mr{Var}[\widehat{\eta }-\mb{z}’\bgamma ]}$](images/statug_glimmix0278.png)
StdErr
NOBLUP
Standard deviation of marginal linear predictor
![$\sqrt {\mr{Var}[\widehat{\eta }_ m]}$](images/statug_glimmix0279.png)
StdErrPA
ILINK
Standard deviation of mean
![$\sqrt {\mr{Var}[g^{-1}(\widehat{\eta }-\mb{z}’\bgamma )]}$](images/statug_glimmix0280.png)
StdErr
NOBLUP ILINK
Standard deviation of marginal mean
![$\sqrt {\mr{Var}[g^{-1}(\widehat{\eta }_ m)]}$](images/statug_glimmix0281.png)
StdErrMuPA
RESIDUAL
Default
Residual
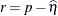
Resid
NOBLUP
Marginal residual
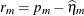
ResidPA
ILINK
Residual on mean scale
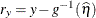
ResidMu
NOBLUP ILINK
Marginal residual on mean scale
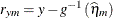
ResidMuPA
PEARSON
Default
Pearson-type residual
![$r / \sqrt {\widehat{\mr{Var}}[p|\bgamma ]}$](images/statug_glimmix0286.png)
Pearson
NOBLUP
Marginal Pearson-type residual
![$ r_ m / \sqrt {\widehat{\mr{Var}}[p_ m]}$](images/statug_glimmix0287.png)
PearsonPA
ILINK
Conditional Pearson-type mean residual
![$ r_ y / \sqrt {\widehat{\mr{Var}}[Y|\bgamma ]} $](images/statug_glimmix0288.png)
PearsonMu
STUDENT
Default
Studentized residual
![$r / \sqrt {\widehat{\mr{Var}}[r]}$](images/statug_glimmix0289.png)
Student
NOBLUP
Studentized marginal residual
![$r_ m / \sqrt {\widehat{\mr{Var}}[r_ m]}$](images/statug_glimmix0290.png)
StudentPA
LCL
Default
Lower prediction limit for linear predictor
LCL
NOBLUP
Lower confidence limit for marginal linear predictor
LCLPA
ILINK
Lower prediction limit for mean
LCLMu
NOBLUP ILINK
Lower confidence limit for marginal mean
LCLMuPA
UCL
Default
Upper prediction limit for linear predictor
UCL
NOBLUP
Upper confidence limit for marginal linear predictor
UCLPA
ILINK
Upper prediction limit for mean
UCLMu
NOBLUP ILINK
Upper confidence limit for marginal mean
UCLMuPA
VARIANCE
Default
Conditional variance of pseudo-data
![$\widehat{\mr{Var}}[p|\bgamma ]$](images/statug_glimmix0291.png)
Variance
NOBLUP
Marginal variance of pseudo-data
![$\widehat{\mr{Var}}[p_ m]$](images/statug_glimmix0292.png)
VariancePA
ILINK
Conditional variance of response
![$\widehat{\mr{Var}}[Y|\bgamma ]$](images/statug_glimmix0293.png)
Variance_Dep
NOBLUP ILINK
Marginal variance of response
![$\widehat{\mr{Var}}[Y]$](images/statug_glimmix0294.png)
Variance_DepPA
Studentized residuals are computed only on the linear scale (scale of the link), unless the link is the identity, in which case the two scales are equal. The keywords RESIDUAL, PEARSON, STUDENT, and VARIANCE are not available with the multinomial distribution. You can use the following shortcuts to request statistics: PRED for PREDICTED, STD for STDERR, RESID for RESIDUAL, and VAR for VARIANCE. Output statistics that depend on the marginal variance
![$\mr{Var}[Y_ i]$](images/statug_glimmix0295.png) are not available with METHOD=
LAPLACE
or METHOD=
QUAD
.
are not available with METHOD=
LAPLACE
or METHOD=
QUAD
.
Table 44.16 summarizes the options available in the OUTPUT statement.
Table 44.16: OUTPUT Statement Options
Option
Description
Computes all statistics
Determines the confidence level (
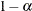 )
)
Changes the way in which marginal residuals are computed
Adds derivatives of model quantities to the output data set
Outputs only observations used in the analysis
Requests that names not be made unique
Requests that variables from the input data set not be added to the output data set
Writes statistics to output data set only for the response level corresponding to the observed level of the observation
Adds computed variables to the output data set
You can specify the following options in the OUTPUT statement after a slash (/).
- ALLSTATS
-
requests that all statistics are computed. If you do not use a keyword to assign a name, the GLIMMIX procedure uses the default name.
- ALPHA=number
-
determines the coverage probability for two-sided confidence and prediction intervals. The coverage probability is computed as 1 – number. The value of number must be between 0 and 1; the default is 0.05.
- CPSEUDO
-
changes the way in which marginal residuals are computed when model parameters are estimated by pseudo-likelihood methods. See the section Notes on Output Statistics for details.
-
DERIVATIVES
DER -
adds derivatives of model quantities to the output data set. If, for example, the model fit requires the (conditional) log likelihood of the data, then the DERIVATIVES option writes for each observation the evaluations of the first and second derivatives of the log likelihood with respect to _LINP_ and _PHI_ to the output data set. The particular derivatives produced by the GLIMMIX procedure depend on the type of model and the estimation method.
- NOMISS
-
requests that records be written to the output data only for those observations that were used in the analysis. By default, the GLIMMIX procedure produces output statistics for all observations in the input data set.
- NOUNIQUE
-
requests that names not be made unique in the case of naming conflicts. By default, the GLIMMIX procedure avoids naming conflicts by assigning a unique name to each output variable. If you specify the NOUNIQUE option, variables with conflicting names are not renamed. In that case, the first variable added to the output data set takes precedence.
- NOVAR
-
requests that variables from the input data set not be added to the output data set. This option does not apply to variables listed in the BY statement or to computed variables listed in the ID statement.
- OBSCAT
-
requests that in models for multinomial data statistics be written to the output data set only for the response level that corresponds to the observed level of the observation.
-
SYMBOLS
SYM -
adds to the output data set computed variables that are defined or referenced in the program.