-
ACFPLOT <(options</ display-options>)>
-
displays the traditional autocorrelation function plots of parameters from iterations. The ACFPLOT option is applicable only
if ODS Graphics is not enabled.
The available options are as follows.
-
COV <( < variables > < variable1*variable2 > < …variable1*variable2 > ) >
-
displays plots of variances for variables in the list and covariances for pairs of variables in the list. When the option
COV is specified without variables, variances for all variables and covariances for all pairs of variables are used.
-
MEAN <( variables )>
-
displays plots of means for variables in the list. When the option MEAN is specified without variables, all variables are
used.
-
WLF
-
displays the plot for the worst linear function.
When the ACFPLOT is specified without the preceding options, the procedure displays plots of means for all variables that
are used.
The display options provide additional information for the autocorrelation function plots. The available display options are
as follows:
-
CCONF=color
-
specifies the color of the displayed confidence limits. The default is CCONF=BLACK.
-
CFRAME=color
-
specifies the color for filling the area enclosed by the axes and the frame. By default, this area is not filled.
-
CNEEDLES=color
-
specifies the color of the vertical line segments (needles) that connect autocorrelations to the reference line. The default
is CNEEDLES=BLACK.
-
CREF=color
-
specifies the color of the displayed reference line. The default is CREF=BLACK.
-
CSYMBOL=color
-
specifies the color of the displayed data points. The default is CSYMBOL=BLACK.
-
HSYMBOL=number
-
specifies the height of data points in percentage screen units. The default is HSYMBOL=1.
-
LCONF=linetype
-
specifies the line type for the displayed confidence limits. The default is LCONF=1, a solid line.
-
LOG
-
requests that the logarithmic transformations of parameters be used to compute the autocorrelations; it is generally used
for the variances of variables. When a parameter has values less than or equal to zero, the corresponding plot is not created.
-
LREF=linetype
-
specifies the line type for the displayed reference line. The default is LREF=3, a dashed line.
-
NAME=’string’
-
specifies a descriptive name, up to eight characters, that appears in the name field of the PROC GREPLAY master menu. The
default is NAME=’MI’.
-
NLAG=number
-
specifies the maximum lag of the series. The default is NLAG=20. The autocorrelations at each lag are displayed in the graph.
-
SYMBOL=value
-
specifies the symbol for data points in percentage screen units. The default is SYMBOL=STAR.
-
TITLE=’string’
-
specifies the title to be displayed in the autocorrelation function plots. The default is TITLE=’Autocorrelation Plot’.
-
WCONF=number
-
specifies the width of the displayed confidence limits in percentage screen units. If you specify the WCONF=0 option, the
confidence limits are not displayed. The default is WCONF=1.
-
WNEEDLES=number
-
specifies the width of the displayed needles that connect autocorrelations to the reference line, in percentage screen units.
If you specify the WNEEDLES=0 option, the needles are not displayed. The default is WNEEDLES=1.
-
WREF=number
-
specifies the width of the displayed reference line in percentage screen units. If you specify the WREF=0 option, the reference
line is not displayed. The default is WREF=1.
For example, the following statement requests autocorrelation function plots for the means and variances of the variable y1, respectively:
acfplot( mean( y1) cov(y1) /log);
Logarithmic transformations of both the means and variances are used in the plots. For a detailed description of the autocorrelation
function plot, see the section Autocorrelation Function Plot; see also Schafer (1997, pp. 120–126) and the
SAS/ETS User's Guide.
-
CHAIN=SINGLE | MULTIPLE
-
specifies whether a single chain is used for all imputations or a separate chain is used for each imputation. The default
is CHAIN=SINGLE.
-
DISPLAYINIT
-
displays initial parameter values in the MCMC method for each imputation.
-
GOUT=graphics-catalog
-
specifies the graphics catalog for saving graphics output from PROC MI. The default is WORK.GSEG. For more information, see
“The GREPLAY Procedure” in
SAS/GRAPH: Reference.
-
IMPUTE=FULL | MONOTONE
-
specifies whether a full-data imputation is used for all missing values or a monotone-data imputation is used for a subset
of missing values to make the imputed data sets have a monotone missing pattern. The default is IMPUTE=FULL. When IMPUTE=MONOTONE
is specified, the order in the VAR statement is used to complete the monotone pattern.
-
INEST=SAS-data-set
-
names a SAS data set of TYPE=EST that contains parameter estimates for imputations. These estimates are used to impute values
for observations in the DATA= data set. A detailed description of the data set is provided in the section Input Data Sets.
-
INITIAL=EM <(options)>
INITIAL=INPUT=SAS-data-set
-
specifies the initial mean and covariance estimates for the MCMC method. The default is INITIAL=EM.
You can specify INITIAL=INPUT=SAS-data-set to read the initial estimates of the mean and covariance matrix for each imputation from a SAS data set. See the section
Input Data Sets for a description of this data set.
With INITIAL=EM, PROC MI derives parameter estimates for a posterior mode, the highest observed-data posterior density, from
the EM algorithm. The MLE from the EM algorithm is used to start the EM algorithm for the posterior mode, and the resulting
EM estimates are used to begin the MCMC method. The prior information specified in the PRIOR= option is also used in the process
to compute the posterior mode.
The following four options are available with INITIAL=EM:
-
BOOTSTRAP < =number >
-
requests bootstrap resampling, which uses a simple random sample with replacement from the input data set for the initial
estimate. You can explicitly specify the number of observations in the random sample. Alternatively, you can implicitly specify
the number of observations in the random sample by specifying the proportion 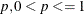 , to request [np] observations in the random sample, where n is the number of observations in the data set and [np] is the integer part of np. This produces an overdispersed initial estimate that provides different starting values for the MCMC method. If you specify
the BOOTSTRAP option without the number, p = 0.75 is used by default.
, to request [np] observations in the random sample, where n is the number of observations in the data set and [np] is the integer part of np. This produces an overdispersed initial estimate that provides different starting values for the MCMC method. If you specify
the BOOTSTRAP option without the number, p = 0.75 is used by default.
-
CONVERGE=p
XCONV=p
-
sets the convergence criterion. The value must be between 0 and 1. The iterations are considered to have converged when the
change in the parameter estimates between iteration steps is less than p for each parameter—that is, for each of the means and covariances. For each parameter, the change is a relative change if
the parameter is greater than 0.01 in absolute value; otherwise, it is an absolute change. By default, CONVERGE=1E–4.
-
ITPRINT
-
prints the iteration history in the EM algorithm for the posterior mode.
-
MAXITER=number
-
specifies the maximum number of iterations used in the EM algorithm. The default is MAXITER=200.
-
NBITER=number
-
specifies the number of burn-in iterations before the first imputation in each chain. The default is NBITER=200.
-
NITER=number
-
specifies the number of iterations between imputations in a single chain. The default is NITER=100.
-
OUTEST=SAS-data-set
-
creates an output SAS data set of TYPE=EST. The data set contains parameter estimates used in each imputation. The data set
also includes a variable named _Imputation_ to identify the imputation number. See the section Output Data Sets for a description of this data set.
-
OUTITER <( options )> =SAS-data-set
-
creates an output SAS data set of TYPE=COV that contains parameters used in the imputation step for each iteration. The data
set includes variables named _Imputation_ and _Iteration_ to identify the imputation number and iteration number.
The parameters in the output data set depend on the options specified. You can specify the options MEAN, STD, COV, LR, LR_POST,
and WLF to output parameters of means, standard deviations, covariances, –2 log LR statistic, –2 log LR statistic of the posterior
mode, and the worst linear function, respectively. When no options are specified, the output data set contains the mean parameters
used in the imputation step for each iteration. See the section Output Data Sets for a description of this data set.
-
PLOTS <( LOG )> <= plot-request>
PLOTS <( LOG )> <= ( plot-request <…plot-request> )>
-
requests statistical graphics via the Output Delivery System (ODS). To request these graphs, ODS Graphics must be enabled
and you must specify options in the MCMC statement. For more information about ODS Graphics, see Chapter 21: Statistical Graphics Using ODS.
The global plot option LOG requests that the logarithmic transformations of parameters be used. The plot request options include
the following:
-
ACF < ( acf-options ) >
-
displays plots of the autocorrelation function of parameters from iterations. The default is ACF( MEAN).
-
ALL
-
produces all appropriate plots.
-
NONE
-
suppresses all plots.
-
TRACE < ( trace-options ) >
-
displays trace plots of parameters from iterations. The default is TRACE( MEAN).
The available acf-options are as follows:
-
NLAG=n
-
specifies the maximum lag of the series. The default is NLAG=20. The autocorrelations at each lag are displayed in the graph.
-
COV <( < variables > < variable1*variable2 > …)>
-
displays plots of variances for variables in the list and covariances for pairs of variables in the list. When the option
COV is specified without variables, variances for all variables and covariances for all pairs of variables are used.
-
MEAN < ( variables ) >
-
displays plots of means for variables in the list. When the option MEAN is specified without variables, all variables are
used.
-
WLF
-
displays the plot for the worst linear function.
The available trace-options are as follows:
-
COV <( < variables > < variable1*variable2 > …)>
-
displays plots of variances for variables in the list and covariances for pairs of variables in the list. When the option
COV is specified without variables, variances for all variables and covariances for all pairs of variables are used.
-
MEAN < ( variables ) >
-
displays plots of means for variables in the list. When the option MEAN is specified without variables, all variables are
used.
-
WLF
-
displays the plot of the worst linear function.
-
PRIOR=name
-
specifies the prior information for the means and covariances. Valid values for name are as follows:
- JEFFREYS
-
specifies a noninformative prior.
- RIDGE=number
-
specifies a ridge prior.
- INPUT=SAS-data-set
-
specifies a data set that contains prior information.
For a detailed description of the prior information, see the section Bayesian Estimation of the Mean Vector and Covariance Matrix and the section Posterior Step. If you do not specify the PRIOR= option, the default is PRIOR=JEFFREYS.
The PRIOR=INPUT= option specifies a TYPE=COV data set from which the prior information of the mean vector and the covariance
matrix is read. See the section Input Data Sets for a description of this data set.
-
START=VALUE | DIST
-
specifies that the initial parameter estimates are used either as the starting value (START=VALUE) or as the starting distribution
(START=DIST) in the first imputation step of each chain. If the IMPUTE=MONOTONE option is specified, then START=VALUE is used
in the procedure. The default is START=VALUE.
-
TIMEPLOT <( options < / display-options > ) >
-
displays the traditional trace (time series) plots of parameters from iterations. The TIMEPLOT option is applicable only if
ODS Graphics is not enabled.
The available options are as follows:
-
COV <( < variables > < variable1*variable2 > …) >
-
displays plots of variances for variables in the list and covariances for pairs of variables in the list. When the option
COV is specified without variables, variances for all variables and covariances for all pairs of variables are used.
-
MEAN < (variables)>
-
displays plots of means for variables in the list. When the option MEAN is specified without variables, all variables are
used.
-
WLF
-
displays the plot of the worst linear function.
When the TIMEPLOT is specified without the preceding options, the procedure displays plots of means for all variables that
are used.
The display options provide additional information for the trace plots. The available display options are as follows:
-
CCONNECT=color
-
specifies the color of the line segments that connect data points in the trace plots. The default is CCONNECT=BLACK.
-
CFRAME=color
-
specifies the color for filling the area enclosed by the axes and the frame. By default, this area is not filled.
-
CSYMBOL=color
-
specifies the color of the data points to be displayed in the trace plots. The default is CSYMBOL=BLACK.
-
HSYMBOL=number
-
specifies the height of data points in percentage screen units. The default is HSYMBOL=1.
-
LCONNECT=linetype
-
specifies the line type for the line segments that connect data points in the trace plots. The default is LCONNECT=1, a solid
line.
-
LOG
-
requests that the logarithmic transformations of parameters be used; it is generally used for the variances of variables.
When a parameter value is less than or equal to zero, the value is not displayed in the corresponding plot.
-
NAME=’string’
-
specifies a descriptive name, up to eight characters, that appears in the name field of the PROC GREPLAY master menu. The
default is NAME=’MI’.
-
SYMBOL=value
-
specifies the symbol for data points in percentage screen units. The default is SYMBOL=PLUS.
-
TITLE=’string’
-
specifies the title to be displayed in the trace plots. The default is TITLE=’Trace Plot’.
-
WCONNECT=number
-
specifies the width of the line segments that connect data points in the trace plots, in percentage screen units. If you specify
the WCONNECT=0 option, the data points are not connected. The default is WCONNECT=1.
For a detailed description of the trace plot, see the section Trace Plot and Schafer (1997, pp. 120–126).
-
WLF
-
displays the worst linear function of parameters. This scalar function of parameters 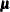 and
and 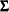 is “worst” in the sense that its values from iterations converge most slowly among parameters. For a detailed description of this statistic,
see the section Worst Linear Function of Parameters.
is “worst” in the sense that its values from iterations converge most slowly among parameters. For a detailed description of this statistic,
see the section Worst Linear Function of Parameters.

 Descriptive StatisticsEM Algorithm for Data with Missing ValuesStatistical Assumptions for Multiple ImputationMissing Data PatternsImputation MethodsMonotone Methods for Data Sets with Monotone Missing PatternsMonotone and FCS Regression MethodsMonotone and FCS Predictive Mean Matching MethodsMonotone Propensity Score MethodMonotone and FCS Discriminant Function MethodsMonotone and FCS Logistic Regression MethodsFCS Methods for Data Sets with Arbitrary Missing PatternsChecking Convergence in FCS MethodsMCMC Method for Arbitrary Missing Multivariate Normal DataProducing Monotone Missingness with the MCMC MethodMCMC Method SpecificationsChecking Convergence in MCMCInput Data SetsOutput Data SetsCombining Inferences from Multiply Imputed Data SetsMultiple Imputation EfficiencyImputer’s Model Versus Analyst’s ModelParameter Simulation versus Multiple ImputationSummary of Issues in Multiple ImputationODS Table NamesODS Graphics
Descriptive StatisticsEM Algorithm for Data with Missing ValuesStatistical Assumptions for Multiple ImputationMissing Data PatternsImputation MethodsMonotone Methods for Data Sets with Monotone Missing PatternsMonotone and FCS Regression MethodsMonotone and FCS Predictive Mean Matching MethodsMonotone Propensity Score MethodMonotone and FCS Discriminant Function MethodsMonotone and FCS Logistic Regression MethodsFCS Methods for Data Sets with Arbitrary Missing PatternsChecking Convergence in FCS MethodsMCMC Method for Arbitrary Missing Multivariate Normal DataProducing Monotone Missingness with the MCMC MethodMCMC Method SpecificationsChecking Convergence in MCMCInput Data SetsOutput Data SetsCombining Inferences from Multiply Imputed Data SetsMultiple Imputation EfficiencyImputer’s Model Versus Analyst’s ModelParameter Simulation versus Multiple ImputationSummary of Issues in Multiple ImputationODS Table NamesODS Graphics EM Algorithm for MLEMonotone Propensity Score MethodMonotone Regression MethodMonotone Logistic Regression Method for CLASS VariablesMonotone Discriminant Function Method for CLASS VariablesFCS Method for Continuous VariablesFCS Method for CLASS VariablesFCS Method with Trace PlotMCMC MethodProducing Monotone Missingness with MCMCChecking Convergence in MCMCSaving and Using Parameters for MCMCTransforming to NormalityMultistage Imputation
EM Algorithm for MLEMonotone Propensity Score MethodMonotone Regression MethodMonotone Logistic Regression Method for CLASS VariablesMonotone Discriminant Function Method for CLASS VariablesFCS Method for Continuous VariablesFCS Method for CLASS VariablesFCS Method with Trace PlotMCMC MethodProducing Monotone Missingness with MCMCChecking Convergence in MCMCSaving and Using Parameters for MCMCTransforming to NormalityMultistage Imputation