The SEQDESIGN Procedure
-
Overview

- Getting Started
-
Syntax

-
Details
 Fixed-Sample Clinical TrialsOne-Sided Fixed-Sample Tests in Clinical TrialsTwo-Sided Fixed-Sample Tests in Clinical TrialsGroup Sequential MethodsStatistical Assumptions for Group Sequential DesignsBoundary ScalesBoundary VariablesType I and Type II ErrorsUnified Family MethodsHaybittle-Peto MethodWhitehead MethodsError Spending MethodsAcceptance (beta) BoundaryBoundary Adjustments for Overlapping Lower and Upper beta BoundariesSpecified and Derived ParametersApplicable Boundary KeysSample Size ComputationApplicable One-Sample Tests and Sample Size ComputationApplicable Two-Sample Tests and Sample Size ComputationApplicable Regression Parameter Tests and Sample Size ComputationAspects of Group Sequential DesignsSummary of Methods in Group Sequential DesignsTable OutputODS Table NamesGraphics OutputODS Graphics
Fixed-Sample Clinical TrialsOne-Sided Fixed-Sample Tests in Clinical TrialsTwo-Sided Fixed-Sample Tests in Clinical TrialsGroup Sequential MethodsStatistical Assumptions for Group Sequential DesignsBoundary ScalesBoundary VariablesType I and Type II ErrorsUnified Family MethodsHaybittle-Peto MethodWhitehead MethodsError Spending MethodsAcceptance (beta) BoundaryBoundary Adjustments for Overlapping Lower and Upper beta BoundariesSpecified and Derived ParametersApplicable Boundary KeysSample Size ComputationApplicable One-Sample Tests and Sample Size ComputationApplicable Two-Sample Tests and Sample Size ComputationApplicable Regression Parameter Tests and Sample Size ComputationAspects of Group Sequential DesignsSummary of Methods in Group Sequential DesignsTable OutputODS Table NamesGraphics OutputODS Graphics -
Examples
 Creating Fixed-Sample DesignsCreating a One-Sided O’Brien-Fleming DesignCreating Two-Sided Pocock and O’Brien-Fleming DesignsGenerating Graphics Display for Sequential DesignsCreating Designs Using Haybittle-Peto MethodsCreating Designs with Various Stopping CriteriaCreating Whitehead’s Triangular DesignsCreating a One-Sided Error Spending DesignCreating Designs with Various Number of StagesCreating Two-Sided Error Spending Designs with and without Overlapping Lower and Upper beta BoundariesCreating a Two-Sided Asymmetric Error Spending Design with Early Stopping to Reject H0Creating a Two-Sided Asymmetric Error Spending Design with Early Stopping to Reject or Accept H0Creating a Design with a Nonbinding Beta BoundaryComputing Sample Size for Survival Data That Have Uniform AccrualComputing Sample Size for Survival Data with Truncated Exponential Accrual
Creating Fixed-Sample DesignsCreating a One-Sided O’Brien-Fleming DesignCreating Two-Sided Pocock and O’Brien-Fleming DesignsGenerating Graphics Display for Sequential DesignsCreating Designs Using Haybittle-Peto MethodsCreating Designs with Various Stopping CriteriaCreating Whitehead’s Triangular DesignsCreating a One-Sided Error Spending DesignCreating Designs with Various Number of StagesCreating Two-Sided Error Spending Designs with and without Overlapping Lower and Upper beta BoundariesCreating a Two-Sided Asymmetric Error Spending Design with Early Stopping to Reject H0Creating a Two-Sided Asymmetric Error Spending Design with Early Stopping to Reject or Accept H0Creating a Design with a Nonbinding Beta BoundaryComputing Sample Size for Survival Data That Have Uniform AccrualComputing Sample Size for Survival Data with Truncated Exponential Accrual - References
This example demonstrates a one-sided fixed-sample design and a two-sided fixed-sample design. The following statements request a fixed-sample design with an upper alternative:
ods graphics on;
proc seqdesign pss
;
OneSidedFixedSample: design nstages=1
alt=upper
alpha=0.025 beta=0.10
;
samplesize model=onesamplemean(mean=0.25);
run;
ods graphics off;
In the DESIGN statement, the label OneSidedFixedSample identifies the design in the output tables. The NSTAGES=1 option specifies that the design has only one stage; this corresponds
to a fixed-sample design. In the SEQDESIGN procedure, the null hypothesis for the design is ![]() and the ALT=UPPER option specifies an upper alternative hypothesis
and the ALT=UPPER option specifies an upper alternative hypothesis ![]() . The MEAN=0.25 option in the SAMPLESIZE statement specifies the upper alternative reference
. The MEAN=0.25 option in the SAMPLESIZE statement specifies the upper alternative reference ![]() .
.
The options ALPHA=0.025 and BETA=0.10 specify the Type I error probability level ![]() and the Type II error probability level
and the Type II error probability level ![]() . That is, the design has a power
. That is, the design has a power ![]() at
at ![]() .
.
The "Design Information" table in Output 89.1.1 displays design specifications and the derived statistics such as power. As expected, the derived statistics such as maximum information and average sample number (in percentage of its corresponding fixed-sample information) are 100 for the fixed-sample design (NSTAGES=1). Also, for a fixed-sample design, the STOP= and METHOD= options in the DESIGN statement are not applicable.
Output 89.1.1: One-Sided Fixed-Sample Design Information
| Design Information | |
|---|---|
| Statistic Distribution | Normal |
| Boundary Scale | Standardized Z |
| Alternative Hypothesis | Upper |
| Alternative Reference | 0.25 |
| Number of Stages | 1 |
| Alpha | 0.025 |
| Beta | 0.1 |
| Power | 0.9 |
| Max Information (Percent of Fixed Sample) | 100 |
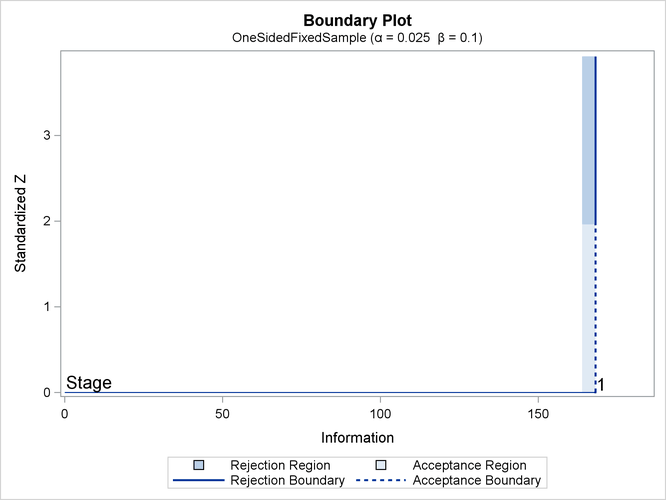
| Max Information | 168.1188 |
| Null Ref ASN (Percent of Fixed Sample) | 100 |
| Alt Ref ASN (Percent of Fixed Sample) | 100 |
The "Method Information" table in Output 89.1.2 displays the ![]() and
and ![]() error levels. It also displays the derived drift parameter, which is the standardized reference improvement,
error levels. It also displays the derived drift parameter, which is the standardized reference improvement, ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the alternative reference and
is the alternative reference and ![]() is the maximum information for the design. If either
is the maximum information for the design. If either ![]() or
or ![]() is specified, the other statistic is derived in the SEQDESIGN procedure. For a fixed-sample design,
is specified, the other statistic is derived in the SEQDESIGN procedure. For a fixed-sample design,
The "Boundary Information" table in Output 89.1.3 displays information level, alternative reference, and boundary value at each stage. The information proportion indicates the proportion of maximum information available at the stage. With only one stage for a fixed-sample design, the proportion is 1. With the SAMPLESIZE statement, the required sample size N is also displayed under the heading "Information Level."
By default (or equivalently if you specify BOUNDARYSCALE=STDZ), output alternative references and boundaries are displayed
with the standardized normal Z scale. The alternative reference on the standardized Z scale at stage 1 is given by ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the information level at stage 1. With a boundary value 1.96, the hypothesis of
is the information level at stage 1. With a boundary value 1.96, the hypothesis of ![]() is rejected if the standardized normal statistic
is rejected if the standardized normal statistic ![]() .
.
With ODS Graphics enabled, a detailed boundary plot with the rejection and acceptance regions is displayed, as shown in Output 89.1.4. The boundary values in the "Boundary Information" table in Output 89.1.3 are displayed in the plot.
The "Sample Size Summary" table in Output 89.1.5 displays parameters for the sample size computation of the test for a normal mean.
The "Sample Sizes (N)" table in Output 89.1.6 displays the derived sample sizes, in both fractional and integer numbers. With the resulting integer sample sizes, the corresponding information level is slightly larger than the level from the design. This can increase the power slightly if the integer sample size is used in the trial.
The following statements request a two-sided fixed-sample design with a specified alternative reference:
ods graphics on;
proc seqdesign altref=1.2
pss
;
TwoSidedFixedSample: design nstages=1
alt=twosided
alpha=0.05 beta=0.10
;
samplesize model=twosamplemean(stddev=2 weight=2);
run;
ods graphics off;
In the SEQDESIGN procedure, the null hypothesis for the design is ![]() . The ALT=TWOSIDED option specifies a two-sided alternative hypothesis
. The ALT=TWOSIDED option specifies a two-sided alternative hypothesis ![]() . The ALTREF=1.2 option in the PROC SEQDESIGN statement specifies the alternative reference
. The ALTREF=1.2 option in the PROC SEQDESIGN statement specifies the alternative reference ![]() .
.
The ALPHA=0.05 option (which is the default) specifies the two-sided Type I error probability level ![]() . That is, the lower and upper Type I error probabilities
. That is, the lower and upper Type I error probabilities ![]() . The BETA=0.10 option (which is the default) specifies the Type II error probability level
. The BETA=0.10 option (which is the default) specifies the Type II error probability level ![]() , and the design has a power
, and the design has a power ![]() at the alternative reference
at the alternative reference ![]() .
.
The "Design Information" table in Output 89.1.7 displays design specifications and the derived power. With a specified alternative reference, the maximum information is derived.
Output 89.1.7: Two-Sided Fixed-Sample Design Information
| Design Information | |
|---|---|
| Statistic Distribution | Normal |
| Boundary Scale | Standardized Z |
| Alternative Hypothesis | Two-Sided |
| Alternative Reference | 1.2 |
| Number of Stages | 1 |
| Alpha | 0.05 |
| Beta | 0.1 |
| Power | 0.9 |
| Max Information (Percent of Fixed Sample) | 100 |
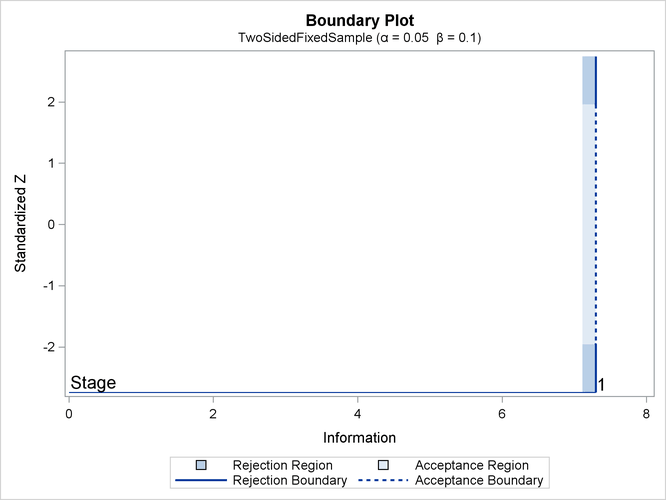
| Max Information | 7.296822 |
| Null Ref ASN (Percent of Fixed Sample) | 100 |
| Alt Ref ASN (Percent of Fixed Sample) | 100 |
The "Method Information" table in Output 89.1.8 displays the ![]() and
and ![]() errors, alternative references, and drift parameter. For a fixed-sample design, the derived drift parameter
errors, alternative references, and drift parameter. For a fixed-sample design, the derived drift parameter
With a specified alternative reference ![]() , the maximum information
, the maximum information
The default "Boundary Information" table in Output 89.1.9 displays information level, alternative reference, and boundary values. By default (or equivalently if you specify BOUNDARYSCALE=STDZ),
the alternative reference and boundary values are displayed with the standardized normal Z scale. Thus, the standardized alternative references ![]() are displayed.
are displayed.
With boundary values of –1.96 and 1.96, the hypothesis of ![]() is rejected if the standardized normal statistic
is rejected if the standardized normal statistic ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
With ODS Graphics enabled, a detailed boundary plot with the rejection and acceptance regions is displayed, as shown in Output 89.1.10 . The boundary values in the "Boundary Information" table in Output 89.1.9 are displayed in the plot.
The "Sample Size Summary" table in Output 89.1.11 displays parameters for the sample size computation of the test for a normal mean.
The "Sample Sizes (N)" table in Output 89.1.12 displays the derived sample sizes, in both fractional and integer numbers. With the WEIGHT=2 option, the allocation ratio is 2 for the first group and 1 for the second group. With the resulting integer sample sizes, the corresponding information level is slightly larger than the level from the design. This can increase the power slightly if the integer sample size is used in the trial.